-
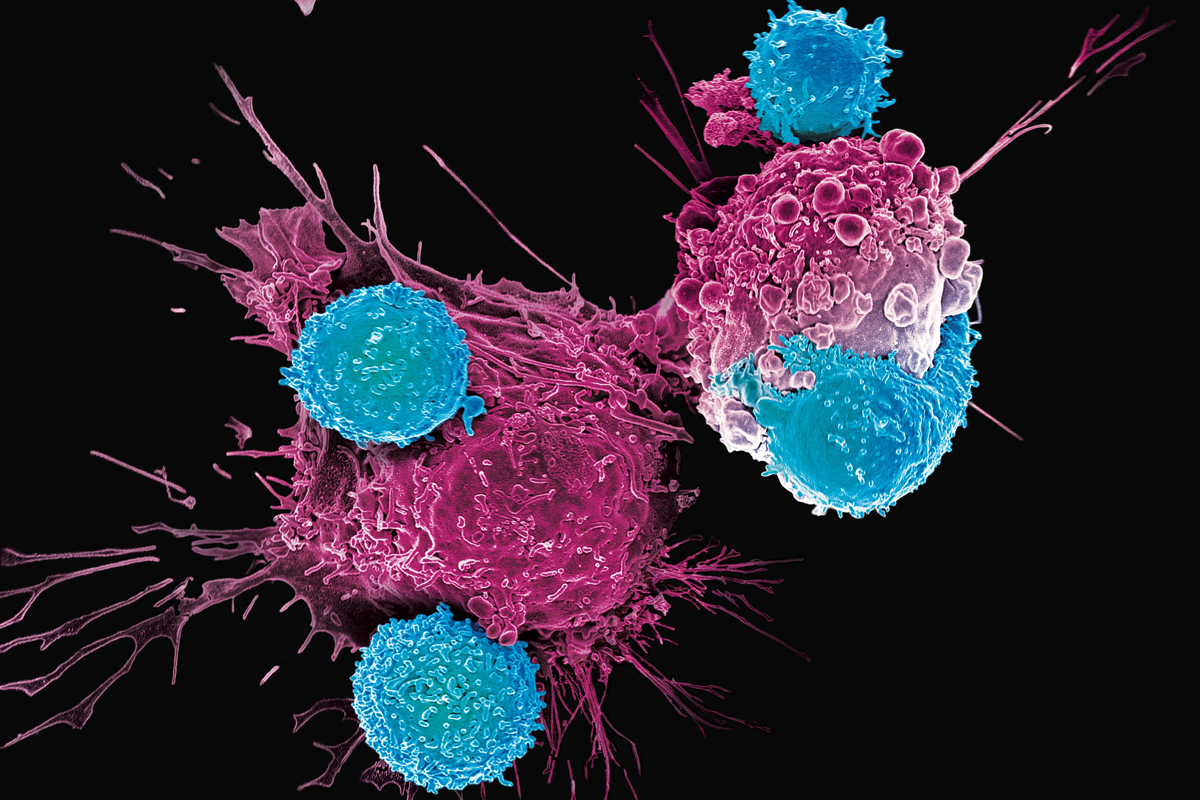 Medical articles
CAR T therapy: helps treat cancer when other methods fail
Medical articles
CAR T therapy: helps treat cancer when other methods fail
-
 Medical articles
Cancer incidence is steadily increasing: disappointing WHO forecast for 2050
Medical articles
Cancer incidence is steadily increasing: disappointing WHO forecast for 2050
-
 Medical articles
Stem cells bring hope to millions of people suffering from hearing loss
Medical articles
Stem cells bring hope to millions of people suffering from hearing loss
-
 Medical articles
TOP 10 clinics for oncology treatment 2023
Medical articles
TOP 10 clinics for oncology treatment 2023
-
 Medical articles
New methods for diagnosing cancer diseases
Medical articles
New methods for diagnosing cancer diseases
All news
Clinics for the treatment of transplant
Transplantology:
- The method of treatment, which saves hundreds of thousands of lives,
- About 150,000 transplants are performed annually,
- More than 17 transplants take place every hour around the world,
- One person can donate 15 different organs and tissues.
MedTour patients recommend clinics for the treatment of transplant:
Doctors for the treatment of transplantology
Patient reviews
Frequently Asked Questions
Transplantology — science of transplantation of organs, tissues and cells.
Transplantation — replacement of diseased or missing organs with a healthy one.
When a vital organ stops working and all treatments have been exhausted, a transplant is often the last chance to survive.
Donor — an organism from which organs, tissues or cells are taken for transplantation.
Recipient — human to whom the necessary materials are transplanted.
Allocate transplantation:
- Organs: heart, lungs, kidneys, liver, pancreas, intestines,
- Tissues: cornea of the eye, skin, heart valves, ligaments, bones,
- Cells: cartilage, bone marrow stem cells, blood and umbilical cord blood, eggs.
Such operations are performed by specialists only in transplant centers — clinics that have received special permission for transplantation.
Depending on the origin of grafts, different types of transplantation are distinguished:
- Autotransplantation — transplantation of material from patient himself (hair, skin),
- Isotransplantation — from genetically identical person (identical twin),
- Allotransplantation — from stranger,
- Xenotransplantation — from animals (pig heart valve).
There are two types of donation:
- Living, in which a healthy person voluntarily transfers an organ to another person,
- Posthumous — after a person’s death .
Several lives can be saved with a single posthumous donor: many different organs and tissues can be removed from a deceased donor. After that, they will again take on important functions in the body of another person.
When human organs are severely damaged and all other therapies are ineffective, transplantation is the last resort.
Indications for transplantation:
- Complete irreversible loss of organ function,
- Heart failure,
- Liver cirrhosis,
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Severe burns and injuries of skin, limbs,
- Leukemia.
Absolute contraindications include:
- Severe infectious diseases,
- Malignant tumors with metastases,
- Psychosis or alcohol dependence in the recipient.
Relative contraindications:
- HIV infection, AIDS,
- Multiple organ failure,
- Generalized atherosclerosis.
There are 4 main stages of transplantation:
- Examination for possible transplantation,
- Waiting for a transplant,
- Transplant surgery,
- Follow-up with regular check-ups and lifelong medication for rejection.
Number of patients awaiting donation exceeds the number of available donor components. For this reason, patients often wait for a suitable one from several months to several years.
Today, transplants are routine operations for doctors.
Long-term survival depends on various factors:
- Patient’s health condition,
- Graft condition,
- Possible rejection reaction,
- Use of immunosuppressants.
Chances of success and improvement in quality of life depend on qualifications and experience of a doctor, as well as the clinic where transplant takes place.
The immune system protects the body from foreign transplants by developing rejection of transplanted materials.
- The main reason for incompatibility of patients,
- Rejection of graft occurs in 10-30% of cases and leads to graft damage,
- Allocate hyperacute, acute and chronic rejection.
In order to avoid rejection reactions, it is very important that follow-up care is carried out regularly in a specialized center by experienced doctors.
The prevention and treatment of rejection reaction is based on continuous immunosuppressive therapy (immune system suppression).
Rejection is well treated with medication. Thanks to immunosuppressants, the chances that the donor organ will function well in the recipient’s body for many years have been greatly increased.
If hyperacute rejection develops (1% of cases), graft removal and re-transplantation should be discussed.
Published:
Updated:






Храпач Василій Васильович , самий лутший доктор,доцент і пластіческій хірург.🙏🙏🙏