Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
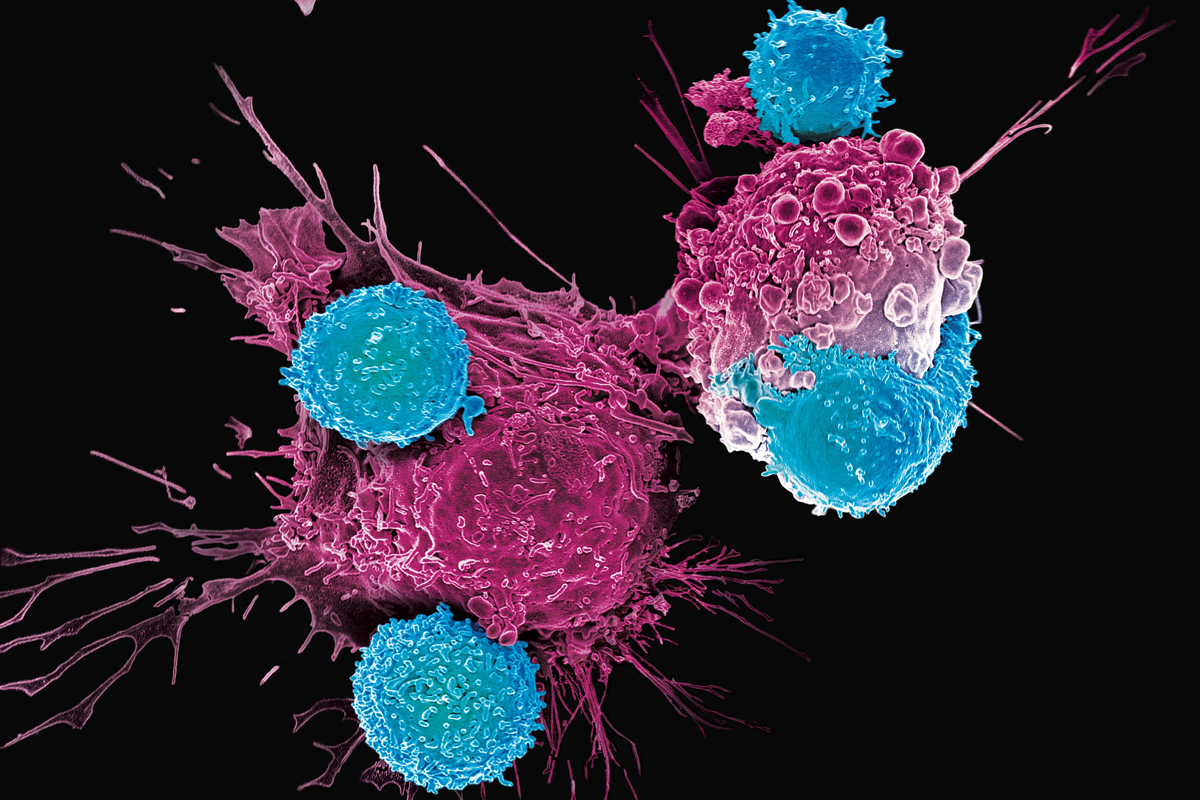
CAR T-cell therapy is a revolutionary, highly specialized and individualized treatment for leukemia, lymphoma and multiple myeloma. Currently, this technique is available in only a few cancer centers around the world.
MedTour, together with the biotechnological company BioPro Stem Technology, offers you the opportunity to undergo CAR T-cell therapy in Ukraine or Spain. This method opens up new prospects in the treatment of cancer. We are ready to provide comprehensive support in organizing your treatment. MedTour will provide professional advice, help with paperwork and provide comfortable conditions during therapy.
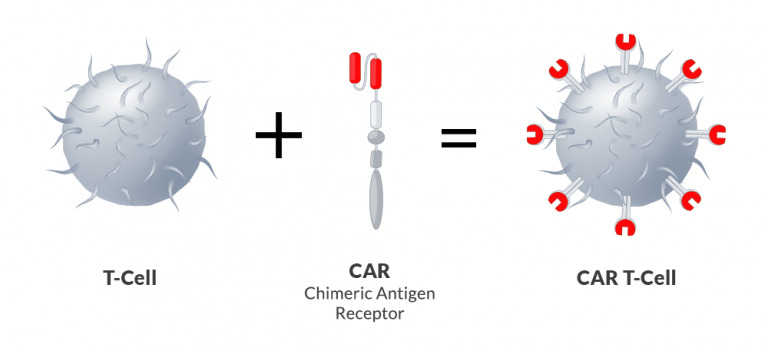
Chimeric antigen receptor therapy (CAR T-cell therapy) is an innovative, personalized treatment option. It involves using the body’s own immune system to destroy tumor cells. Typically, human T cells are responsible for detecting non-cancerous pathogens such as viruses and bacteria. However, after genetic modification they become able to recognize and destroy malignant cells.
CAR T-cell therapy helps achieve remission in many patients who have not responded to other cancer treatments.
Currently, this treatment method is used to treat hemoblastosis – a group of malignant diseases of the hematopoietic system and lymphatic tissue.
It is one of the malignant diseases of the blood and bone marrow. It is characterized by aggressive progression. The disease occurs at any age, but is more common in children. ALL is accompanied by excessive production of immature lymphocytes called lymphoblasts. These abnormal cells do not function properly and block the production of other types of healthy blood cells, such as red blood cells and platelets.
This is a rapidly developing type of leukemia. It can occur at any age, but most often affects older people. The average age at diagnosis is 65 years. AML is characterized by damage to the bone marrow in which it begins to produce immature white blood cells. They do not develop into adult healthy blood cells, but remain immature and multiply rapidly, displacing red blood cells, platelets and white blood cells.
In some cases, AML can also spread to other organs, such as the brain, spinal cord, liver, or spleen. Without timely treatment, AML is life-threatening.
This is a cancer that affects the lymphatic system, one of the main functions of which is to protect the body from disease. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma affects lymphocytes and is more common in adults than children. The malignancy has several subtypes, the most common of which are diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma.
A form of blood cancer that starts in plasma cells (important components of the immune system). They are a special type of white blood cell that produces antibodies (immunoglobulins) to search for and attack pathogens, thereby fighting infections.
In MM, plasma cells multiply abnormally quickly, crowding out healthy blood cells. Instead of producing antibodies to fight infection, they produce abnormal proteins (monoclonal immunoglobulins) that accumulate in the bones and blood. As multiple myeloma progresses, plasma cells spread from the bone marrow throughout the body, affecting other organs and systems of the body.
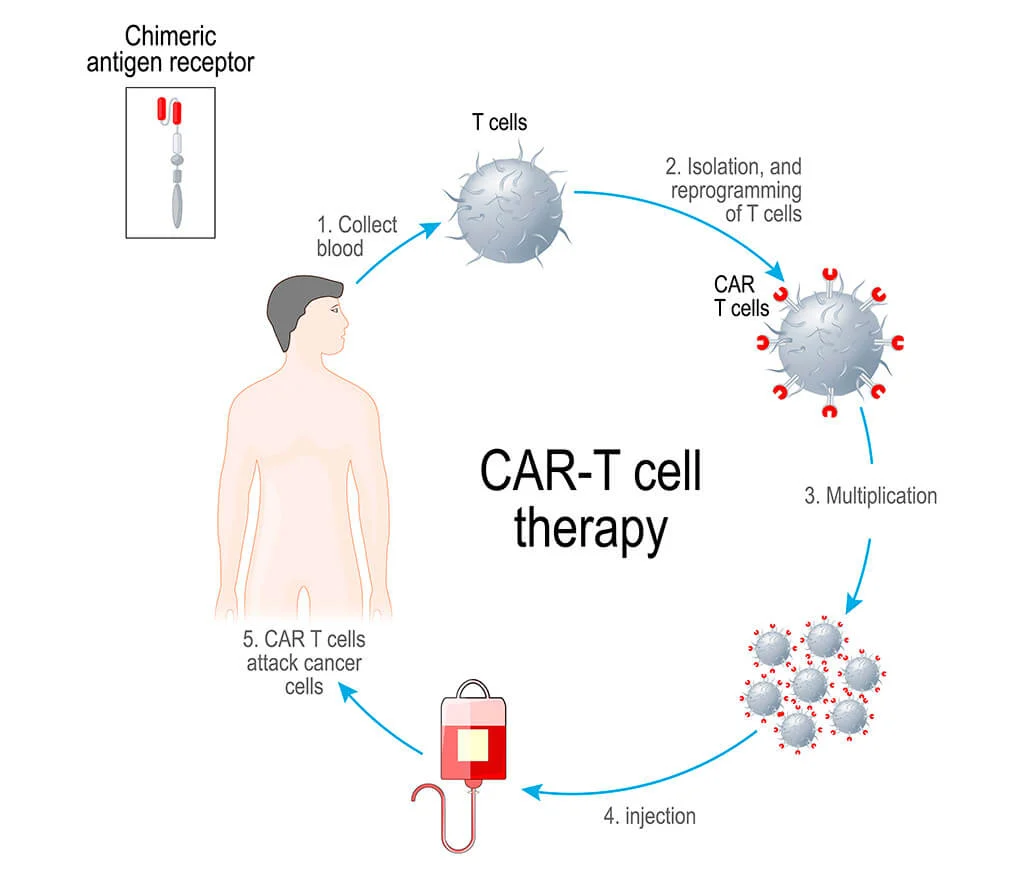
CAR T-cell therapy includes the following steps:
At this stage, a doctor determines whether the patient is an appropriate candidate for treatment. A specialist conducts various laboratory and instrumental studies to assess whether CAR T-cell therapy will be useful in a particular case. Patients should note that, as a rule, it is prescribed after standard treatment has not been successful.
The patient’s blood is taken from a vein. After this, using a special apheresis machine, the T lymphocytes are separated from the rest of the blood cells. This process is called leukapheresis. Then the resulting cells are frozen.
The cellular material is sent to a laboratory where the cells are genetically modified. They add a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR), which binds to certain proteins in cancer cells.
The modified T cells are grown in the laboratory to reach numbers in the millions. This process takes about a week.
Before CAR T therapy, a short course of chemotherapy is given to deplete existing T cells. It also aims to suppress the immune system so that it does not reject CAR T cells after they are administered. After treatment, patients may experience side effects such as nausea, fatigue and low blood counts.
Some time after chemotherapy, the patient is infused with CAR T cells, which, once released into the bloodstream, continue to multiply. They now have the ability to recognize and attack cancer cells.
The patient will need to stay in the hospital for a while so doctors can monitor his condition and monitor for side effects if necessary. Recovery usually takes about 2-3 months.
Follow-up care after receiving CAR T-cell therapy plays a very important role in monitoring the results of treatment. The patient will need to undergo regular examinations, including monitoring of blood counts, immune system function and general health.
It is important to note that there are different CAR T therapy protocols, so the treatment steps may vary. For example, a basic course of T-cell therapy, which is provided by BioPro Stem Technology, includes 3 cell injections with a week break in between.
CAR T therapy may cause certain side effects. They are caused by the rapid growth of CAR-T cells. In addition, T-lymphocytes begin to massively attack cancer cells, which leads to the development of inflammation in the body, similar to how the body reacts to infection.
All antitumor treatment methods have side effects. With CAR T therapy, side effects are usually temporary and treatable. The two most common side effects associated with T-cell therapy are:
Careful monitoring of patients’ condition during the recovery period allows for monitoring and timely elimination of undesirable consequences of treatment. When comparing CAR T to chemotherapy, the latter affects all the rapidly dividing cells in the body and is therefore associated with more serious side effects.
Since 2009, BioPro Stem Technology has been engaged in continuous research in the field of cell treatment and application of the results in medical practice. One of the company’s latest achievements was the development of its own T-cell therapy protocol (based on CAR-T cell technology). The technique is used to treat hemoblastoses, solid tumors, stop and prevent metastasis of cancer tumors.
If you are interested in the possibility of undergoing T-cell therapy, leave a request on this page. The coordinating doctor will contact you shortly and provide all the necessary information. The medical coordinator will help you choose the most suitable clinic for the therapy and resolve all organizational issues. We do not charge for our services. The patient pays for treatment directly at the selected clinic.
Please rate the work of MedTour
