Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
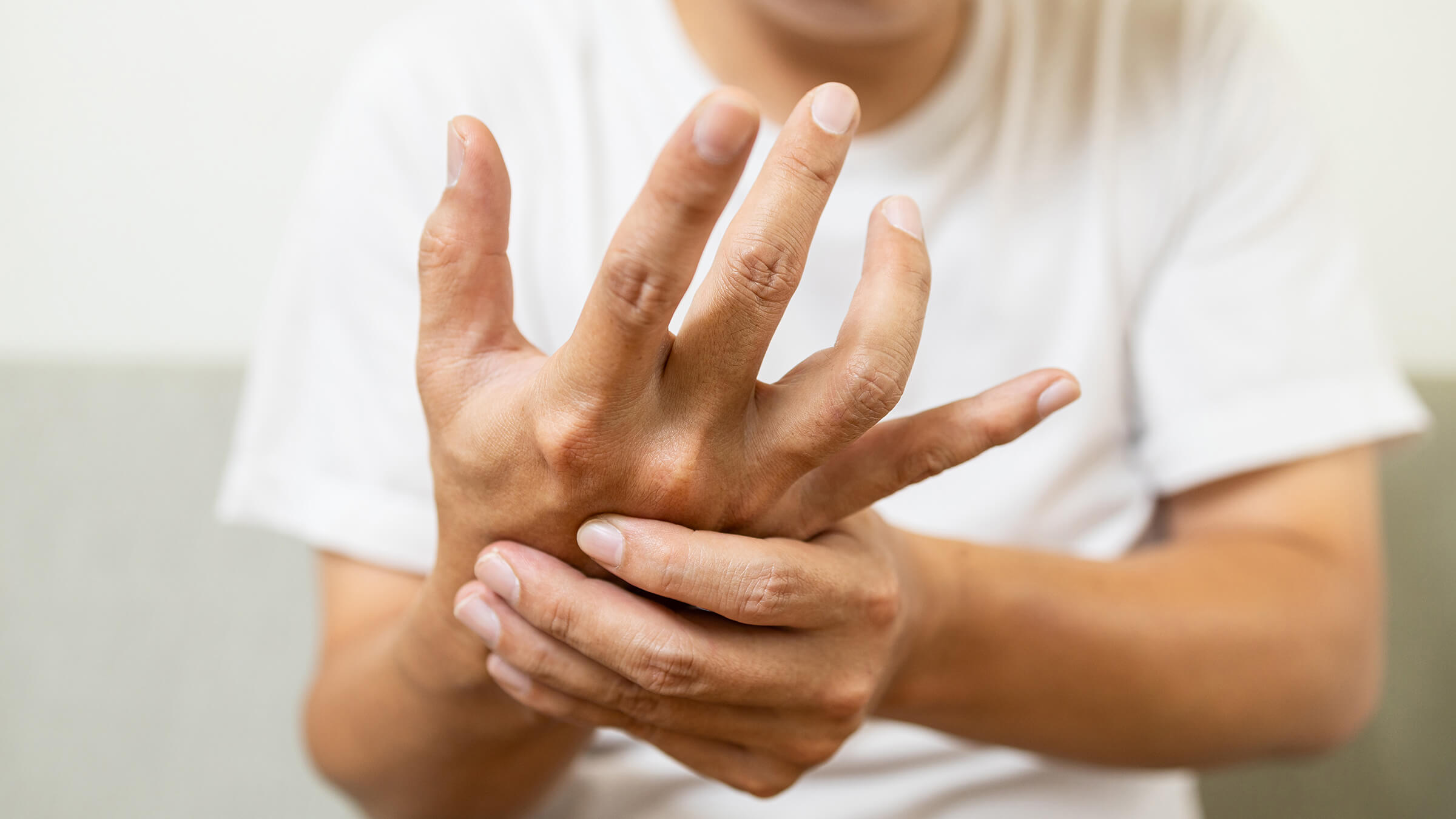

Parkinson’s disease is one of the most common neurodegenerative diseases. It is characterized by the gradual death of neurons in certain areas of the brain, which leads to impaired motor functions (hand tremor, loss of balance, slowness of movement, etc.).
In the deepest regions of the brain is a cluster of nerve cells known as the basal ganglia. They help control body movements. In a person with Parkinson’s disease, these nerve cells are damaged and do not work properly.
Basal ganglion cells produce a brain chemical called dopamine to send messages to other parts of the brain to coordinate movements. In Parkinson’s disease, dopamine levels are low, so the body isn’t getting the right signals. A person has trembling in the arms and legs, impaired gait and coordination of movements.
The disease develops due to the loss of neurons that produce dopamine, a chemical responsible for transmitting signals between nerve cells. Factors that can negatively affect nerve cells include:
However, the exact causes of the disease are not exactly known. It is believed that they are associated with a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors.
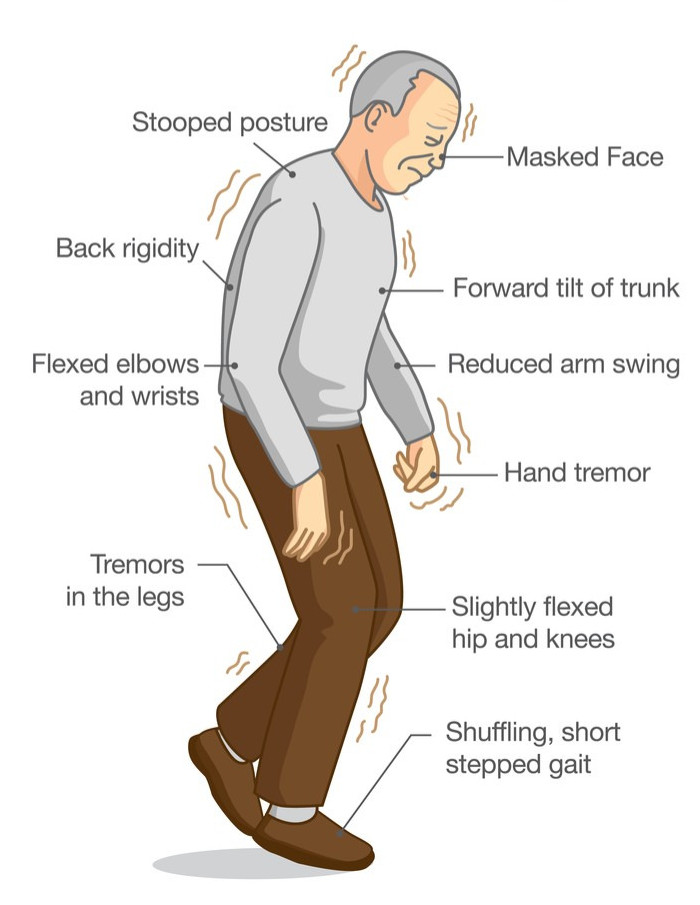
The main symptoms of the disease are:
A medical examination may include the following diagnostic measures:
Other methods, such as electroencephalography (EEG), tests for genetic mutations, and CSF analysis, can be used to clarify the diagnosis.
At the moment, there is no blood test that can determine the presence of Parkinson’s disease. However, active research is being carried out in this direction. Recently, scientists have found that a blood test can detect changes in the level of the alpha-synuclein protein, which is associated with the development of Parkinson’s disease. This can form the basis for creating a simple diagnostic test.
Currently, the treatment of Parkinson’s disease is limited to symptomatic drug therapy. However, it only improves the patient’s quality of life to some extent, but does not affect the cause of the disease.
The basis of standard treatment is the use of dopaminergic drugs to restore the concentration of dopamine in the striatum (an accumulation of gray matter in the depths of the cerebral hemispheres) with subsequent improvement in motor function.
Although these drugs do not change the course of the disease or treat the non-motor manifestations of Parkinson’s disease, they significantly improve motor symptoms in most patients, especially in the early stages of the disease. But such treatment has a serious drawback, which is expressed in problematic side effects. Drug therapy with antiparkinsonian drugs is accompanied by hallucinations, cognitive impairment, dyskinesia (impaired motor activity).
It was the severe side effects of antiparkinsonian drugs that prompted Thomas Matson from the UK to look for alternative treatments. The first symptoms of the disease appeared in a man at only 42 years old, and over the course of 17 years it progressed. Thomas says those were very difficult years. And the worst thing is that the drugs taken on an ongoing basis have changed his personality, causing serious psychological addictions.
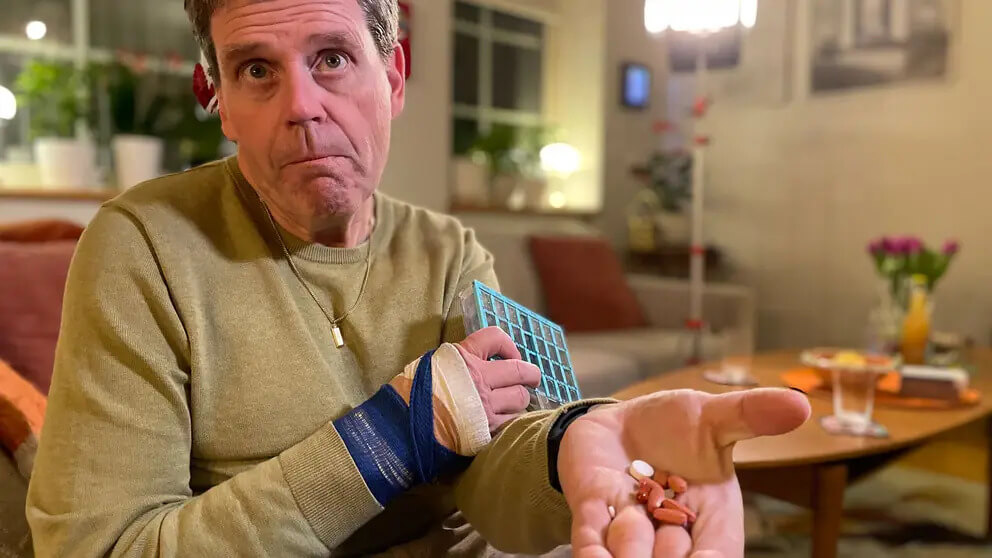 In February 2023, scientists from Lund University came to the aid of the man in collaboration with Skåne University Hospital and the University of Cambridge. They transplanted stem cells into Thomas, which transformed into dopamine-producing cells, replacing brain tissue destroyed by Parkinson’s disease. The experiment continues, but now the man was able to refuse the drugs and notes a significant improvement in his condition.
In February 2023, scientists from Lund University came to the aid of the man in collaboration with Skåne University Hospital and the University of Cambridge. They transplanted stem cells into Thomas, which transformed into dopamine-producing cells, replacing brain tissue destroyed by Parkinson’s disease. The experiment continues, but now the man was able to refuse the drugs and notes a significant improvement in his condition.
Mya S. Schiess, MD, a movement disorder specialist at UTHealth Neurosciences, said: “We have methods that effectively treat Parkinson’s symptoms, but we don’t have anything that stops the rate of progression of the disease.”
The inflammatory response is a normal part of the immune system response. It usually helps protect the body from foreign agents such as viruses and bacteria. But in people with Parkinson’s disease, chronic inflammation interferes with normal brain function and eventually leads to neuronal death.
In an effort to slow the progression of Parkinson’s disease, Mya Schiess led the first FDA-approved clinical trial using mesenchymal stem cells to “turn off” inflammation in the brain.
“Mesenchymal stem cells, derived from the bone marrow of healthy adult volunteers, help block inflammation-causing molecules in the brain. At the same time, they also allow you to repair damaged neurons” – commented Schiess .
Schiess and her team conducted the first phase of clinical trials to evaluate the safety of the treatment, which ended in September 2019. At this stage, none of the patients developed adverse immune responses to the infusions. At the same time, they had a significant decrease in inflammatory markers and a decrease in the severity of symptoms. This proves that intravenous administration of mesenchymal cells is an effective and safe treatment for Parkinson’s disease.
The MedTour company closely follows innovations in the field of treatment of various diseases. Today, cell therapy is one of the most promising areas. Stem cell therapy makes it possible to achieve success where standard methods are powerless. Call us by phone or use the feedback form to get a free consultation from a MedTour coordinating doctor about the use of regenerative medicine for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease.
At the moment, there is no way to prevent the disease, but studies have shown that certain measures can help reduce the risk of developing the disease or slow its progression:
Although these measures do not guarantee complete protection against Parkinson’s disease, they can help reduce the risk of developing it.
Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease are two different neurological diseases that affect the brain and can lead to problems with motor coordination, memory, and thinking.
Parkinson’s disease usually begins with a movement disorder, which is expressed in trembling of the hands and feet, decreased muscle strength, and changes in gait. The disease is caused by the death of nerve cells that control body movements.
Alzheimer’s disease, in turn, begins with impaired memory and thinking. Patients often forget names, places, and events, have difficulty finding their way around, and gradually lose the ability to carry out daily activities independently. In Alzheimer’s disease, nerve cells die and the connections between them are disrupted, especially in the area of the hippocampus responsible for memory.
Although the causes and mechanisms of Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease are different, both diseases can have similar symptoms, such as changes in mood, sleep, and behavior. It is also possible that some patients may have features of both diseases at the same time, which complicates diagnosis and treatment.
To prevent worsening symptoms and accelerating the progression of the disease, doctors do not recommend the following to patients:
In addition, patients should not drive a car without the permission of a doctor, as this can be dangerous for the patient and the people around him.
MedTour company cooperates with the world’s best medical centers that treat neurological diseases. We are currently offering a unique opportunity for stem cell therapy for Parkinson’s disease. This is an innovative technique that has already managed to prove its effectiveness and safety during clinical trials. Contact our medical coordinator by phone or using the feedback form to get a free consultation about the treatment of Parkinson’s disease with stem cells.
Collaborating with the best doctors who provide services in the field of cell therapy, MedTour will help you choose the most suitable specialist.
You can get an online consultation about stem cell treatment from Andrey Kovalchuk, surgeon, candidate of medical sciences. In his interview, Dr. Kovalchuk talks about the development of regenerative medicine and the treatment of various diseases with stem cells.
How do stem cells help with Parkinson’s disease?
Studies have shown that intravenous infusions of autologous (own) stem cells in patients with Parkinson’s disease help:
Can Parkinson’s disease be stopped?
Unfortunately, standard antiparkinsonian drugs can only reduce the severity of symptoms, but do not affect the rate of disease progression. However, stem cell therapy in this case shows encouraging results. Possessing pronounced anti-inflammatory properties, stem cells stop chronic inflammation of the brain and promote the restoration of neurons. To learn more about the new treatment method, please contact our medical coordinator by phone or using the feedback form.
How does Parkinson’s disease affect the psyche?
The disease has a negative impact on the mental state of the patient. One of the most common psychological symptoms of Parkinson’s disease is depression, which can occur as a result of changes in the neurochemical processes of the brain, as well as as a result of social isolation, decreased activity and loss of self-confidence.
In addition to depression, Parkinson’s disease also causes other psychological disorders, such as anxiety, restlessness, sleep and concentration disorders, panic attacks, aggressiveness, apathy, etc.
An additional disadvantage is that the drugs used to treat Parkinson’s disease also negatively affect the mental state of patients. They increase the symptoms of depression, lead to the development of addictive conditions (addictions to alcohol, drugs, games, etc.). The solution to this problem may be a new method of treatment – stem cell therapy, which is well tolerated by patients and has no serious side effects. To find out more, get a free consultation with a medical coordinator of MedTour.
Please rate the work of MedTour
