Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
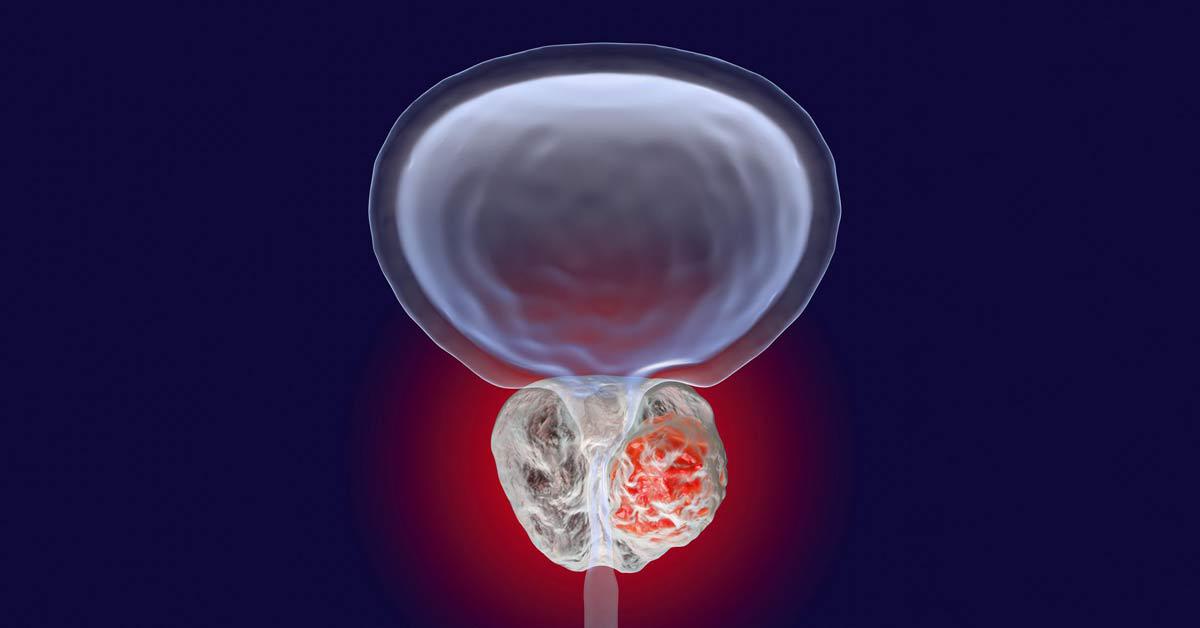
Prostate cancer is one of the most common malignant diseases in men — in most countries it ranks third after lung cancer and stomach cancer. At the same time, the first stages of the disease are asymptomatic. In addition, despite the fact that 70% of cases of the disease are men over 70 years of age, and is the cause of death of 10% of men in this age category, prostate cancer is more and more common in men aged 40 years.
In such a situation, a natural question arises — is it possible to somehow influence the incidence of prostate cancer or at least diagnose it at an early stage?
There is no method that would completely eliminate the risk of prostate cancer, however, it is possible to significantly reduce its probability. Prevention of this disease can be divided into primary and secondary. Primary prevention includes a set of measures that will not increase the risk of prostate cancer, most often, this means avoiding certain factors. Such factors include:
Thus, by maintaining moderate physical activity, harmonizing your sex life and diet, as well as choosing a safe profession or observing safety measures at work, you can significantly reduce the risk of prostate cancer.
Secondary prevention of prostate cancer is associated with the timely diagnosis of prostate cancer and precancerous diseases. To do this, it is important to remember about risk factors and conduct a more thorough diagnosis in the relevant population groups. These risk factors are:
A blood test for prostate-specific antigen (PSA, PSA) is a reliable analysis for an oncomarker, its reliability is more than 95%, however, in the case of excessive consumption of fatty foods a day before the study, stimulation of the prostate gland (often occurs when performing ultrasound before the test) and some drugs, the level of antigen may be higher. In the presence of oncological pathology, the PSA level is usually not at the upper limit of the norm, but increases tenfold, however, any deviation from the norm is a reason for further examination.
To diagnose prostate pathology, a trans-abdominal ultrasound is used (ineffective) and a transrectal ultrasound is informative and allows you to perform a biopsy if necessary. It is performed through the rectum, so this ultrasound is called transrectal ultrasound or TRU. It allows you to get information about the absence or presence of formations in the prostate gland, their shape and size, creates the necessary visualization for performing a biopsy. But this method allows only indirectly to assess the malignancy of the formation.
This study is performed after a number of other diagnostic measures that suggest the presence of a malignant process in the prostate gland. For patients without an allergic reaction to contrast agents, as a rule, computed tomography of 3 zones is performed — the chest, abdominal cavity and pelvis. This is done so that in case of detection of metastases in one of the areas not to repeat the procedure and not to expose the patient to additional radiation.
This method is used as an additional one in relation to computed tomography in common stages of the disease. It allows you to understand the location of the tumor in the most accurate way, whether it sprouts vessels, surrounding organs and tissues. Magnetic resonance imaging is needed if a large-scale surgical intervention or radiation therapy is planned. It is also performed with contrast if there are no critical contraindications.
Preventive examination to detect prostate cancer is subject to all men starting from the age of 45 years. In order to perform a proper and complete examination, every man needs to visit a urologist 1 time a year and undergo a transrectal examination of the prostate gland. Also, it is necessary to take an analysis for prostate-specific antigen 1 time in 8 years.
These recommendations apply to healthy men without significant risk factors in their health and medical history. For men who have such factors, the frequency of visits to the doctor and preventive measures should be determined by the attending oncourologist.
As mentioned above, the first and second stages of prostate cancer are
asymptomatic with rare exceptions. Later , the patient begins to worry about the following signs:
Most of the symptoms are a reason to consult a specialist, but should not frighten the patient — most likely they indicate a more common disease — prostate adenoma.
This pathology is not life-threatening and does not cause serious harm to health, but it can significantly worsen the quality of life. In addition, prostate adenoma is a precancerous disease, and if left untreated, it can lead to the appearance of a malignant tumor. The most alarming symptom is the appearance of blood during urination and sexual intercourse. It also does not always necessarily indicate the presence of cancer, but in this case, a visit to the doctor can not be postponed.
According to the latest data from large-scale cancer research, every 4 cases of cancer in the world can be prevented. Therefore, timely and competent preventive measures with regular repetition save lives and prevent tragic consequences.
Please rate the work of MedTour
