Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
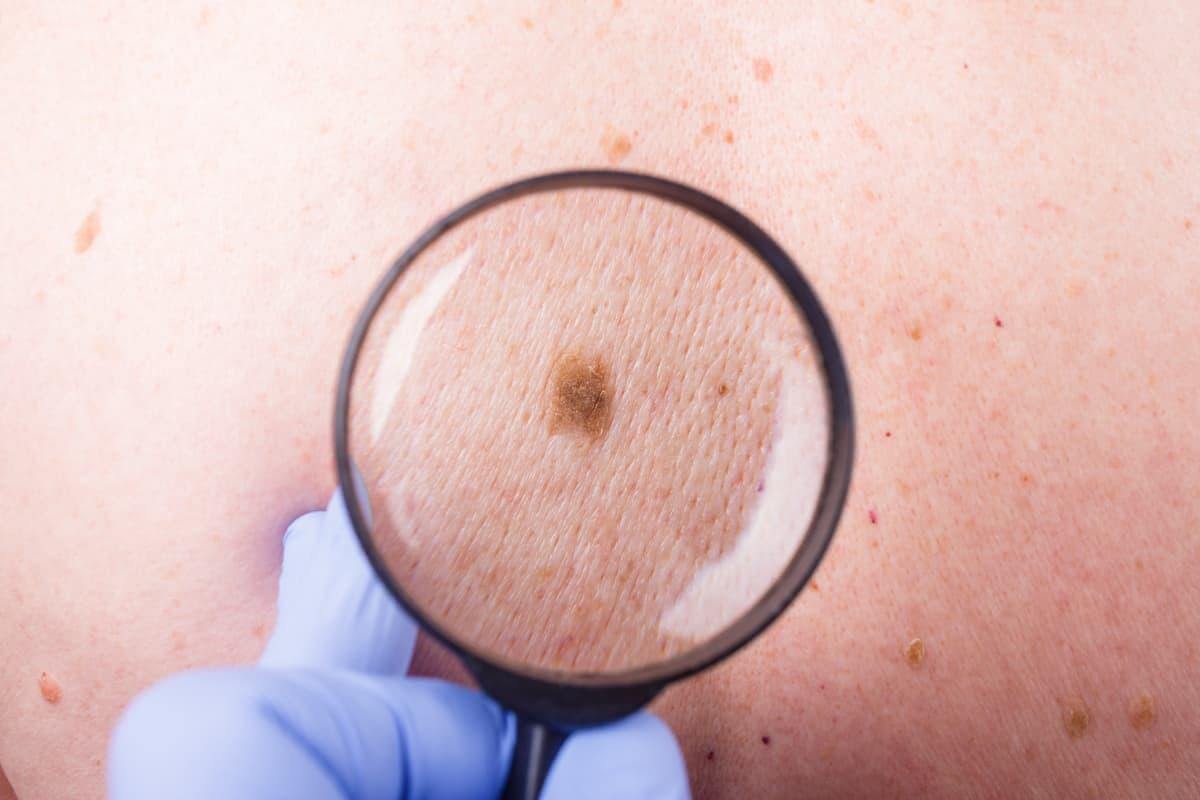
Melanoma is the most aggressive of all skin cancers. The median age at which it is diagnosed is 50, while other types of cancer are more common in people aged 65-70. In recent years, melanoma has increasingly affected patients under the age of 30.
The main danger of melanoma is that it develops imperceptibly and spreads very quickly. Most often, malignancy of moles already existing on the human body occurs. If cancer cells have managed to penetrate into the surrounding tissues, surgical removal of the tumor does not always lead to a cure. Therefore, the search for new effective methods of treating melanoma is currently underway, and the antitumor vaccine is one of the most promising areas in this area (below, we will tell you more about this innovative treatment method).
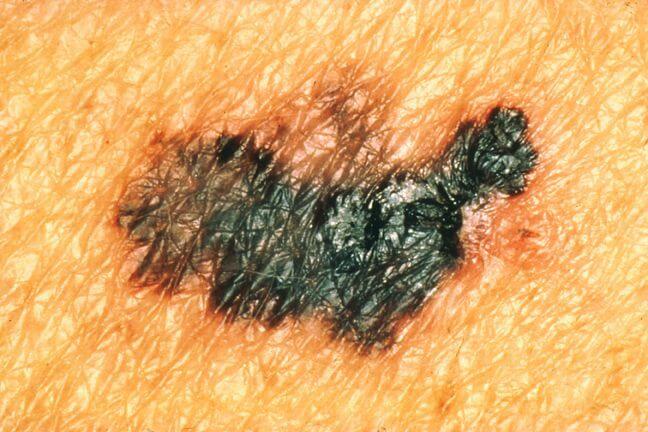
There are two main warning signs of melanoma development:
In order to recognize melanoma in time, it is enough to remember a simple rule called ABCDE, where:
Other signs of melanoma are the following:
Later symptoms of melanoma are associated with metastasis (spread) of the primary tumor to other organs and tissues. Symptoms of the disease depend on the location of metastases:
Metastatic melanoma is difficult to treat, so it is important to be able to recognize the early signs of this dangerous tumor and consult a doctor when the first alarming symptoms appear.
The MedTour company cooperates with the world’s best clinics and specialists in the diagnosis and treatment of skin cancer. We will select a clinic and a doctor free of charge that meet your individual needs and possibilities.
Doctors distinguish between five stages of melanoma – from 0 to IV. Some of them have subgroups, denoted by letters from A to D. The higher the number and letter, the more severe the stage of the disease and the worse the prognosis. For example, stage II is more severe than stage I, and stage IIIC is more severe than stage IIIB.
Stage 0 melanoma (in situ)
“In situ” in Latin means “on the spot”. In stage 0, the cancer is limited to the top layer of the skin. Cancer cells are found only in the epidermis and do not grow deeper (into the dermis). The cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes or distant parts of the body.
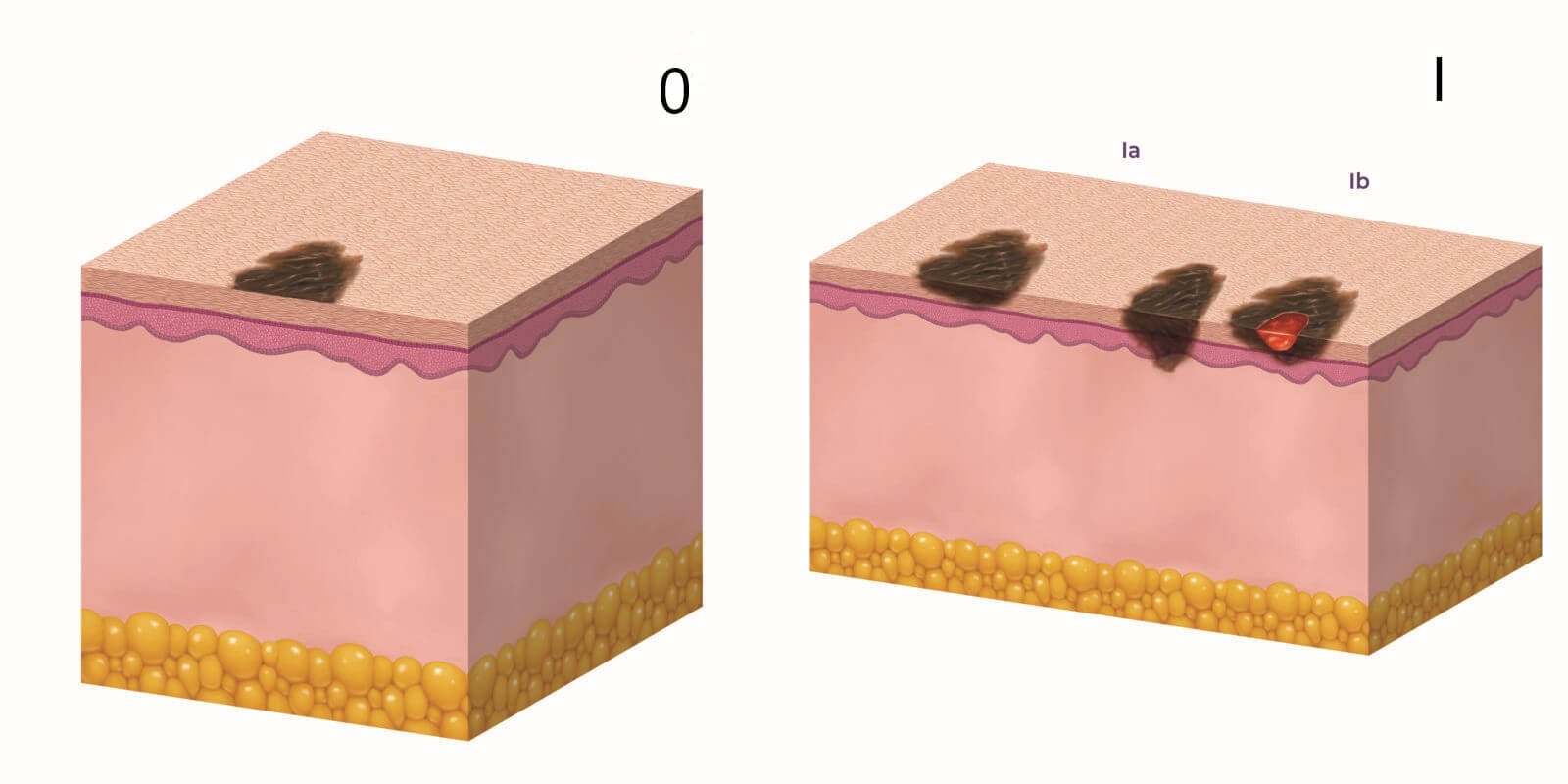
Stage I melanoma (localized tumor)
In stage I melanoma, cancer cells are present in both the epidermis and dermis. The tumor is up to 2 mm thick, and may or may not be ulcerated. The malignant process has not spread to the lymph nodes or distant parts of the body. There are two subgroups of stage I melanoma: IA and IB. They differ in the depth of penetration of the tumor and the presence of ulceration.
Stage II melanoma (localized tumor)
Stage II melanoma is determined by the thickness of the tumor and ulceration. Cancer cells are found in both the epidermis and the dermis. The cancer has not spread to lymph nodes or distant parts of the body. There are three subgroups of stage II: IIA, IIB, IIC, where stage IIA has the best, and stage IIC has the worst prognosis. Subgroups differ in the depth of penetration of the tumor and the presence of expression.
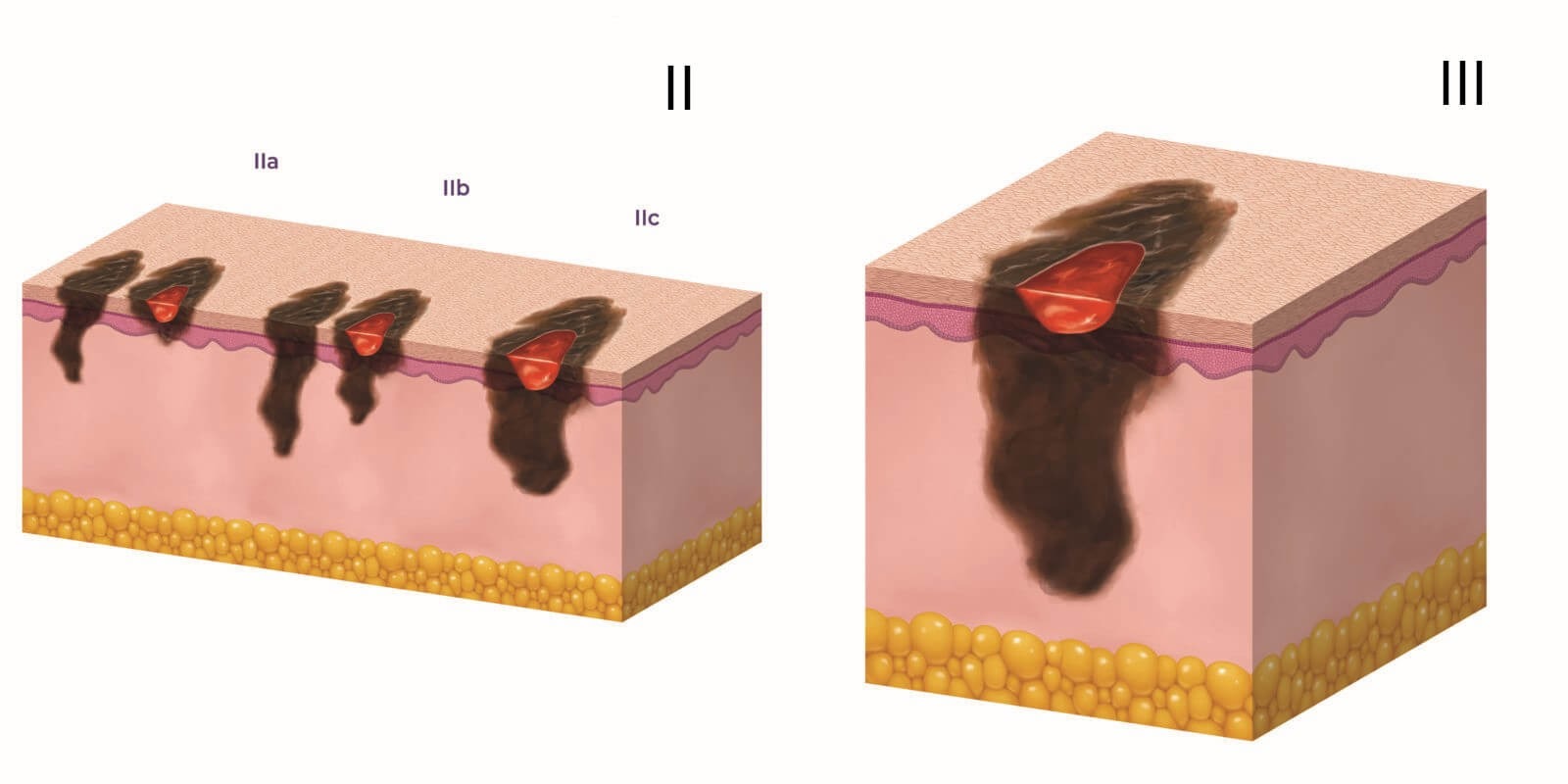
Stage III melanoma (regional spread)
Stage III melanoma is defined by the level of lymph node involvement and ulceration. The cancer has spread to one or more regional lymph nodes, or there are transit metastases (located in the epidermis or dermis more than 2 cm from the primary tumor but closer than the regional lymph nodes). There are no signs of metastasis to distant organs and tissues.
Stage IV melanoma (metastases outside of regional lymph nodes)
In stage IV melanoma, the cancer spreads beyond the primary tumor site and regional lymph nodes to more distant parts of the body. The most common sites of metastasis are distant lymph nodes, followed by the lungs, liver, brain, bones, and/or intestines.
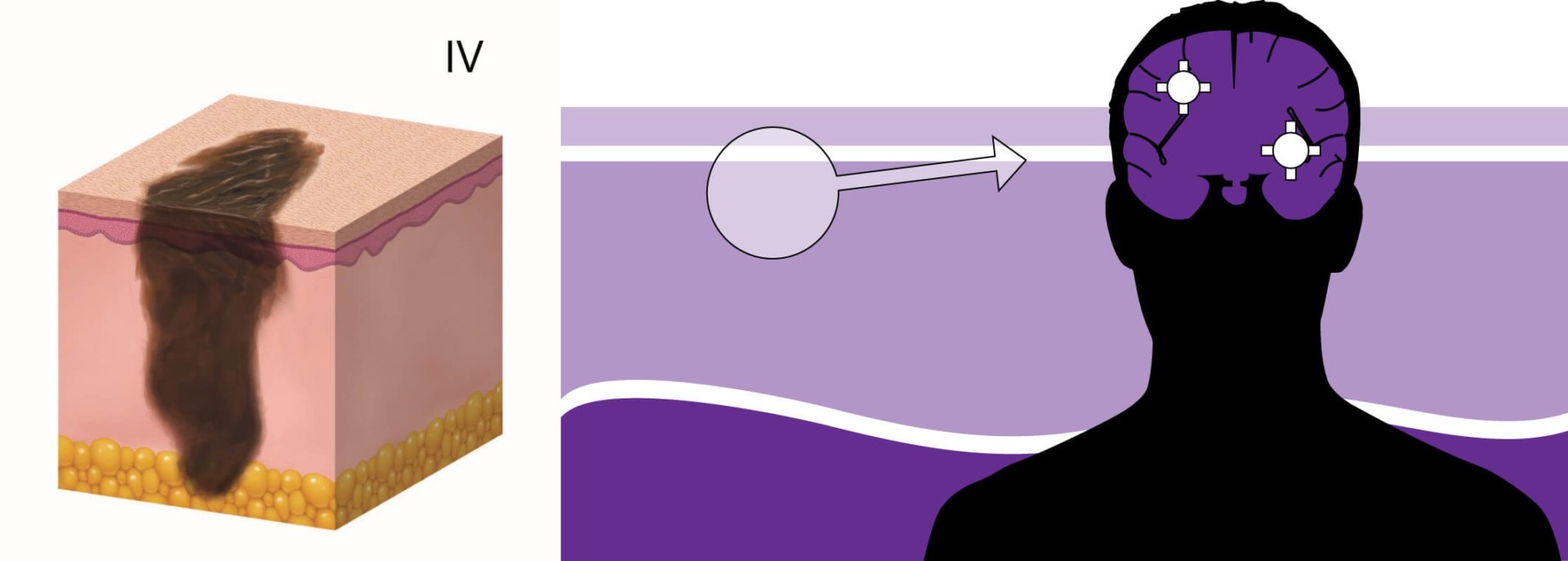
Metastasis to the brain
This is a specific form of stage IV melanoma, which is the most difficult to treat. Brain metastases develop in about 60% of patients with melanoma. However, there are factors that increase the risk of their occurrence. Brain metastasis is more likely if:
The brain is protected by a structure called the blood-brain barrier. The complexity of the treatment of melanoma lies in the fact that this barrier does not let through not only harmful substances, but also anticancer drugs. Therefore, in recent years, doctors are looking for alternative methods of therapy. One of them is the use of anticancer vaccines. Vaccines work differently than chemotherapy drugs. Instead of directly killing cancer cells, it stimulates the immune system to fight the tumor. We will tell you more about this new technique in the section “Melanoma treatment”.
The main method of diagnosing melanoma is a biopsy. The procedure involves the removal of part or the entire mole for subsequent histological analysis. If malignant cells are found in the sample, the doctor may prescribe additional research methods to determine the stage of the disease and choose the most effective method of treatment.
Blood tests are not used to diagnose melanoma, but some tests may be done before or after treatment, especially in the later stages of the disease.
Doctors often test the blood for lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels before choosing a therapy. A high concentration of this enzyme may mean that cancer cells have spread throughout the body.
There are currently several treatments for melanoma. They can be used both independently and in combination. The choice of therapeutic approach depends on the location and stage of the tumor, as well as the age and general health of the patient.
Surgery is the standard treatment for all stages of melanoma. The goal of surgery is to remove the neoplasm as completely as possible. During the procedure, the doctor excised the tumor, as well as part of the underlying and surrounding tissues, into which cancer cells could spread.
Mohs micrographic surgery can be used to treat melanoma at an early stage. During the operation, the surgeon removes the affected tissues in layers, immediately checking them under a microscope for the presence of cancer cells. This approach allows doctors to preserve the maximum amount of healthy tissue, which is especially important if the tumor is located on the face or other exposed parts of the body.
Radiation therapy involves the use of high-energy x-rays to destroy tumor cells. Doctors prescribe this method in the following cases:
For the treatment of melanoma, doctors can perform both remote radiation therapy, when the radiation source is located at a distance from the patient’s body, and brachytherapy, in which the so-called radioactive seed is injected into the body in the immediate vicinity of the tumor.
Targeted drugs are able to recognize and block certain mechanisms that are necessary for the growth and survival of cancer cells.
Some patients with melanoma have mutations in the BRAF, C-KIT, and NRAS genes that serve as specific targets. Targeted drugs recognize mutations in cancer cells and identify them. After that, they either destroy them directly or block the functions that are needed for the survival of cancer cells. For example, some drugs stop the growth of new blood vessels that supply the tumor with oxygen and nutrients.
The main advantage of targeted therapy is its selectivity: the drugs act only on tumor cells without damaging healthy cells. But there is a downside: only those patients who have specific mutations in cancer cells receive therapeutic benefit from the treatment.
The immune system identifies and protects the body from viruses, bacteria, and other potentially harmful agents. However, in the case of cancer, it is difficult for her to fight the disease, since the malignant tumor develops mechanisms that make it invisible to the “soldiers of the immune system”. To solve this problem, methods have been developed that help the immune system recognize and destroy cancer cells.
The main immunotherapies currently used to treat melanoma are checkpoint inhibitors and cancer vaccines. Immune checkpoint inhibitors work by removing blocking mechanisms from immune cell receptors. After that, they begin to recognize and destroy cancer cells. We will tell you more about the method of antitumor vaccination.
The principle of operation of conventional vaccines is clear: weakened microorganisms are introduced into the body, to which the immune system forms a response. Cancer vaccines work a little differently. They contain substances that help the immune system prevent the development of cancer or more effectively fight an existing tumor in the body.
Currently, there are several types of vaccines used for melanoma. One of them was developed by Ukrainian scientists and was named СANCERAX. This is an antitumor vaccine used to treat a wide range of cancers, including melanoma. The effectiveness of the drug has been proven in clinical trials.
There are two types of CANCERAX vaccine:
Autovaccine
The autovaccine is intended for patients who are planning surgery and want to protect themselves from cancer recurrence or improve their chances of a successful cure. For the manufacture of the vaccine, blood is taken from the patient, from which dendritic cells and a sample of the tumor are inserted. Dendritic cells mature in the laboratory in an environment where tumor proteins are present. In this way, they “learn” to recognize cancer cells. After the introduction of CANCERAX autovaccine into the body, dendritic cells migrate to the lymph nodes, where they transmit information to T-lymphocytes (soldiers of the immune system). “Trained” lymphocytes gain the ability to recognize and destroy cancer cells, thus fighting the tumor.
Xenovaccine
The xenovaccine was developed for patients who had surgery a long time ago and did not save a tumor sample. The vaccine contains quail tumor-associated antigens of embryonic origin, which are structurally similar to tumor antigens. In response to them, the immune system learns to identify and attack cancer cells. CANCERAX xenovaccine can also be used to prevent the development of melanoma in patients at high risk.
To find out more about the CANCERAX vaccine, get a consultation from the medical coordinator of MedTour.
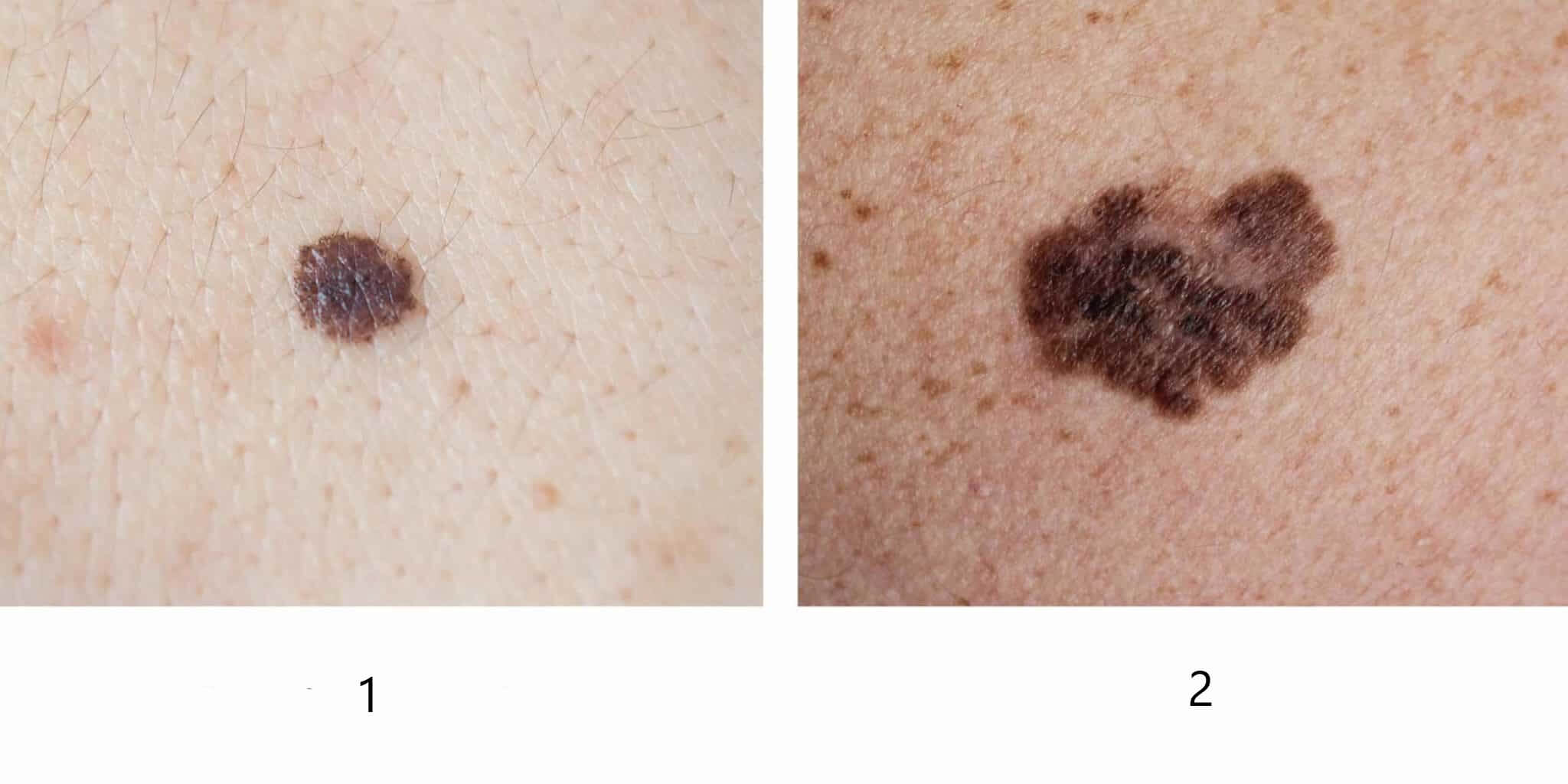
1. Normal mole 2. Melanoma
Normal moles are usually small, symmetrical and flat. They have smooth borders and uniform coloring. Melanomas are often asymmetrical, larger than 6 mm, and elevated. They have uneven borders and uneven coloring. And the main difference: malignant nevi changes over time. Therefore, any changes in moles are a reason to see a doctor.
The prognosis depends on the stage of the cancer. The survival rate for melanoma is generally higher in women than in men. Scientists do not know what it is connected with. Perhaps women are more likely to see a doctor about new growths on the skin or changed moles, which allows diagnosing cancer at an early stage.
According to the average indicators, the 5-year survival rate for melanoma is:
Therefore, early detection and treatment are very important.
The MedTour company cooperates with leading cancer centers specializing in the treatment of melanoma around the world. We strive to make innovative cancer therapies, such as personalized therapy, more accessible to patients. The medical coordinator of MedTour will select for free a clinic that best suits your personal needs and capabilities.
The MedTour platform contains a large number of profiles of doctors with whom we cooperate. These are doctors who specialize in the treatment of skin cancer and work both in the largest multidisciplinary clinics and in private medical centers. The medical coordinator of MedTour will select a specialist, taking into account the nature of your disease and personal wishes.
Please rate the work of MedTour
