Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
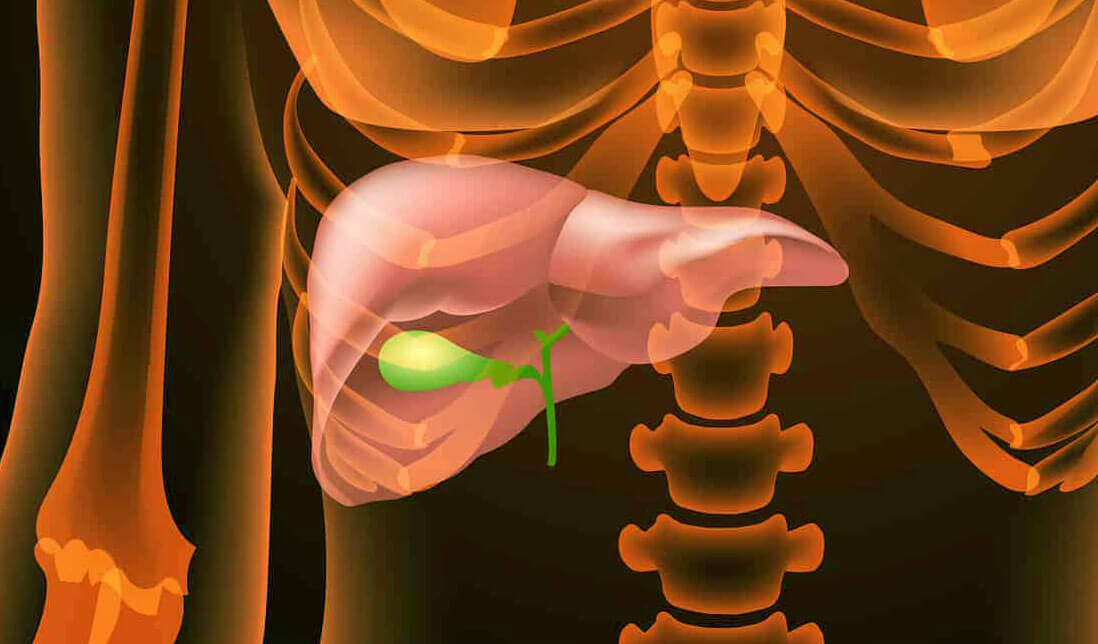
Gallbladder cancer is an oncological pathology in which a neoplasm is formed from the tissues of the gallbladder. This is a fairly rare pathology, accounting for less than 5% of the total number of malignant diseases. More often the tumor forms in women aged 50-60 years.
At first, the neoplasm is most often localized in the neck and bottom of the gallbladder. It can then attack the liver, pancreas and other tissues. This is a rather complex disease, the likelihood of successful treatment of which is greatly reduced at later stages of development. However, accurate diagnosis with determination of the histological characteristics of the tumor and a personalized approach to treatment will significantly increase the possibilities of therapy and increase the chances of bringing the disease under control.
The exact causes of this disease have not yet been determined. Among the factors that can provoke the development of this pathology are:
Gallbladder cancer can be preceded by a number of diseases, for example, cholelithiasis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, chronic cholecystitis, biliary cirrhosis. The likelihood of tumor formation in the gallbladder increases with congenital fibrosis and polycystic liver disease.
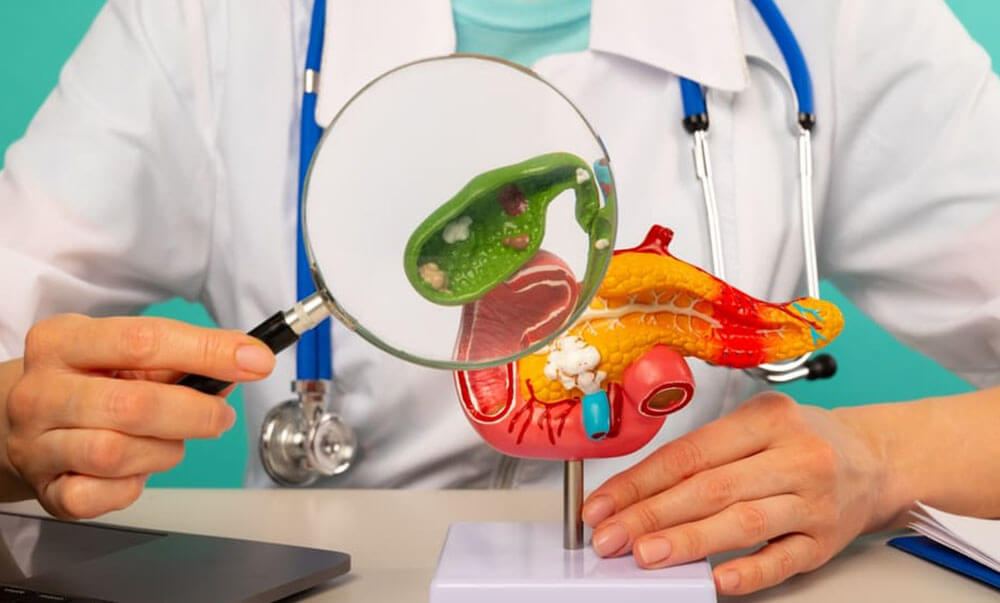
The peculiarities of the structure and location of the gallbladder lead to the fact that there are no early symptoms of gallbladder cancer. However, as the pathological neoplasm grows, typical symptoms of gallbladder oncology arise, which include:
As the liver becomes involved in the pathological process, jaundice develops, and liver failure appears and progresses. At the very later stages, ascites develops, and abdominal carcinomatosis may occur.
In most cases, adenocarcinoma of the gallbladder is diagnosed. The formation of this tumor occurs in the epithelial layer of the gallbladder mucosa. Less commonly, in about 20%, squamous cell or small cell carcinoma is detected.
Quite rarely, sarcomas and carcinoids can occur in the gallbladder. Histological diagnosis is necessary to accurately determine the type of tumor.
Doctors distinguish several stages of pathology, each of which has characteristic features:
When the disease progresses and begins to metastasize, the nearby lymph nodes are most often affected first, and the liver is affected. Then metastases can affect organs that are located at a distance from the tumor. Most often the duodenum and sections of the large intestine are affected. Abdominal carcinomatosis may develop. In addition, metastases can be found in the ovaries and bones.

Ultrasound diagnostics is the first stage in detecting pathology. It is able to detect a tumor, determine its location and approximate size. Often, a tumor is first detected by ultrasound during a routine examination or in the process of diagnosing other diseases.
This test allows doctors to get an idea of how far the tumor has spread and whether the liver is involved. There are direct and indirect signs of cancer; an experienced diagnostician knows them and can conclude about the presence of pathology based on the information received. If an ultrasound detects a neoplasm, as a rule, additional studies are prescribed that will allow an accurate diagnosis to be made.
Doctors usually prescribe a comprehensive examination to make an accurate diagnosis if cancer is suspected. In addition to ultrasound, the following diagnostic methods are most often used:

Laboratory tests are usually prescribed when gall bladder cancer is detected. A standard blood test is performed to determine the levels of bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, and aspartate aminotransferase. Measurements of these liver parameters can indicate problems in the liver and biliary system.
Also, specific tests: analysis of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), tumor marker CA 19-9 can be prescribed if this type of cancer is suspected.
Laboratory tests also include the latest cancer diagnostic methods such as genetic testing. Using certain tests, it is possible to identify mutations in tumor genes and, based on this, select a treatment that will be effective specifically for this type of tumor. Today you can get tested in special laboratories in different countries of the world.
To get more information about the latest methods for diagnosing cancer and the possibility of conducting examinations in different countries, contact the MedTour coordinating doctor.
Prognosis for this pathology depends on the stage and type of tumor.
According to statistics, the five-year survival rate of patients is:
However, much depends on the choice of treatment tactics. If you get to good oncologists and your treatment is personalized taking into account the specifics of the tumor, the prognosis can significantly improve.

The most common treatment involves surgery for a diagnosis of gallbladder cancer. In addition, special medications are prescribed, and radiotherapy, immunotherapy and other methods are often used.
It is possible to obtain more detailed information about the possibilities of vaccination with cancer vaccines, the use of targeted therapy and other treatment methods from the MedTour coordinating doctor.
The MedTour platform works with the best clinics for the treatment of gallbladder cancer. We cooperate with large centers, university clinics, private medical institutions from around the world, we know who specializes in the treatment of pathologies of this type, what methods and protocols are used by certain clinics and what results they achieve.
The MedTour coordinator will provide you with detailed information on clinics, tell you the nuances of applying for treatment abroad, and advise you on prices.
It is important to find the best specialists in this field so that the treatment is as productive as possible. You can do this using the MedTour website. We will help you choose a doctor who has extensive clinical experience and uses the latest methods for treating tumors of the biliary system.
Contact us to receive comprehensive information on doctors as part of a free consultation and make the best choice of specialist for your needs.
Please rate the work of MedTour
