Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
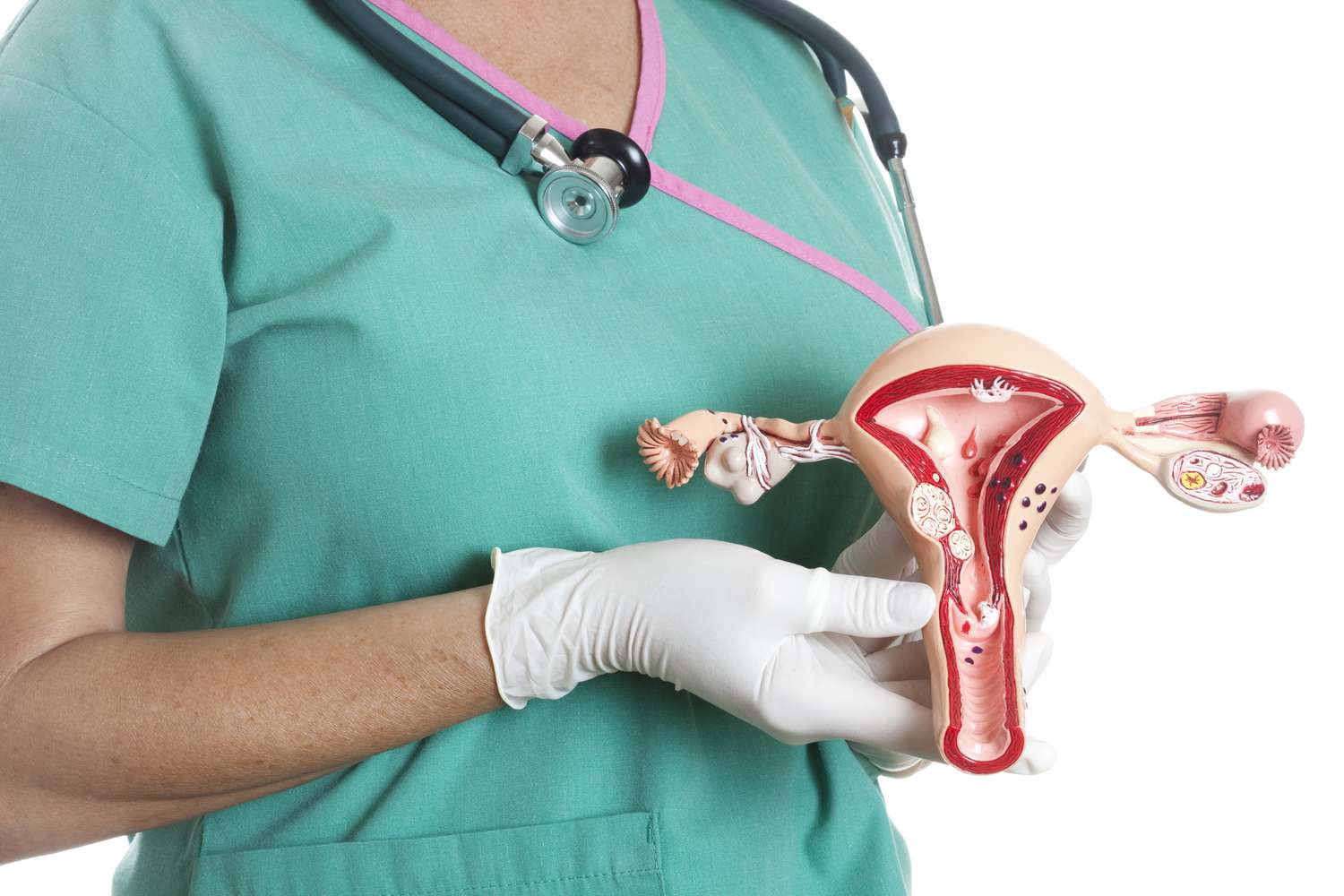
Endometrial hyperplasia is an abnormal growth of the inner layer of the uterus (endometrium) caused by excessive cell division. This condition may be associated with hormonal imbalances, such as excess estrogen or lack of progesterone, as well as chronic inflammatory processes or metabolic changes.
Without timely treatment, the disease can lead to serious consequences. Abnormal uterine bleeding contributes to the development of anemia and decreased hemoglobin levels. Furthermore, atypical hyperplasia is considered a precancerous condition. Without medical intervention, the risk of developing endometrial cancer increases to 30%. This condition can also cause infertility due to disruption of the normal functioning of the endometrial tissue.
Timely consultation with a physician allows for an accurate determination of the causes of the pathology, selection of effective treatment and prevention of serious complications. MedTour, as one of the leaders in medical tourism, provides patients with access to the best clinics and doctors both in Ukraine and abroad. The company’s specialists help develop personalized solutions for each patient, taking into account their needs, preferences, and medical indications.
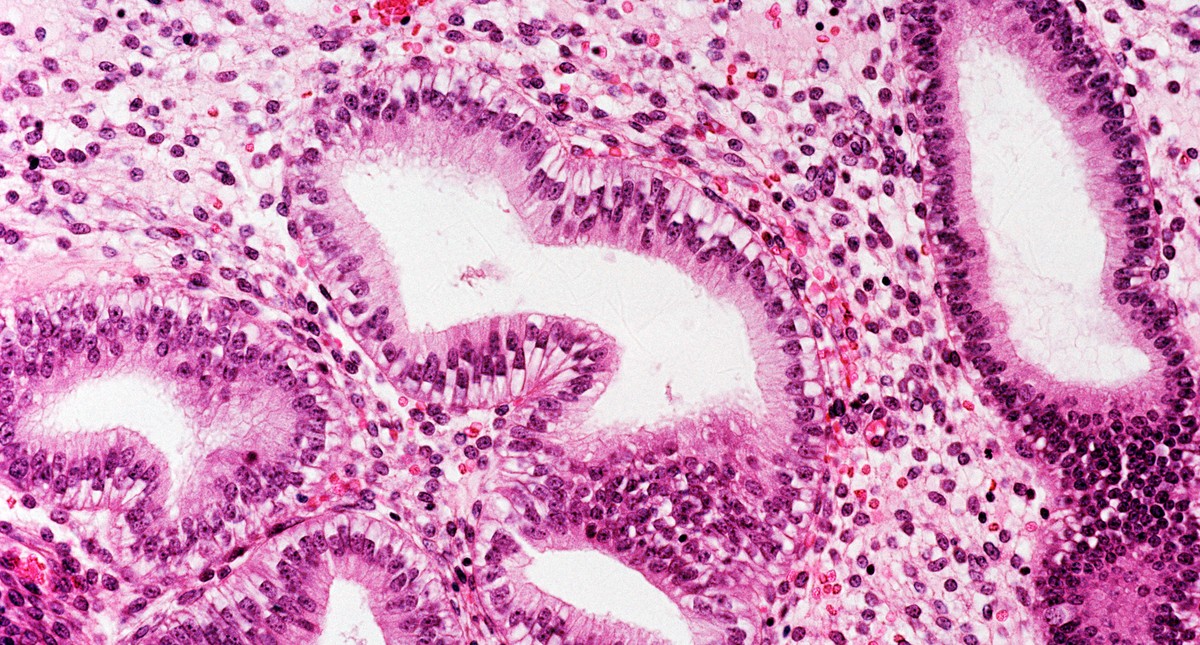
The endometrium is the tissue that lines the inner surface of the uterus. It plays a key role in the female reproductive system. The endometrium consists of epithelial cells and underlying connective tissue, providing favorable conditions for the attachment and development of the fertilized egg. During each menstrual cycle, the endometrium undergoes hormonal changes: its cells grow and thicken under the influence of estrogens, and then, under the influence of progesterone, prepare for a possible pregnancy.
If the hormonal balance is disrupted, the process of regulating cell division in the endometrium can get out of control, leading to its excessive thickening. This condition is called hyperplasia. To better understand what endometrial hyperplasia is, it is important to know that it is not just an increase in the thickness of the layer, but a pathological process accompanied by proliferation (excessive growth and division) of cells.
Endometrial hyperplasia develops under the influence of various factors, the main one of which is hormonal disorders. Excessive exposure to estrogens on endometrial tissue, combined with a lack of progesterone, leads to uncontrolled growth of the cells in the inner uterine layer.
Understanding the risk factors allows individuals to pay timely attention to changes in their bodies and seek medical assistance to prevent possible complications.

The disease is classified according to the nature of cellular changes and the degree of their severity. Its main forms are described below.
Glandular endometrial hyperplasia is an excessive growth of the glands of the inner layer of the uterus. This form is considered the mildest and is often benign. With glandular endometrial hyperplasia, the structure of the glands is preserved, but their number increases significantly. The main reason for its development is hormonal disorders, such as excess estrogen combined with a lack of progesterone.
This type is characterized by local thickening of the endometrial tissue in certain areas. These changes are often associated with the formation of polyps, which can be either benign or precancerous.
Symptoms of focal endometrial hyperplasia include irregular menstruation, pain, and discomfort in the lower abdomen. Diagnosis typically includes pelvic ultrasound, hysteroscopy, and biopsy to determine the nature of the changes. Early detection helps prevent complications and begin treatment in a timely manner.
It is a proliferation of endometrial glands with the formation of cystic cavities. Such changes occur due to the accumulation of secretions inside the glands, which leads to their expansion.
This form of hyperplasia is also associated with hormonal disorders and requires a comprehensive treatment approach. Hormonal therapy is most commonly used to restore the balance of estrogens and progesterone, as well as surgical intervention in cases of complications or when conservative treatment proves ineffective. Treatment for glandular-cystic endometrial hyperplasia is aimed not only at eliminating symptoms, but also at preventing the risk of malignant transformation.
The disease can manifest itself with various symptoms, depending on the degree and form of pathological changes. The main symptoms of endometrial hyperplasia include:
Diagnosis requires a comprehensive approach, including modern imaging methods and laboratory tests:
Timely diagnosis makes it possible to choose the correct therapeutic tactics and avoid complications.

The choice of treatment strategy depends on the form of the disease, the patient’s age, and reproductive plans. Treatment for endometrial hyperplasia can be either a conservative or surgical approach.
Hormonal therapy forms the basis of treatment, aimed at restoring the balance of estrogens and progesterone. The following medications are commonly prescribed:
This type of treatment is especially effective for glandular and glandular-cystic hyperplasia.
When medication proves ineffective or in cases of complex forms of hyperplasia, the following procedures are used:
Without timely treatment, the disease can lead to severe consequences:
To reduce the risk of hyperplasia, it is important to:
Following these recommendations will help maintain women’s health and prevent the development of serious diseases.
 The MedTour company offers comprehensive assistance in choosing a clinic and doctor, as well as organizing effective treatment for endometrial hyperplasia. We cooperate with leading medical centers and experienced specialists in Ukraine and abroad, providing our patients with access to modern diagnostic and therapeutic methods. Call the phone number listed on the website or fill out the feedback form to receive a free consultation with a coordinating doctor and take the first step towards a healthy life.
The MedTour company offers comprehensive assistance in choosing a clinic and doctor, as well as organizing effective treatment for endometrial hyperplasia. We cooperate with leading medical centers and experienced specialists in Ukraine and abroad, providing our patients with access to modern diagnostic and therapeutic methods. Call the phone number listed on the website or fill out the feedback form to receive a free consultation with a coordinating doctor and take the first step towards a healthy life.
Please rate the work of MedTour
