Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
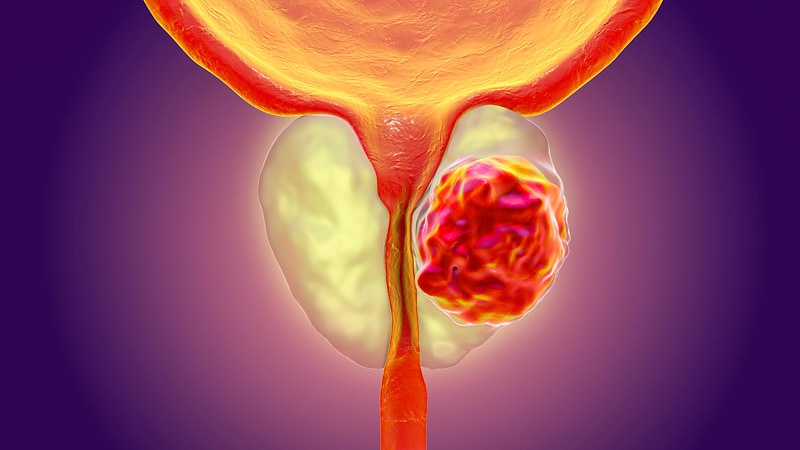
Prostate cancer is a malignant disease that arises from the epithelium of the alveolar cell elements of the prostate gland. This is one of the most common oncological diseases in the world — every year there are more than 400,000 new cases in the world. This is the most common cancer in men over the age of 60.
According to the degree of differentiation of the tumor:
By localization:
Prostate cancer risk factors by degree of significance in descending order:
The tactics of prostate cancer treatment depends on the stage and age of the patient. An
important feature in the choice of tactics for the treatment of prostate cancer is the absence of a difference in survival with the main methods of treatment — radical surgical treatment and treatment with brachytherapy — a type of radiation therapy in which the radiation source is injected into the affected organ. At the same time, each method has its advantages.. When using surgical treatment, the frequency of local relapses is lower and the psychological state of the patient is better, but this method is available only for small tumors (stage I, sometimes stage II), otherwise there is a risk of non-radical removal of the tumor and disease progression. Treatment with brachytherapy allows minimal disruption of sexual function, is suitable for any size of the tumor, reduces the risk of recurrence of the disease with lymph node damage, but treatment can be prolonged, as well as the risk of local recurrence at the site of the tumor with this method of treatment is higher than with surgical removal of the tumor.
It is performed in an open, endoscopic or robotic way. The latter two have significantly less effect on sexual function, do not cause significant pain syndrome and do not cause urinary incontinence, but endoscopic removal is possible only if the tumor size is no more than 2 cm and it is possible to remove it together with the capsule. In most cases, there is a complete removal of the prostate gland together with the seminal vesicles (glandular organs involved in the mechanism of ejaculation) — the exception is very small highly differentiated tumors.
Prostate brachytherapy can be performed in two ways — high-dose and low-dose. With high-dose brachytherapy, 2 catheters are inserted into the prostate gland and the entire radiation dose is administered in 10-20 minutes. This procedure is outpatient, that is, the patient can immediately go home after the procedure. With low-dose therapy, the isotope is injected in a special capsule, from which it is gradually released. The entire treatment takes from 6 months to 1 year, but such treatment is more effective compared to high-dose. However, sometimes the clinical situation requires a high-dose procedure, so only a doctor can determine which tactics of brachytherapy will be chosen.
Surgical removal removal of the prostate gland within healthy tissues together with seminal vesicles is rarely used in young men due to high traumatism in the presence of alternative methods of treatment;
Treatment at this stage already requires complex methods, so the methods listed below can be combined, exactly how the attending physician determines, depending on the degree of damage to the surrounding organs and tissues. Applied methods:
A complete cure at this stage is impossible, the treatment tactic is to increase life expectancy and improve the quality of life. Surgical treatment is not used at this stage. Methods used:
In the CIS countries, preference is usually given to the surgical method of treatment, which is not always justified and does not always lead to better oncological results and a better quality of life. The MedTur team will help to organize a remote consultation in clinics in Germany, Austria and Israel in order to get a second opinion and choose the most appropriate and reasonable method of treatment.
Please rate the work of MedTour
