Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
Epilepsy is a chronic neurological disease characterized by recurrent episodes of seizures. They are caused by abnormal electrical activity in the brain. In some people, epilepsy can be controlled with medication, but in 30% of cases, anticonvulsants are ineffective. To relieve symptoms, a doctor may recommend surgery.
There are different types of surgeries for epilepsy. The choice of surgical approach depends on the type of disease and its severity. According to studies, in about 80% of cases, surgery helps to significantly reduce the frequency and severity of epileptic seizures, and 15-20% of patients get rid of them completely.
About a third of people with epilepsy suffer from seizures that cannot be controlled with medication. This has a severe negative impact on their quality of life, including learning and work difficulties, loss of independence, social isolation, and an increased risk of injury and depression. Patients with uncontrolled epilepsy also have an increased long-term mortality rate, with the most common cause being sudden death syndrome in epilepsy. For such people, surgery can be an effective solution.
The decision on surgical intervention is considered in the following cases:
The operation is prescribed after a thorough diagnostic examination of the patient, as well as an assessment of the therapeutic benefits and possible surgical risks.
The purpose of the diagnostic examination is to determine the area of the brain in which the epileptogenic focus that provokes seizures is located. As a rule, patients are prescribed the following studies:
In addition, doctors conduct tests that assess the general health of the patient.
The course of the operation depends on the chosen surgical technique. Currently, there are a number of surgical interventions that are performed for various forms of epilepsy.
During the operation, the area of the brain that causes seizures is removed. The part of the brain that is removed is called an epileptogenic focus. This is the most common type of surgery for epilepsy. It is suitable for patients whose seizures start in one area of the brain.
Removal of the temporal lobe of the brain. This operation has the highest success rate. After surgery, 70% of patients get rid of seizures. In 20% of people, seizures remain, but their number is reduced by more than 85%. Only in 10% of patients the operation does not lead to success.
The essence of the operation is to remove the frontal lobe of the brain, in which there is an abnormal electrical activity that provokes seizures. The success rate of this surgical intervention is somewhat lower than that of a temporal lobectomy, however, it helps to get rid of seizures in 50% of patients.
If the epileptogenic focus is located in the occipital lobe, convulsive seizures are accompanied by visual impairment (narrowing of the visual field, visual hallucinations, ictal blinking). In the parietal lobe, the pathological focus is rarely localized and is usually associated with the presence of a tumor or cortical dysplasia (anomalies in the structure of the cerebral cortex). The essence of the operation is to remove the neoplasm or lesion that provokes epileptic activity.
This operation is performed if the area of the brain in which the epileptogenic focus is located cannot be safely removed. During the intervention, the surgeon makes a series of shallow incisions in the gray matter of the brain, dissecting the nerve fibers that spread abnormal electrical activity. Sometimes subpial transection is performed in combination with surgical resection if the lesion is in a critical region of the brain and cannot be completely removed.
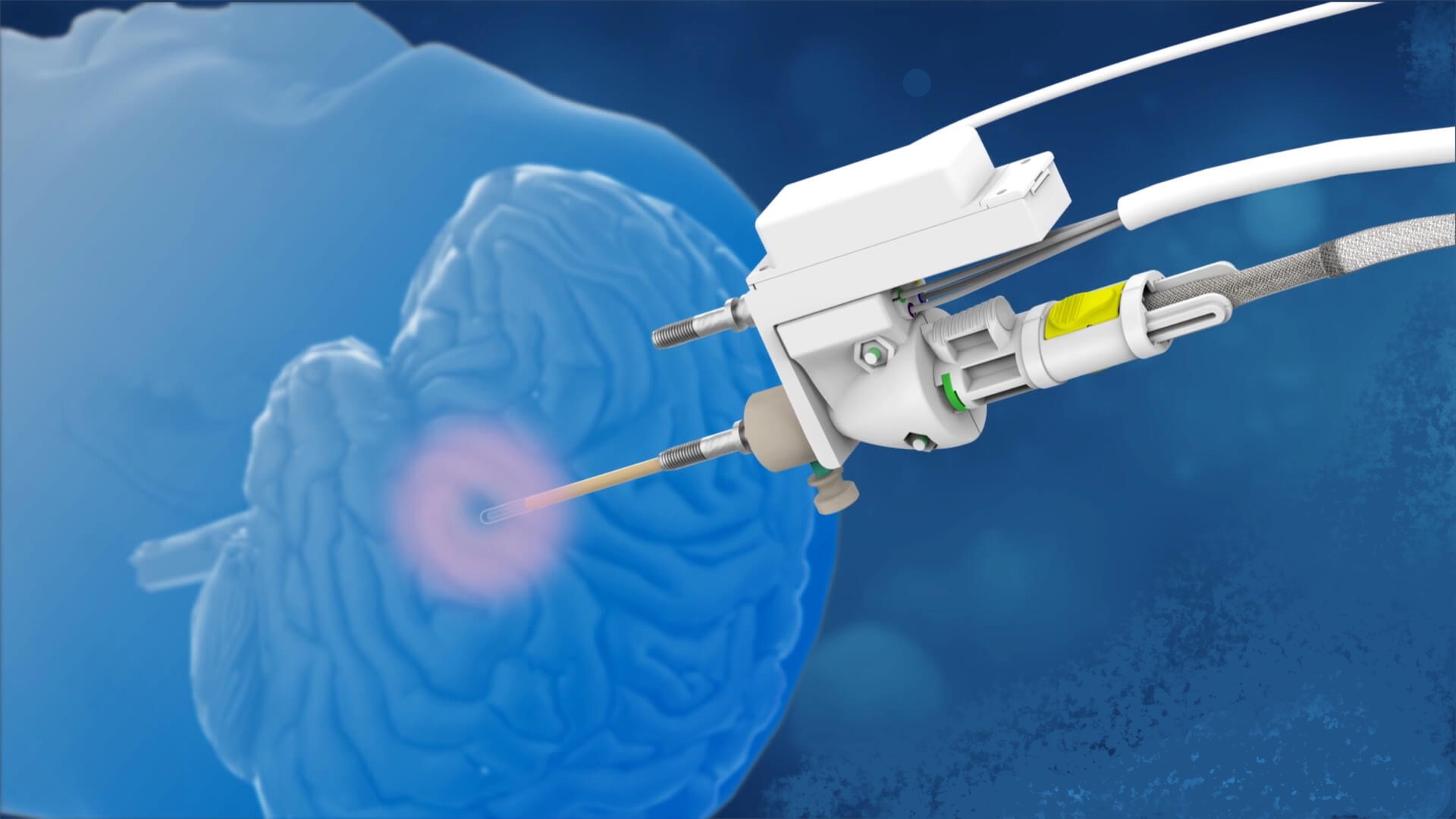
During the operation, the doctor, under MRI control, inserts a probe into the epileptogenic focus through a small hole in the skull and destroys the pathological tissues using precisely directed laser energy. This is a minimally invasive procedure that does not require a craniotomy. Epilepsy laser treatment is suitable for patients with a well-defined focus of abnormal electrical activity.
The operation is indicated for children whose seizures are caused by damage to a large area of one of the hemispheres of the brain. There are several types of surgical intervention.
The results of these surgical interventions are very good. More than 80% of patients experience a decrease in the number and severity of seizures, some of them manage to get rid of seizures completely.
Recommended for patients suffering from severe generalized epilepsy, in which both hemispheres of the brain are affected. The essence of the operation is to cut the corpus callosum to prevent the spread of pathological electrical activity from one hemisphere of the brain to another.
This is a treatment method that does not require opening the skull. The epileptogenic focus is destroyed by a focused x-ray beam. 3D imaging is used to precisely target the affected brain tissue with high-dose radiation. The main advantage of this technique is the preservation of healthy surrounding tissues.
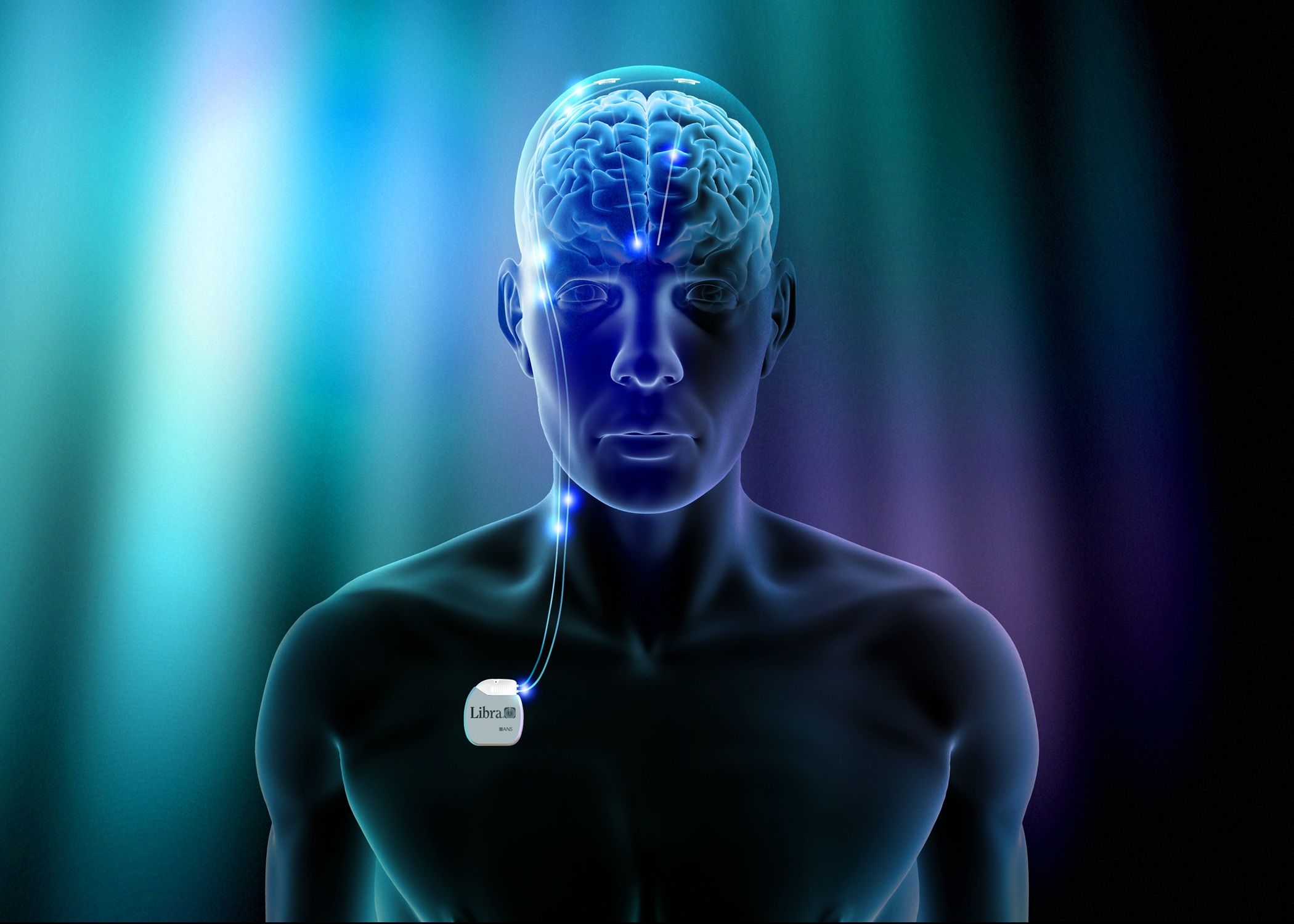

Currently, three methods of neurostimulation are approved for the treatment of drug-resistant epilepsy:
Only a highly qualified and experienced doctor can choose the most effective method of treating epilepsy. The MedTour company cooperates with the best epileptologists from the world’s leading clinics. We will help you choose an affordable specialist for effective diagnosis and treatment of epilepsy.
Recovery from epilepsy surgery can take some time. Most people can return to work or school within about 4-6 weeks. The duration of the rehabilitation period varies depending on the type of surgery, the general health of the patient and the presence of concomitant diseases. Typically, recovery from minimally invasive procedures such as laser induction thermotherapy is faster.
After a successful operation, patients can live a full life: study, work, travel, and actively participate in social life. Many people manage to reduce their dosage or completely stop taking anticonvulsants, which have serious side effects.
Sign up for a procedure epilepsy surgery
The cost of surgery for epilepsy largely depends on the chosen method of surgery. Also, the price is influenced by such factors as: the level of prestige of the clinic, the duration of hospitalization and the surgeon’s fee. To find out the approximate cost of the operation, contact the medical coordinator of MedTour and get a free consultation.
Fill in your details and our medical coordinator will contact you for a consultation
Pay for the ProcedureThe risks of surgical treatment of epilepsy depend on the degree of complexity of the operation and the area of the brain in which it is performed. The most common of these are:
Adverse reactions do not develop in all patients and in many cases are temporary.
The most common side effects that occur in the first week after surgery are:
These symptoms go away on their own after some time. If they continue for several weeks, you must inform your doctor.
How long do people live after epilepsy surgery?
Life expectancy after surgery for epilepsy depends on many factors, including the type of disease, the success rate of surgery, and the need for further therapy.
In some patients, surgery can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of epileptic seizures or completely eliminate them. In such cases, the patient’s life expectancy can be almost the same as that of people without epilepsy. However, in other people, surgery does not achieve complete seizure control, and their life expectancy depends on the frequency and severity of epileptic seizures.
Can epilepsy be cured?
Nowadays, epilepsy is considered a curable disease. However, much depends on the form of the disease and the chosen methods of therapy. Therefore, it is very important that an experienced epileptologist handles the treatment. MedTour cooperates with the best doctors in the world specializing in the treatment of epilepsy. Our physician coordinator will help you select a qualified epileptologist based on your individual needs.
Can epilepsy be cured with surgery?
Yes it is possible. According to studies, surgery helps 80% of patients. In some of them, seizures disappear completely, in others they remain, but their frequency and severity are reduced by 85%. Call by phone or fill out the feedback form, and our coordinating doctor will advise you in detail about the possibility of surgical treatment of epilepsy.
We are always happy to help you. Write your question by filling out the form. We are happy to answer all your questions.
Please rate the work of MedTour
