Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
Not so long ago, organ and tissue transplantation was a science fiction field. To date, both the technical barriers to such operations and the barriers of immune incompatibility have been overcome. This enables patients to extend their lives for many years.
Organ transplantation is a surgical operation to replace missing or damaged organs and tissues of a patient with healthy ones. The organism from which organs or tissues are taken for transplantation is called the donor, and the one to whom the transplant is taken is called the recipient.
Due to serious pathologies, sometimes human organs are seriously damaged, and all other methods of therapy remain ineffective, except for transplantation.
These pathologies may include:
Depending on the situation, the patient can undergo one of the possible transplant options:
When transplanting from a living donor, it is possible to remove only those organs or tissues, without which he can continue a full life – a kidney or a part of the liver. By agreeing to such an operation, the donor takes a certain risk. First of all, this is the risk associated with the operation itself to remove the organ, as well as with the possibility of undesirable consequences occurring months or years after the operation. But, such risks exist with any surgical intervention.
Another reason – inhibiting factors (outdated protocols, inflexible legislative framework, lack of a single, honest mechanism for the collection and distribution of organs) in the CIS countries and some other states, organ transplantation is practically not developing. This affects thousands of patients who need urgent treatment and may not always be able to obtain one or another organ. The way out can be a trip to a foreign medical center.
In many countries, only spouses and close relatives can become donors during their lifetime. For example, a mother may donate a kidney or part of a liver for her daughter.
At the moment, the ratio of those who need transplants to donors is appallingly disproportionate. Demand has always exceeded, and will continue to exceed supply.
Close relatives, which now include only parents, siblings, are far from always able to help. Expanding the concept of a close relative would improve the situation. Natural aunts, uncles, cousins and nephews could be included in a number of close relatives. That is why cross organ transplantation is gaining popularity in many countries now. Such operations are performed by transplantologists in Turkey, Israel and Spain.
Cross-donation is one of the ways to solve the problem of the lack of donors. This practice exists in a number of countries. The bottom line is this: when it becomes necessary to transplant a paired organ or part of it, there will always be a loved one who will be ready to take this step. But not everything depends on the desire to help alone, since a potential donor may not be suitable for medical reasons. At the same time, a similar situation occurs in another family. As a result of cross donation, two people exchange organs to save their loved ones.
The first crossover took place in Istanbul. Turkish doctors successfully transplanted a kidney according to the “domino” principle in seven patients at once. It was the first time in the history of organ donation and transplantation in the world that 14 patients were operated on at the same time.
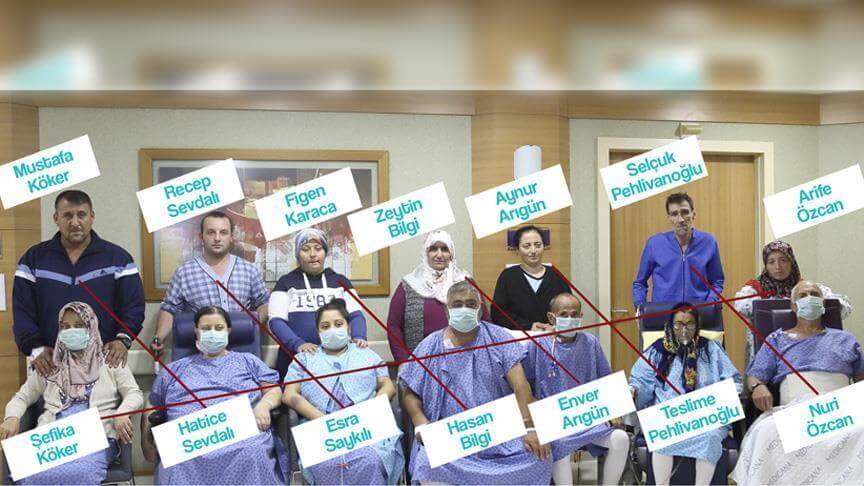

A team of qualified doctors led by Professor Murat Tunger and Professor Muzaffer Saryyar used seven operating rooms at the Medicana clinic in Istanbul for this.
In an organ transplant, someone from one genetically incompatible recipient-donor pair provided or used an organ from another family.
Turkey is one of the leading medical tourism destinations in 2021. This is due to the availability of all types of medical services during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Istinye Liv Hospital has one of the reference organ transplant departments in Turkey with international standards.

The following types of transplantation are performed here:
Liv Istinier’s team has extensive experience in transplantation:
Istinye Liv advantages:

The following types of transplantation are performed here:
Cross-over kidney transplantation is available at Medical for foreign patients.
The Medicana team performs about 500 kidney transplants per year. According to the statistics of the medical center, the success rate of kidney transplants is 99% (99 out of 100 patients survive the turn of 5 years). 30 liver transplant operations. The transplant success rate is 80%.
Benefits of Medicana clinic:

Rambam Medical Center is Israel’s leading public hospital with a scientific foundation, located in the city of Haifa. The Rambam Clinic was founded on the basis of the Technion University, where three Nobel Prize winners work: prof. Irwin Rose, prof. Arona Chekhanovera and prof. Abraham Gershko.
The following types of transplantation are performed here:
Every year, the center is used by about a million people from all over the world, 100 thousand of whom are in the hospital.
Benefits of the Rambam clinic:

ESSEN Clinic is located in Germany and officially cooperates with the National Bone Marrow Donation Program (USA), and is a member of the European BMT Society.
The following types of transplantation are performed here:
The advantages of the ESSEN clinic:
The cost of an operation is always a delicate issue. There are many factors here, for example, the general pricing policy of the clinic, the presence of concomitant diseases, which may require a longer diagnosis and stay in the intensive care unit.
Average cost of kidney transplant abroad:
Average cost of liver transplantation in foreign clinics:
If you still have questions about transplantation, leave a request on the MedTour website. The coordinating doctor will contact you and help you choose the best clinic for the organ transplant.
Please rate the work of MedTour
