Thyroid cancer is a malignant tumor that occurs when cells divide abnormally in the tissues of an organ. A healthy thyroid gland performs vital functions: it controls the amount of calcium in the blood, heart rate, body temperature, and the rate at which food is converted into energy (metabolism). Cancer of the thyroid gland interferes with the production of hormones and can be fatal.

Thyroid cancer responds well to treatment. According to statistics from the American Society of Clinical Oncology, up to 99% of patients with the initial stage, and about 56% in the later stages of the disease, pass the 5-year milestone. To get an early diagnosis and start treatment for thyroid cancer as early as possible, leave a request on the MedTour website.
Why does thyroid cancer occur
According to the US National Cancer Institute, the highest risk of developing thyroid cancer occurs in people aged 25-65. According to statistics, by the age of 40, the likelihood of thyroid disease increases by 50%. The most dangerous are malignant tumors.
What contributes to the development of thyroid cancer:
- Hereditary predisposition to cancer;
- Chronic inflammatory processes in the thyroid gland;
- Tumor processes of the genital area and mammary glands;
- Long-term exposure to radiation on the body;
- Conditions associated with changes in hormonal levels (male and female menopause);
- The presence of genetic abnormalities, such as familial medullary thyroid cancer, multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2A or 2B;
- Iodine deficiency.

There is a genetic test that is used to check for altered BRAF, KRAS and RAS genes. If the gene is found in a patient, other family members may also be tested to see if they are at increased risk of thyroid cancer.
Thyroid cancer symptoms
Symptoms in the early stages of thyroid cancer are almost not pronounced. But it must be remembered that malignant tumors sometimes occur against the background of a benign goiter (struma) that has appeared.
How to suspect thyroid cancer in a patient: a rapid increase in the already existing stroma, its induration and tuberosity. On examination, the doctor can palpate the tumor by palpating the thyroid gland and cervical lymph nodes.
The most common symptoms of thyroid cancer are:
- Lump (nodule) on the neck;
- Neck pain;
- Enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes;
- Swelling in the neck;
- Hoarseness of the voice;
- Difficulty swallowing;
- Choking attacks;
- A cough not associated with a respiratory infection;
- Hair loss;
- Weight loss or rapid weight gain for no apparent reason;
- Decreased libido;
- Deterioration of attention.
The signs of thyroid cancer will become more active as the tumor grows.
Diagnosis of thyroid cancer
To diagnose thyroid cancer and determine the stage of the disease, doctors do a variety of tests. Blood tests for hormones are mandatory, since the thyroid gland is an organ that produces thyroxine and triiodothyronine. These hormones are responsible for the processes of maturation and growth of tissues, metabolism in the body.
How is thyroid cancer diagnosed:
- Initial examination and consultation with an endocrinologist. Doctors conduct a face-to-face examination of the patient in order to feel the lymph nodes, identify nodules or swelling in the neck, and evaluate the work of the vocal apparatus.
- Laryngoscopy. A procedure in which a doctor examines the larynx using a speculum or laryngoscope. The laryngoscope is a thin, tube-shaped instrument with a light and a viewing lens. A tumor in the thyroid gland can press on the vocal cords. A laryngoscopy is done to see if the vocal cords are moving normally.
- Research on blood hormones. Laboratory analysis to check blood samples. The specialist measures the amount of certain hormones released into the blood by the thyroid gland. The blood is checked for abnormal levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and other components.
- Studies of the chemical composition of blood. During the analysis, the amount of certain substances, such as calcium, is checked. An unusual (more or less) volume of blood components can be a sign of illness.
- CT scan. During the CT scan, the specialist takes a series of detailed pictures of the neck from different angles. The pictures were taken by a computer connected to an X-ray machine. Contrast can be injected into a vein or orally to create clearer images.
- Ultrasound procedure. An examination in which high-energy sound waves are reflected off the inner tissues of the neck and create an echo. The echo forms a picture called a sonogram. Signs of thyroid cancer on ultrasound: determination of the size of the node in the organ, the presence of fluid in the neoplasm. Ultrasound can also be used to perform fine needle aspiration biopsy.
- Fine needle aspiration biopsy. The procedure is performed to take samples of thyroid tissue for examination. The pathologist examines the material taken under a microscope for the presence of cancer cells.
- Surgical biopsy. It is a procedure to remove a node of a thyroid gland or one lobe of an organ during surgery so that a pathologist can see cells and tissues under a microscope.
- Immunohistochemistry. Analysis of biopsy material for mutations and receptors in order to prescribe the most effective treatment.
- PET-CT or MRI of the chest. These examinations are necessary to detect a malignant process in neighboring structures and lungs.
Examples of the cost of CT examinations (1 body segment):
- Ukraine – от $100;
- Turkey – от $150;
- Israel – от $700;
- Germany – от $800.

Specialists who perform surgical and fine needle biopsies must have extensive experience with the procedures. During such a biopsy, the recurrent nerve can be damaged, then hoarseness and difficulty in swallowing will occur. Therefore, the patient needs to pay attention to the qualifications of the pathologist, since the results of such diagnostics affect further treatment.
Survival for thyroid cancer
Thyroid cancers refer to one of 4 types of malignant organ tumors: papillary, follicular, medullary, or anaplastic. Most often, papillary and follicular tumors occur. When these types of thyroid cancer are detected in the early stages, the prognosis of survival is favorable.
Papillary thyroid cancer can be successfully treated with the right approach. According to statistics, 9 out of 10 patients after surgery can live more than 20 years.
The form of medullary thyroid cancer is more aggressive than papillary and follicular. She metastases in the early stages of the disease.
An approximate forecast of how many people live with thyroid cancer, depending on its stage and form:
- At stage 1 the five-year survival rate for papillary, medullary and follicular cancers is up to 100%;
- At stage 2 with papillary – up to 100%, medullary – about 97%, follicular – up to 98%;
- At stage 3 with papillary form – up to 92%, medullary – about 60%, follicular – up to 70%;
- At stage 4 with papillary – up to 50%, medullary – up to 15%, follicular – about 46%.
The most favorable prognosis is in people aged 25-40 years, while in patients over sixty and under twenty years of age thyroid cancer proceeds with complications.
Stages of thyroid cancer
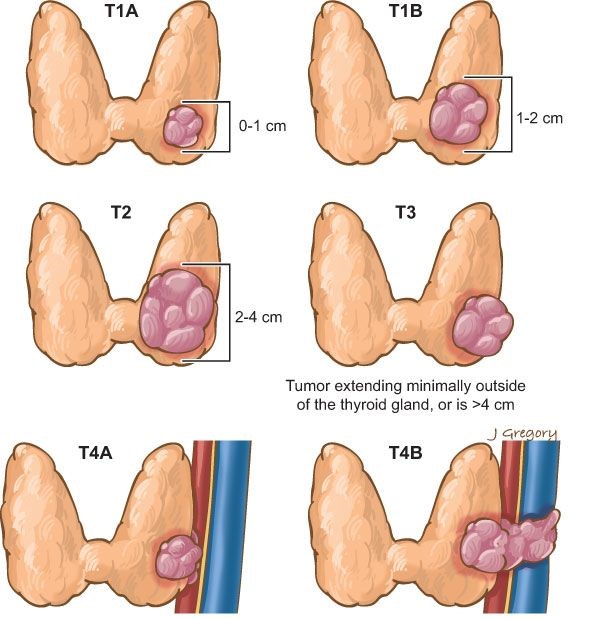
The stage of thyroid cancer indicates at what stage the tumor is developing and how much the malignant process has spread throughout the body. Determining the stage of thyroid cancer is the most important factor by which the doctor chooses the treatment tactics and gives the prognosis to the patient.
The stages of thyroid cancer are accompanied by their clinical manifestations:
- Stage 1 thyroid cancer: a single neoplasm that does not penetrate the organ, there are no metastases in the regional lymph nodes;
- Stage 2: a single tumor without germination and limitation of the mobility of the gland. In the regional lymph nodes, metastases are absent, or can be located on the side of the area affected by cancer;
- Stage 3: single or multiple tumors that grow outside the thyroid gland. The organ’s mobility is limited. Metastases in nearby lymph nodes are not detected, or one or two-sided lesions are found. The neoplasm can compress the esophagus and trachea.
- Stage 4 thyroid cancer: the organ is completely immobilized, metastases spread to regional lymph nodes and distant organs – primarily to the lungs and bones.
Histologically, thyroid cancer has the following forms:
- Papillary thyroid cancer. It occurs in about ⅔ patients with thyroid cancer. The malignant process develops slowly. Localization of the tumor is mainly in one lobe of the gland. The prognosis is favorable: in most cases, there is no relapse for 20 years. Elderly age, metastasis in regional lymph nodes and distant structures contribute to an unfavorable prognosis. The tumor is more than 4 cm in size.
- Follicular thyroid cancer. It occurs in about 15% of cases of thyroid cancer. The source of cancer development is the follicular cells of the gland, which arise when iodine deficiency in the patient’s diet. The prognosis is less favorable than in the papillary form, despite the absence of metastasis in most cases.
- Medullary thyroid cancer. The disease develops from C-cells (parafollicular) of the thyroid gland. This form occurs in 4-5% of cases. Metastases can penetrate into regional lymph nodes and distant organs even before the detection of a primary neoplasm in the thyroid gland. In the blood, the content of cancer embryonic antigen (CEA) and calcitonin, synthesized by malignant cells, increases. The prognosis is poor due to the aggressiveness of the tumor and early metastasis.
- Anaplastic thyroid cancer. Doctors diagnose this form in isolated cases. The disease is characterized by rapid tumor growth, spread to the cervical structures and a poor prognosis. It develops more often in elderly patients with nodular goiter in the neck.

For treatment to be as effective as possible, it is necessary to accurately establish the stage and form of thyroid cancer. The greatest clinical experience is possessed by foreign doctors who accurately diagnose on the basis of modern examination methods.
Thyroid cancer treatment
The choice of treatment is influenced by the type and stage of thyroid cancer, general health and age of the patient. The key treatments are surgery and radiotherapy.
Surgery for thyroid cancer
Doctors can perform surgical interventions for thyroid cancer using different methods: open (through an incision up to 8 cm), endoscopic (through an incision up to 2 cm), without incisions in the neck (through the mouth).
Surgeons perform one of these types of operations:
- Lobectomy – removal of the lobe of the thyroid gland in which a tumor is found. Lymph nodes near the growth can also be removed.
- Thyroidectomy – removal of half of the thyroid gland, sometimes along with lymph nodes located next to the tumor.
- Total thyroidectomy – removal of the entire thyroid gland and regional lymph nodes.
- A tracheostomy – an operation to create a stoma (hole) in the throat so that the patient can breathe (it can be temporary or permanent).
Radiation therapy for thyroid cancer
Radiation therapy is the exposure of cancer cells to high-energy X-rays or other types of radiation in order to prevent their growth or completely destroy the tumor.
Doctors carry out one of two options for the procedure:
- External beam radiation therapy – uses a device outside the body to direct radiation to an area affected by cancer. Sometimes during surgery, radiation is directed directly at the tumor. This is called intraoperative radiation therapy.
- Internal radiation therapy – uses a radioactive substance sealed in needles, seeds, or catheters that are injected directly into or near a tumor. Irradiation occurs inside the area of the organ affected by cancer.
Iodine therapy for thyroid cancer
In some cases, oncologists use radioactive iodine therapy to treat follicular and papillary thyroid cancer. The drug is taken by mouth and accumulates in any remaining thyroid tissue, including cancer cells that have spread to other parts of the body. Radioactive iodine destroys thyroid tumors without damaging healthy tissue.
Chemotherapy to treat thyroid cancer
Chemotherapy is a special medicine that stops the growth and division of cancer cells. When chemotherapy drugs are taken by mouth, injected into a vein or muscle, the drugs enter the bloodstream and can reach cancer cells throughout the body – this is systemic chemotherapy.
If the chemotherapy drug is injected directly into the cerebrospinal fluid or organ, the drugs mainly target cancer cells in those areas with the tumor – this is regional chemotherapy.
The method of chemotherapy for thyroid cancer depends on the type and stage of the disease and is prescribed individually in each case.
Hormone therapy for thyroid cancer
Hormones are biologically active substances that the thyroid gland produces. In the treatment of thyroid cancer, hormone therapy is used to prevent the production of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which can interfere with the growth of cancer cells. Hormone therapy is a treatment with drugs that block the action of thyroid hormones and stop the oncological process.
Because this cancer therapy affects organ function, the thyroid gland cannot produce enough hormones. Patients are given drugs that replace natural thyroid hormones – this is substitution therapy.
Targeted therapy for thyroid cancer
Targeted therapy is a type of treatment that uses drugs to identify and target certain cancer cells. Targeted therapy is less harmful to the body than chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Doctors can prescribe the following targeted therapy options for a patient:
- Tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Therapy for thyroid cancer with tyrosine kinase inhibitors blocks the signals necessary for tumor growth. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor drugs are used to treat certain types of thyroid cancer. New types of tyrosine kinase inhibitors are used to treat late-stage thyroid cancer – drugs that significantly reduce the number of new metastases.
- Protein kinase inhibitor. Treatment for thyroid cancer with protein kinase inhibitors blocks proteins that are required for the growth of cancer cells. Protein kinase inhibitor drugs are used to treat anaplastic thyroid cancer in patients with a specific mutation in the BRAF gene.
Immunotherapy for thyroid cancer
Immunotherapy is a treatment that uses the patient’s immune system to fight cancer. Substances produced by the body or in the laboratory are used to enhance the natural defenses of the immune system to block the oncological process.
This cancer treatment is a type of biological therapy. In some cases, immunotherapy can be effective for thyroid cancer.

Hormonal, targeted and immunotherapy are the most innovative treatments for thyroid cancer. Patient access to such drugs and their rational use by doctors is possible only in progressive medical centers.
Frequently asked questions for thyroid cancer
What is the TSH for thyroid cancer?
Reference values of TSH in adults are from 0.4-0.5 mIU/L to 4.2-5 mIU/L. For children, normal values are determined according to age.
According to current recommendations, with an index exceeding 5 mIU/L TSH, a thorough examination of the patient is required to detect a malignant tumor. In patients with established thyroid cancer, doctors try to prevent hormone levels from rising above 2 mIU/L.
Can ultrasound detect thyroid cancer?
There is no single way to diagnose the stage and form of thyroid cancer. In addition to ultrasound, a patient with suspected cancer needs to undergo blood tests to clarify the diagnosis and other procedures.
How long does thyroid cancer surgery take?
Surgery for thyroid cancer takes 2-4 hours, depending on the volume of the intervention and the technique. Postoperative hospitalization is on average 2-7 days.
Can thyroid cancer be completely cured?
Thyroid cancer can be completely cured if it is detected early. If a relapse occurs, then early detection of metastases also accompanies a favorable prognosis.
Where is thyroid cancer treated?
When choosing a medical center for the treatment of thyroid cancer, it is important to consider:
- Clinic equipment for diagnostics and therapy;
- Qualification of oncologists, surgeons and endocrinologists;
- Treatment standards – they must be in line with international protocols.
Top destinations for cancer treatment are Turkey, Israel and Europe. In those countries, patients receive effective treatment, access to advanced therapy methods and high-level medical service.

To choose the best clinic for the diagnosis and treatment of thyroid cancer, leave a request on the MedTour website. The coordinating doctor will help you choose the best option and tell you about the advantages of oncology departments in Ukraine and abroad.
How much does thyroid cancer treatment cost
The final cost of treatment will depend on the following factors:
- Pricing policy of the clinic where the patient undergoes examinations and receives treatment;
- The scope of diagnostic procedures;
- Stage and form of thyroid cancer;
- Operation and methods of therapy, which are prescribed by the doctor;
- The period of stay in a medical institution with subsequent rehabilitation.
Examples of the cost of treating thyroid cancer in foreign hospitals:
- Radiotherapy – prices range from $4 000 to $9 000 on average;
- Chemotherapy for intravenous administration – from $1 000;
- Immunotherapy – $1 250 per package;
- Thyroidectomy – approximate price range from $6 000 to $20 000.
The cost of drugs for targeted, immuno- and chemotherapy in all foreign clinics is the same. The price of treatment will differ due to the duration of the drug use and related services of the medical staff.

To undergo effective diagnosis and therapy of thyroid cancer in the best clinic, leave a request on the MedTour website. The coordinating doctor will help you find a medical center anywhere in the world and organize the treatment process.




