Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA

Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is a form of hearing loss that occurs due to damage to the hair cells of the cochlea in the inner ear or auditory nerve. Hair cells are the most important elements of the auditory system, converting sound waves into nerve impulses that are transmitted to the brain. When these cells are damaged or die, the transmission of sound signals is disrupted, leading to varying degrees of hearing loss.
SNHL is the most common type of hearing loss, affecting millions of people worldwide. This disorder can develop in both children and adults, and its prevalence increases significantly with age.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), more than 5% of the world’s population suffers from varying degrees of hearing loss, and the majority of cases are sensorineural hearing loss. The issue of SNHL is especially relevant in modern society, where high noise levels, genetic factors and age-related changes contribute to an increase in the number of cases of this disease. Effective diagnostics and modern treatment methods for SNHL, including stem cell therapy, open up new opportunities for restoring hearing and improving patients’ quality of life.

About 50% of all cases of hearing loss in children are related to hereditary causes. Genetic mutations can affect the development and function of hair cells in the cochlea or auditory nerve, leading to varying forms and degrees of hearing loss. In some cases, hearing loss is part of a syndromic disorder, such as Usher syndrome or Waardenburg syndrome, in which hearing impairments are combined with other medical problems..
Age-related changes, known as presbycusis, are one of the most common causes of sensorineural hearing loss. With age, there is a natural degeneration of hair cells and nerve endings in the cochlea, leading to gradual hearing loss. Usually, a person first loses the ability to hear high-frequency sounds, and later low-frequency sounds. Presbycusis most often appears after age 60 and progresses with age.
Infectious diseases such as meningitis, syphilis, and viral infections (eg, cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex virus, mumps virus) can cause inflammation in the inner ear, leading to damage to hair cells and the auditory nerve. Acute or chronic inflammation of the middle ear (otitis media) can also spread to the inner ear, causing sensorineural hearing loss.
Head trauma and acoustic trauma are significant risk factors for developing sensorineural hearing loss. A severe blow to the head or penetrating ear injury can cause direct damage to the cochlea or auditory nerve. Prolonged exposure to loud noise, such as in industrial environments or while listening to loud music, can also cause permanent changes in hair cells.
Some medications, such as aminoglycoside antibiotics, chemotherapy drugs, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (such as aspirin), and diuretics, can be ototoxic, meaning they damage hearing. Toxins such as heavy metals (lead, mercury) and organic solvents, can also cause oxidative stress and inflammation, leading to damage to hair cells and the auditory nerve.
The most common symptoms of the disease include:
Symptoms may vary in intensity and frequency depending on the severity and cause of the hearing loss. Early recognition of disease signs is crucial for effective management and treatment of SNHL.

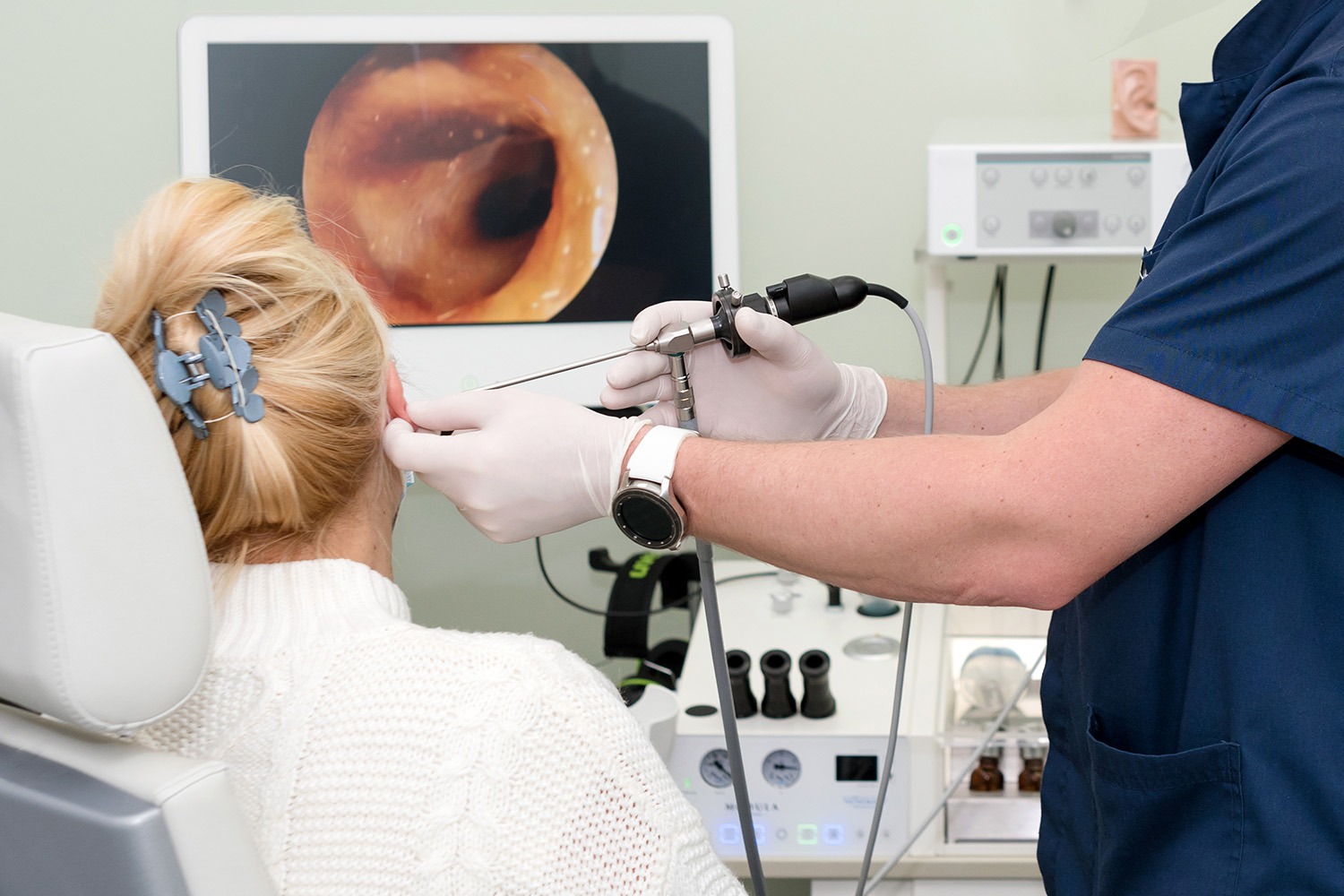
Various methods are used to accurately diagnose SNHL, allowing the identification of the degree and causes of hearing loss:
Comprehensive diagnostics helps to accurately determine the cause and degree of sensorineural hearing loss, which is a key factor in choosing the optimal treatment strategy. Call or write to us and the coordinating doctor will select a good hearing diagnostic clinic for you.
Modern treatment methods for sensorineural hearing loss offer a wide range of options for improving the hearing and quality of life of patients.
Drug therapy
Drug treatment may include the use of corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and swelling in the auditory nerve, as well as antioxidants and neuroprotectants to protect cells from damage. However, the effectiveness of drug therapy is often limited and depends on the stage of the disease and the cause of hearing loss.
Surgical methods
Surgical intervention may be necessary to correct structural problems such as cysts, tumors, traumatic bone injury, etc. Surgical methods are usually used in combination with other treatments to achieve a better therapeutic outcome
Hearing aids and cochlear implants
Hearing aids amplify sounds so they can be heard by intact hearing cells. Cochlear implants, in turn, are more complex devices that convert sounds into electrical signals and directly stimulate the auditory nerve, bypassing damaged areas of the inner ear. These methods are especially effective in patients with moderate to severe hearing loss.
Only 20% of patients with hearing loss are suitable for hearing aids and cochlear implants. Although these devices amplify sound, they do not solve the problem of understanding speech caused by damage to sensorineural cells. The lack of effective treatments has prompted the search for new therapeutic approaches. A significant breakthrough in this area has been the use of stem cells, which have enormous potential in the treatment of SNHL.
Cell therapy is a promising method for treating sensorineural hearing loss. The principle of its action involves using stem cells to restore damaged ear structures and regenerate hair cells. Stem cells have the unique ability to transform into different types of cells, allowing them to replace damaged hair cells.
Research shows that stem cell injections help reduce inflammation and tissue fibrosis in the inner ear, slowing down and sometimes completely stopping the progressive deterioration of hearing. Cell therapy also stimulates the regeneration process of cochlear hair cells, which play a key role in the perception of sound waves.
Efficiency of cell therapy
Stem cell therapy:
The main benefit of stem cell therapy is its ability to stimulate the regeneration of damaged cells and tissues and stop the progression of hearing loss without the need for external devices. Stem cell therapy opens new horizons in the treatment of this complex disease.
If you are interested in stem cell treatment for sensorineural hearing loss, fill out the feedback form below or call us at the phone number listed on the website. A MedTour coordinator will examine your medical issue, provide all the necessary information and help organize treatment. Consultation with a MedTour coordinator is provided free of charge.
The cost of sensorineural hearing loss treatment can vary significantly depending on the chosen method. For example, hearing aid installation costs on average between $1,000 and $5,000. Cochlear implants are more complex and expensive, costing $30,000 – $50,000, including surgery, the device, and post-operative care.
The use of stem cells for the treatment of sensorineural hearing loss is an innovative and promising method. The cost of such treatment can vary from $10,000 to $20,000 per course, depending on the clinic and the complexity of the case. This method, due to its potential benefits, is becoming increasingly popular and accessible to patients.
To get accurate information about the cost of treatment, as well as advice on all possible treatment options, contact MedTour. A coordinating doctor will answer all your questions and help you choose the most suitable treatment method.
MedTour cooperates with the world’s best medical centers specializing in the treatment of hearing problems. We can offer you treatment at the University hospital LIV Istinye or the Medical Park Hospitals Network in Turkey, at the Teknon Medical Center in Spain, at the Helios Hospital in Germany. If you are interested in stem cell treatment, you can undergo it at Polyclinic Tara 70 in Serbia.
Do you need to choose a highly qualified doctor who specializes in treating hearing loss? Call or write to us. A MedTour coordinator will select the best specialist in this field for you. If you are interested in an innovative method of treating sensorineural hearing loss with stem cells, we will arrange for you a consultation with Dr. Ivan Badyin, a leading specialist in the field of regenerative technologies.
In some cases, hearing loss may be temporary and treatable. However, with sensorineural hearing loss associated with damage to hair cells, the process is irreversible. Complete restoration of your own hearing in such cases, unfortunately, is impossible. However, new, promising treatment methods have emerged. Thus, stem cell therapy can stop the progression of sensorineural hearing loss, slow down hearing loss and, in certain cases, even improve its quality.
Although damaged cells cannot be completely restored, the progression of pathological changes can be slowed down. Stem cell therapy helps slow down the process of hair cell damage and the progression of sensorineural hearing loss.
To treat sensorineural hearing loss, various medications are prescribed to improve blood circulation in the ear, relieve inflammation and protect cells. These may be corticosteroids, antioxidants and drugs that improve microcirculation. In some cases, vasodilators and vitamin complexes are also used. It is important to note that stem cell therapy also plays a significant role in halting the progression of sensorineural hearing loss, complementing traditional treatment methods.
Please rate the work of MedTour
