Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
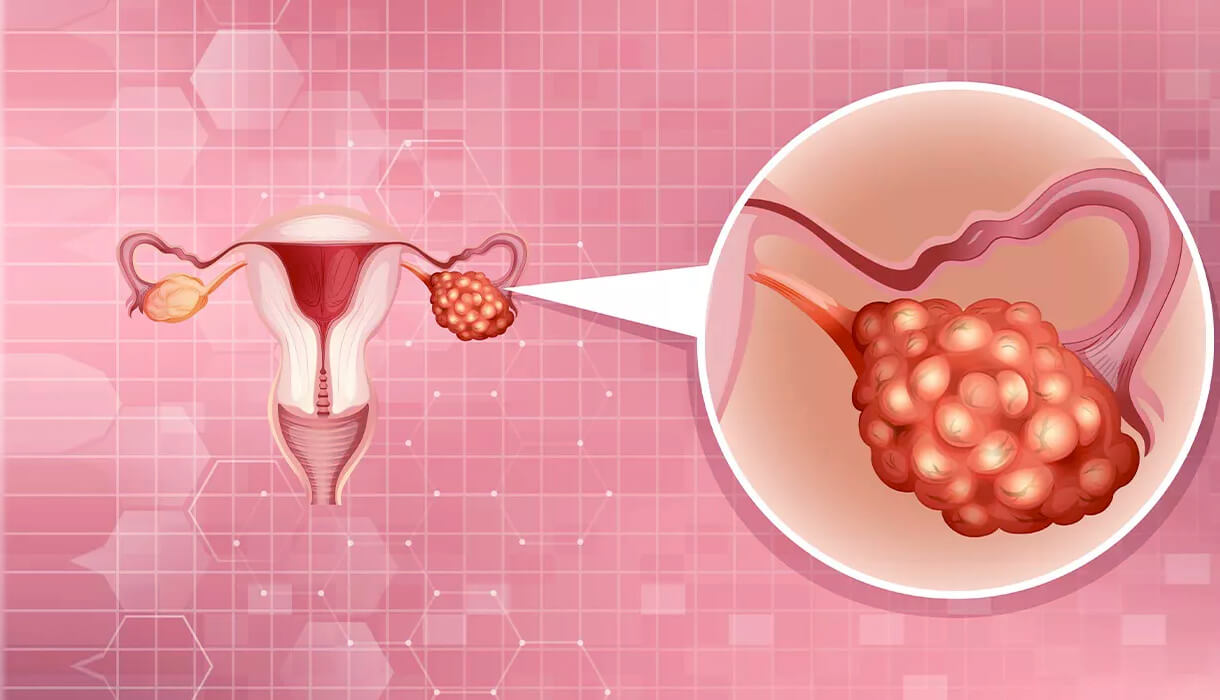
An ovarian cyst is one of the most common female pathologies. It is diagnosed in 30-50% of women of reproductive age and in 6-15% of women after menopause. In most cases, these formations do not cause significant problems and disappear on their own over time. However, there are cases when the appearance of an ovarian cyst can be accompanied by painful symptoms and provoke health risks. For example, an ovarian cyst may rupture, which creates a life-threatening situation. Additionally, some types of these neoplasms can become malignant. Therefore, it is important to conduct an accurate diagnosis and, if necessary, undergo treatment when they are detected.
An ovarian cyst is a benign growth, that is essentially a sac filled with liquid content. There are different types of neoplasms that relate to this pathology. The formation can develop either inside the ovary or be located on it. Functional ovarian cysts and true ovarian cysts may occur, and each of these types has its own varieties. An ovarian cyst can be single-chambered, double-chambered, or multi-chambered. It can be small (1-2 centimeters) or grow to a large size (15-20 centimeters).
Are ovarian cysts dangerous? Despite the fact that an ovarian cyst is benign and is not a dangerous disease, its occurrence can pose certain health risks.
An ovarian cyst may:
In addition, there is a possibility that some types of these formations may transform into malignant forms. Therefore, if symptoms similar to those caused by an ovarian cyst appear, it is important to consult a doctor and undergo an examination. This will help accurately diagnose the condition and determine the specific type of ovarian cyst in your case. Afterward, the doctor will decide on the most suitable course of action.
On the MedTour platform you can find a clinic where you can undergo treatment for gynecological diseases of varying degrees of complexity and use the most advanced and effective treatment methods.
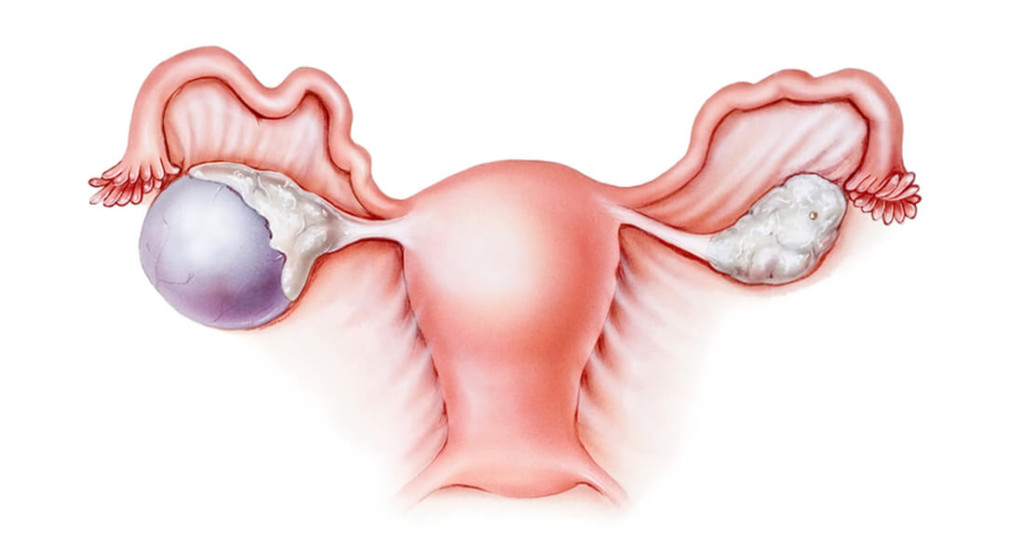
The formation of an ovarian cyst can have various reasons. These growths may periodically appear and disappear during hormonal fluctuations associated with the menstrual cycle in healthy women. In such cases, a functional cyst is diagnosed. Its occurrence is associated with fluctuations in luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones. This type of neoplasm typically does not require serious concern and it often resolves on its own. There are other types of cystic formations whose appearance may be associated with different factors.
Factors that can increase the risk of ovarian cysts include:
The risk of cyst formation also increases after surgeries on the fallopian tubes. Additionally, if a woman has previously been diagnosed with this pathology, the likelihood of recurrence remains high over time. In each case, it is necessary to find out what causes ovarian cysts and whether these growths pose a threat to the woman’s health.
Doctors distinguish several types of ovarian cysts:
MedTour will help you find experienced specialists who can accurately diagnose your condition and select the optimal treatment using the most effective and advanced methods.
In most cases, ovarian cysts do not cause symptoms and are discovered incidentally during an ultrasound examination. However, when the cyst grows increases in size, the following ovarian cyst symptoms may appear:
Pain in the lower abdomen can be caused by various reasons, including ovarian cysts. The nature of the pain may indicate that the cause of such pain is due to a cyst. Typically, the pain is dull and aching. Pain manifestations may change when twisting the torso or change body position. Also, the intensity of pain may vary at different periods of the menstrual cycle.
If torsion or rupture occurs, the pain becomes sharp and severe, and general well-being noticeably worsens. If such symptoms appear, immediate medical attention is necessary, as emergency surgery may be required.
MedTour will help you choose a clinic where you can receive high-qualified medical care, make an accurate diagnosis, and undergo treatment using the latest methods.
If a woman is diagnosed with an ovarian cyst, the following are not recommended:
For more detailed information on what you can and cannot do, consult a gynecologist. By understanding the specifics of your condition, the doctor can provide more accurate recommendations and help develop a plan for further action.
Contact a Medtour coordinating doctor to get information about the best gynecological centers in different countries of the world, where you can undergo diagnosis and treatment for gynecological pathologies of varying complexity.
In order to detect a neoplasm and determine its type and characteristics, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination. Diagnosis of ovarian cysts can be carried out using the following methods:
In some cases, diagnostic laparoscopy with biopsy may be prescribed, but in most cases this invasive diagnostic method is not necessary.
If an ovarian cyst is diagnosed, treatment is selected taking into account the type of neoplasm, its size, growth activity, and whether it causes symptoms or is asymptomatic. The following treatment approaches are commonly used:
For small, asymptomatic cysts, a watchful waiting approach is most often chosen. In such cases the doctor recommends periodic ultrasound to monitor the condition. For example, if a corpus luteum cyst or follicular cyst is detected, it often resolves on its own within 3-4 months, eliminating the need for treatment.
Treatment for ovarian cysts may include the use of anti-inflammatory drugs and hormonal medications. However, drug therapy often provides only temporary relief and does not necessarily eliminate the cyst.
What size of ovarian cyst is dangerous and requires removal? A cyst larger than 3-5 centimeters can be considered dangerous, although radical treatment is not always necessary. The doctor might recommend medication therapy or choose active observation tactics for a certain period, and only in certain cases is surgical treatment preferred.
Removal is indicated when:
Additionally, if an ovarian cyst is detected after menopause, this may also be an indication for removal due to the increased risk of ovarian cancer in postmenopausal women. Any new growths during this period warrant careful attention.
An indication for urgent surgical intervention is a ruptured ovarian cyst (apoplexy). If the membrane of the cyst ruptures, its contents flow into the abdominal cavity. Without surgical correction of the condition, this can lead to severe blood loss, peritonitis, sepsis, or even death.
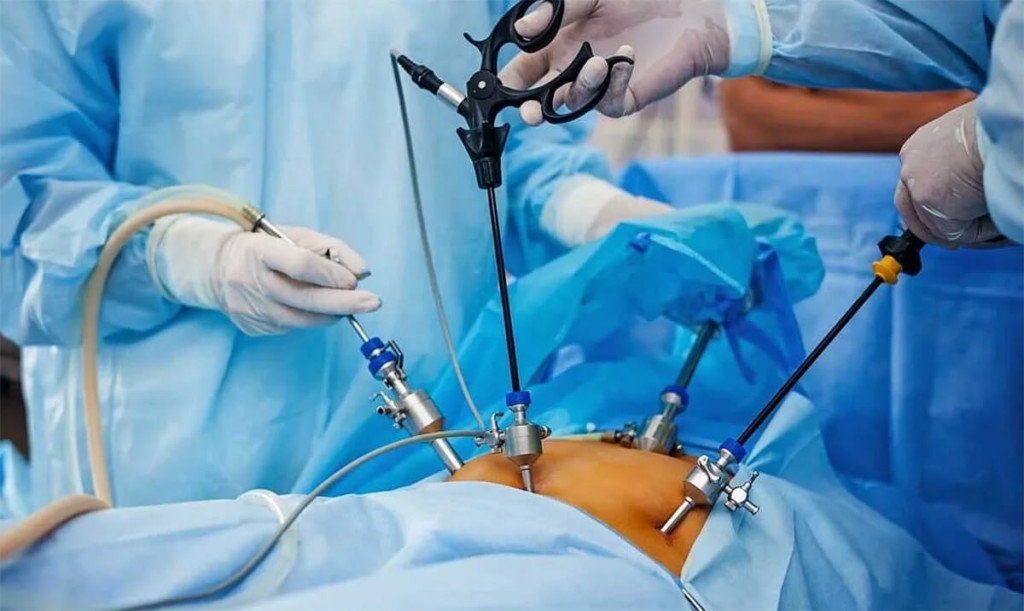
Several surgical methods can be used for ovarian cyst removal:
Typically, only the cyst is removed (cystectomy), preserving the ovary and its function. However, in some cases, it may also be necessary to remove the ovary (oophorectomy) or remove both the ovary and fallopian tube (adnexectomy). The scope of the surgery is determined by the doctor based on the patient’s condition.
The MedTour platform will help you find an experienced specialist who will select the optimal treatment plan for your condition and take into account all the nuances of your case.
The prognosis for this condition is generally favorable. Diagnosis of this pathology usually does not affect life expectancy. Follicular and luteal cysts often resolve on their own without treatment. Other types of cysts are relatively easy to remove surgically. Life-threatening complications may arise if conditions such as cystadenomas are left untreated and develop into malignant tumors. However, even in such a situation, it is possible to find effective treatment that will eliminate the growth and restore health.
The cost of ovarian cyst removal surgery depends on several factors, including:
A MedTour coordinating doctor will provide you with information on surgery costs and treatment options in different countries, helping you choose the best solution for your needs.
On the MedTour platform you can get acquainted with the best clinics dealing with gynecological diseases. We work with medical facilities that specialize in the treatment of gynecological pathologies of any degree of complexity and use the most modern treatment methods. MedTour can organize a trip for you to the best medical centers in different countries of the world, where you can benefit from cutting-edge diagnostic and treatment technologies.
You can choose a country known for its advanced and effective treatment methods. Among the leading countries for gynecological care are: Turkey, Germany, Spain, and Israel.
We cooperate with the best clinics in these countries, renowned globally for the quality of their services. For example, the leading medical institutions in this field include:
To select a medical center, you can independently view the entire list of clinics for the treatment of ovarian cysts. Or you can contact us. Our MedTour coordinating doctor will provide a free consultation about clinics, share pricing details, and answer any of your questions.
MedTour will help you find an experienced doctor specializing in ovarian cyst treatment. We cooperate with the leading specialists from different countries who have extensive experience and rank among the top professionals in their field.
To learn about the best gynecologists available for your treatment, fill out the contact form. A MedTour medical consultant will contact you and help you choose a doctor who is most suitable for you, taking into account your condition and individual needs.
Hemorrhagic cyst when to worry?
Typically, growths of this type are not a cause for concern. As a rule, they resolve on their own within 1-3 months. And their appearance does not cause any health consequences. However, if such a cyst does not disappear within 3-4 cycles, grows larger (8 cm or more), continues to increase in size, or has twisted around its axis, this is an indication for surgical treatment.
What is an ovarian cystoma?
An ovarian cystoma is a benign tumor that develops from the epithelial cells of the ovary. It is often multi-chambered, filled with fluid, and characterized by rapid growth. Since this type of growth can develop into a malignant tumor, it is essential to consult a doctor immediately after diagnosis to determine the appropriate course of action.
How can you tell if a cyst is benign or malignant?
To determine whether a growth is benign or malignant, it is necessary to undergo an examination. Tests for tumor markers, ultrasound examination, computed tomography, and other modern diagnostic methods can help identify the characteristic features of the formation and make an accurate diagnosis.
What is a uterine cyst?
Although often confused with ovarian cysts, uterine cysts are rare and involve the uterine tissue rather than the ovary. They are usually benign and can be diagnosed and treated separately.
Please rate the work of MedTour
