Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
According to statistics, the annual incidence of Hashimoto’s disease is about 2%. The disease is 10 times more common in women than in men. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is the most common cause of hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) in developed countries. Most often (in 50%) cases, the disease develops due to a hereditary factor.
To date, the only effective treatment for Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is lifelong hormone replacement therapy. It allows to maintain the level of thyroid hormones in the patient’s body, but does not lead to a final cure. Therefore, today there is an active search for new, more effective therapeutic approaches, and stem cell treatment is one of the most promising areas in this field.
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is also called autoimmune or chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis. The term “thyroiditis” means inflammation of the thyroid gland. The inflammatory process develops as a result of a malfunction in the immune system, in which it begins to attack healthy thyroid cells. Because of this, the body stops producing enough hormones T3 and T4. A person develops a condition known as hypothyroidism. It can lead to abnormal heart rhythms, cognitive problems, and severe metabolic disorders.
As with other autoimmune diseases, the main cause of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an abnormal activity of the immune system. In addition to disrupting the function of hormone production, invading immune cells cause inflammation and swelling of the thyroid gland, which over time can lead to the development of a goiter.
Scientists still don’t know exactly why the immune system, which is supposed to protect the body from harmful viruses and bacteria, sometimes turns against healthy body tissues. However, there are known risk factors that make a person more susceptible to Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. These include the following:

The disease develops imperceptibly for several years. The first symptoms are the result of chronic damage to the thyroid gland. The signs include the following:
Additional physical signs of Hashimoto’s disease that a doctor may look for during a diagnostic test include:
In some cases, the only sign of autoimmune thyroiditis is a decrease in thyroid hormone levels (subclinical hypothyroidism).
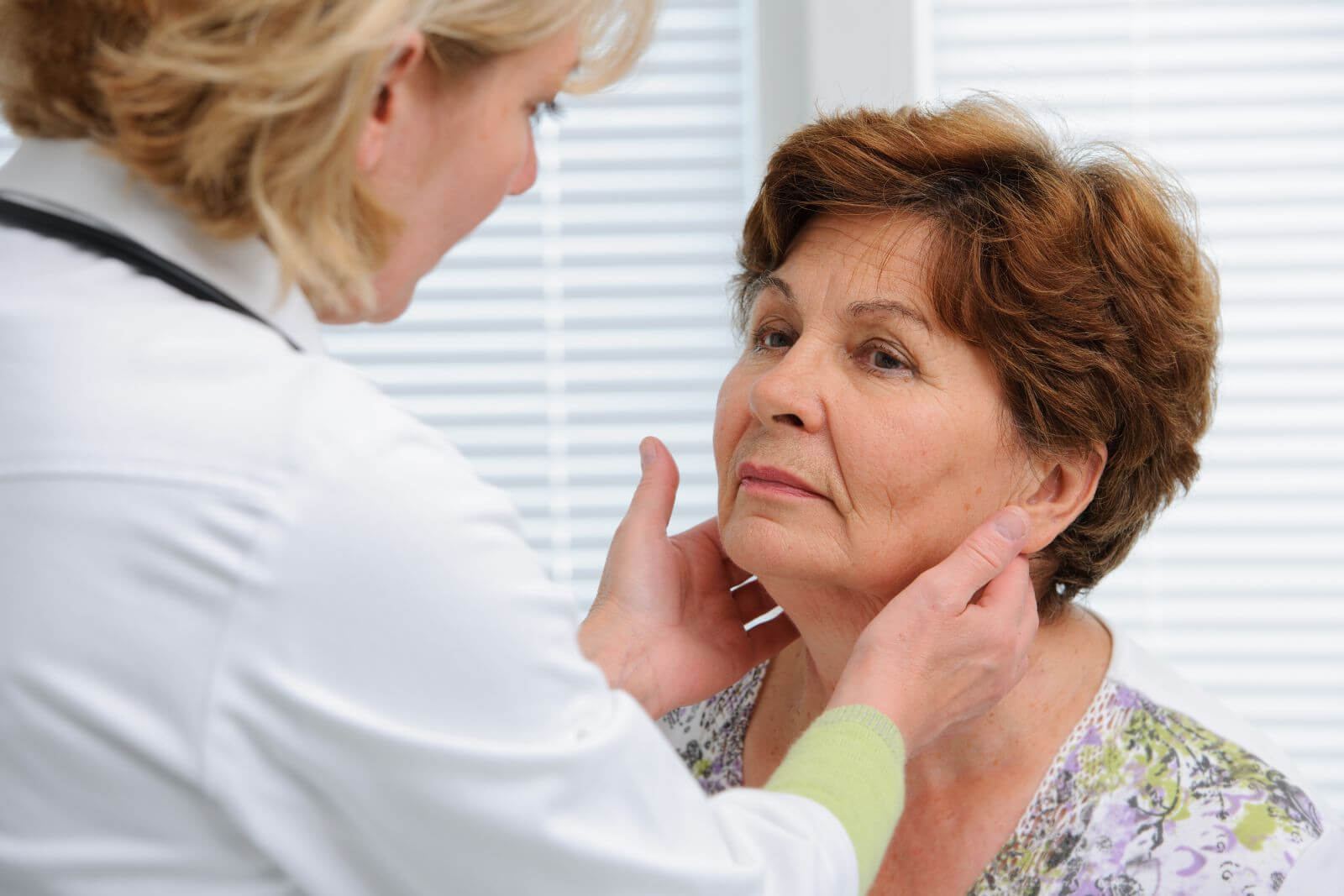
At the initial stage, a doctor takes the patient’s medical history and conducts a physical examination. A specialist performs a thorough visual assessment of the thyroid gland and, if necessary, prescribes an ultrasound examination. Ultrasound of the thyroid gland helps to detect abnormal growths (nodules).
Additionally, doctors prescribe blood tests:
If you need a diagnosis of Hashimoto’s disease, the medical coordinator of MedTour will help you find a clinic that specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of this disease.
The main treatment for Hashimoto’s disease is hormone replacement therapy. Most often, patients are prescribed a synthetic analogue of the thyroid hormone. After the start of therapy, the doctor may regularly (for 6-10 weeks) conduct a TSH test to monitor thyroid function and determine the appropriate dosage.
Hormone replacement therapy helps to maintain the necessary level of thyroid hormones in the blood, but does not affect the cause of the disease. Therefore, scientists are looking for other, more effective methods of therapy. One of the most promising of these is the use of stem cells.
What are mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)?
It is one of the types of stem cells that can differentiate (turn) into other types of cells in the body. And this is not the whole therapeutic potential of MSCs. Anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory and regenerative properties make mesenchymal cells promising candidates for the treatment of autoimmune diseases such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
To obtain MSCs, it is not necessary to use abortive material, they are in the patient’s body. The universal source of mesenchymal stem cells is the bone marrow. However, the procedure for extracting cellular material from the bone marrow, like all invasive techniques, is associated with certain risks. Therefore, methods have been developed to obtain MSCs from adipose tissue and even from the patient’s peripheral blood.
How can mesenchymal stem cells help treat Hashimoto’s thyroiditis?
Numerous studies have demonstrated the immunoregulatory properties of MSCs. They profoundly influence the immune response through interactions with the cellular components of the innate (natural killer cells) and adaptive (dendritic cells, B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes) immune system.
One study published in the journal Stem Cells Translational Medicine examined the use of MSCs in the treatment of autoimmune thyroiditis. Researchers have found that stem cells can reduce inflammation and prevent thyroid tissue from breaking down and decreasing function. These results suggest that MSCs may be a promising treatment option for people with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
Another study published in the Journal of Translational Medicine examined the use of MSCs in combination with conventional thyroid hormone replacement therapy. The researchers found that the combination treatment resulted in improved thyroid function and reduced symptoms compared to substitution therapy alone.
How is Hashimoto’s thyroiditis treated with stem cells?
The therapeutic protocol includes several stages:
After entering the body, stem cells react to signaling substances present in the lesion and are sent to the thyroid gland. There they act by suppressing the abnormal immune response, reducing inflammation and activating the processes of regeneration of damaged thyroid cells.
If Hashimoto’s disease is left untreated, it can lead to various complications and general deterioration in health. Possible consequences are the following:
Complications of Hashimoto’s disease can be quite serious, so it is important to get diagnosed and start treatment in a timely manner.
MedTour is a platform specifically designed to make modern therapies more accessible to patients. We cooperate with the best clinics for the treatment of thyroid diseases. Currently, MedTour offers patients a unique opportunity to treat Hashimoto’s thyroiditis with stem cells. We will select for you the best and most affordable clinics that deal with cell therapy.
MedTour cooperates with the best doctors specializing in the treatment of thyroid diseases and autoimmune disorders. We can also offer advice from doctors who treat various diseases with the help of stem cells. One of them is Ivan Badyin, PhD, with over 20 years of experience in the field of regenerative medicine.
How long do people live with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis?
With adequate treatment, patients with autoimmune thyroiditis can live long and fulfilling lives. Innovative therapies, such as stem cell therapy, help repair damaged thyroid tissue and reduce immune system overactivity, significantly improving prognosis. Learn more about cell therapy from the medical coordinator of MedTour.
How dangerous is Hashimoto’s thyroiditis?
The main danger of the disease is that it develops asymptomatically. The first signs appear only when the tissues of the thyroid gland begin to break down. A new method of treatment – stem cell therapy – promotes the regeneration of damaged tissues and prevents the development of complications of the disease. Book a free consultation to learn more about the new treatment technique.
Can Hashimoto’s thyroiditis be cured?
Standard treatments help maintain hormone levels but do not cure Hashimoto’s disease. An alternative approach is stem cell therapy. They act directly on the cause of the disease, reducing the abnormal activity of the immune system, and also promote the regeneration of thyroid tissue. Call or email us to learn more about this innovative treatment method.
Please rate the work of MedTour
