Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
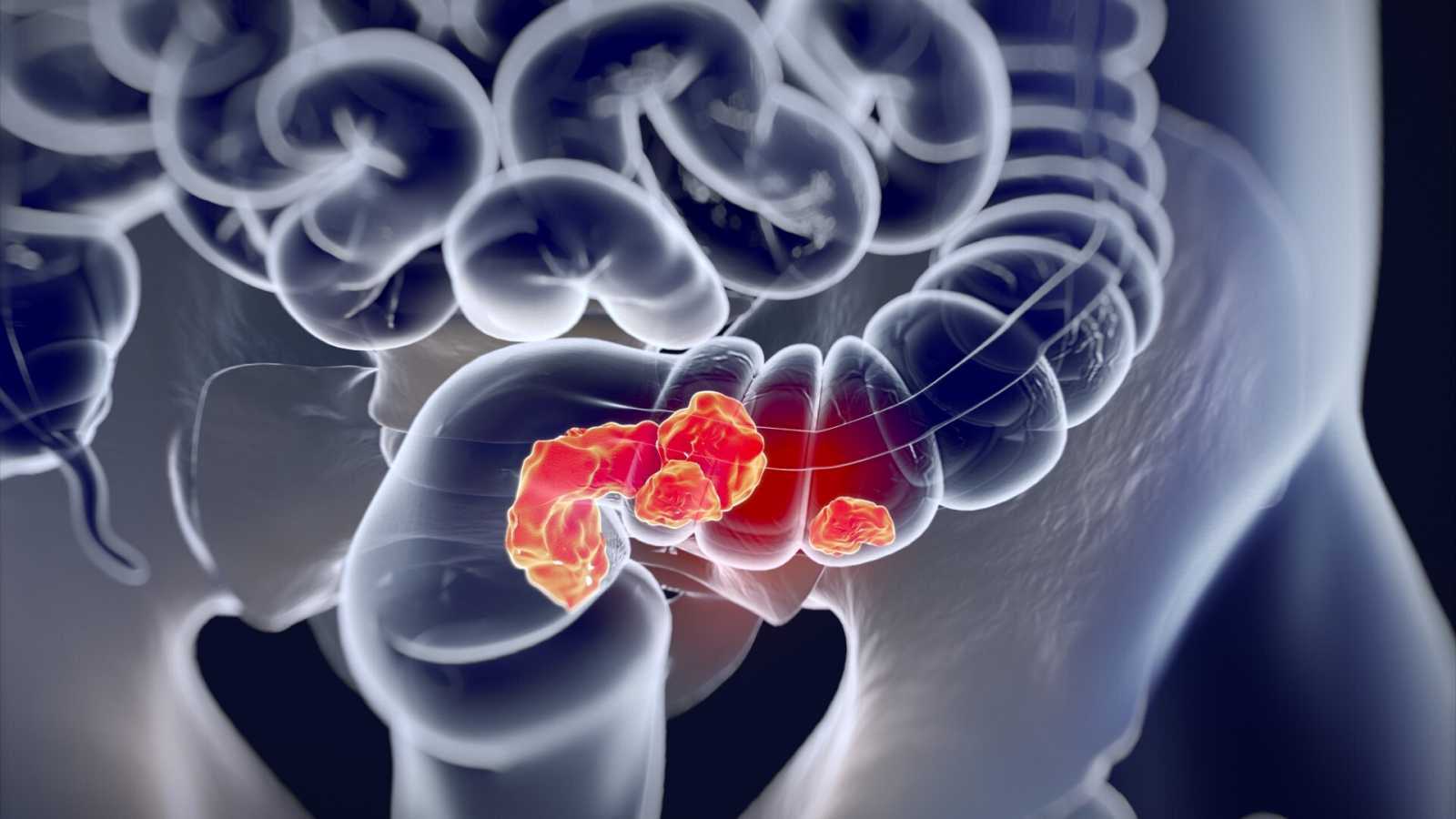
Recently, malignant tumors of the colon and rectum are usually combined into one group, which is called colorectal cancer. It develops from abnormal cells in the large intestine that become cancerous and divide uncontrollably. If the tumor is not detected and treated early, it can spread to nearby tissues and organs, as well as metastasize to distant parts of the body.
Currently, an active search is underway for new, more effective and safe methods of antitumor therapy, and vaccine therapy is one of the most promising areas in this area.
In this article, the medical authors of the MedTour platform have collected all the most up-to-date information about the symptoms, causes, types and stages of colorectal cancer, as well as innovative methods of treating this dangerous cancer.
The main cause of colorectal cancer is a mutation in the DNA of cells in the colon or rectum. It leads to uncontrolled division and growth of cells, resulting in the formation of a tumor. The exact causes of oncogenic mutations are unknown, but certain factors increase the risk of developing this disease.
Risk factors also include smoking, alcohol abuse, a sedentary lifestyle, a diet high in fat and deficient in fiber.
About 20% of patients with colorectal cancer have a family history of the following hereditary diseases:
Age is another risk factor: colorectal cancer is diagnosed predominantly in older people.
The most common symptoms of the disease are:
Recognizing colorectal cancer at an early stage is not easy, because it often does not manifest itself in any way until the tumor reaches a large size and begins to spread to other tissues and organs. Nevertheless, there are ways that help to detect the disease in a timely manner:
The symptoms listed above do not necessarily indicate the development of colorectal cancer. They are also characteristic of other diseases of the digestive tract. However, they cannot be ignored. Call or write to us, and our medical coordinators of MedTour will select for you the best diagnostic clinic and an experienced specialist for free.
Colorectal cancer rarely causes pain in its early stages. As the disease progresses, patients may complain of pain in the abdomen, liver, bones, and other parts of the body where the malignant process has spread. If the tumor presses on a nerve, a person may have back pain.
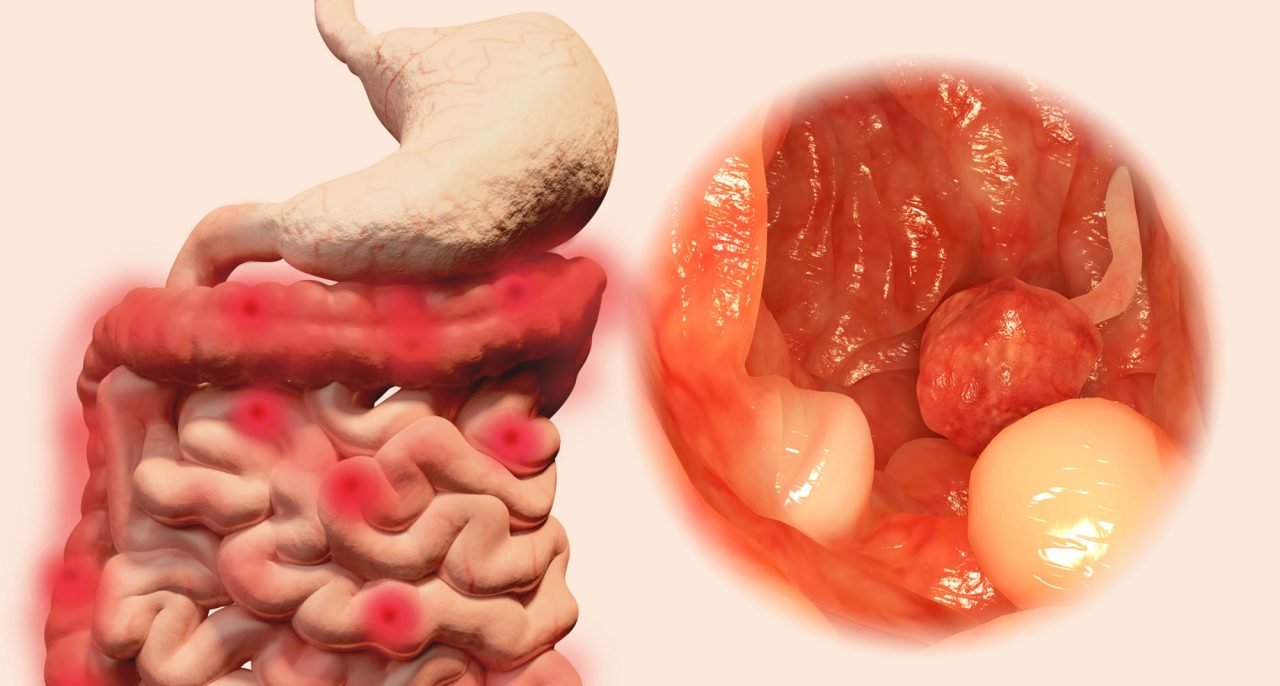
More than 95% of all colorectal cancers are adenocarcinomas of the colon or rectum. They are formed in glandular cells that secrete mucus. Other, less common types are:
There are also primary (newly formed) and secondary (spread from other parts of the body) cancer. Recurrent tumors are those that continue to grow and metastasize after treatment.
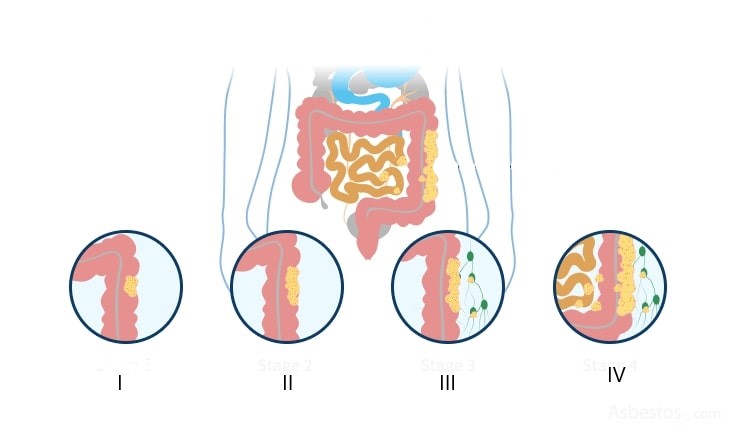
The colorectal cancer staging system has a complex structure, but in general it follows a simplified scheme:
Staging of rectal cancer is crucial in choosing therapeutic tactics and determining the prognosis of the disease.
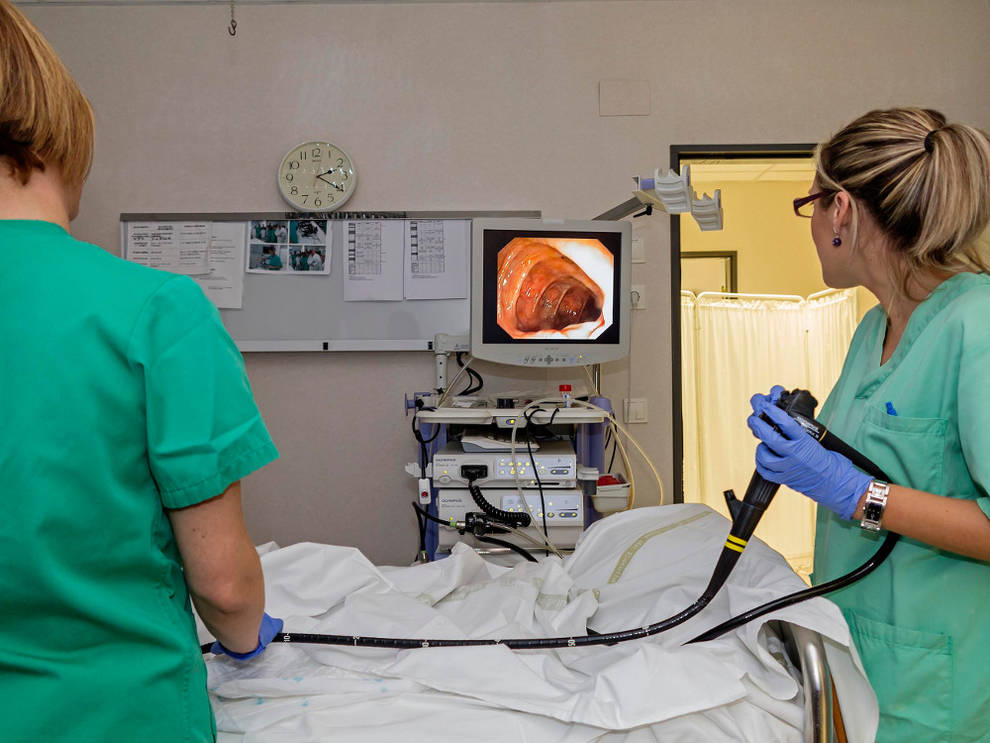
In most cases, a comprehensive diagnostic examination for the detection of intestinal tumors includes:
Accurate diagnosis is essential for an effective treatment plan. Call or email us to find a clinic that has modern equipment and experienced specialists for high-quality colorectal cancer diagnostics.
Surgery is the main treatment for early stage colorectal cancer. The choice of the type of operation depends on the stage of cancer, its localization and the purpose of the surgical intervention.
Minimally invasive surgeries
At an early stage, the tumor can be removed during a colonoscopy. This is a minimally invasive procedure that does not require large incisions. Precancerous polyps are removed with a wire loop by cutting them off the colon wall while coagulating (sealing) the blood vessels to reduce bleeding. Local excision of cancerous tumors at stage I is a more complicated procedure. The neoplasm is removed using microsurgical instruments along with a small amount of healthy tissue.
Colectomy
A colectomy is an operation that involves partial or complete removal of the large intestine. As a rule, regional lymph nodes are also removed at the same time. Colectomy is performed in two ways:
Laparoscopic operations are less traumatic, so patients recover from them faster. However, they are not always possible. Sometimes, to remove the tumor completely, a surgeon needs an open approach.
Stenting and colostomy
In advanced stages, a large tumor can block the intestinal lumen. In this case, the doctor may recommend the placement of a stent, which expands the walls of the intestine and holds them in the correct position.
For advanced colorectal cancer, part of the bowel may need to be removed. The operation is similar to a standard colectomy, only in this case, the parts of the colon are not connected. Instead, one of its ends is brought to the abdominal wall, where a colostomy is formed – an opening for the evacuation of feces. Patients with a colostomy must wear a colostomy bag, a special sealed bag for digestive waste.
To minimize the risk of colorectal cancer recurrence, complex therapy is carried out, which includes not only surgery, but also other methods of antitumor treatment. These include:
The choice of treatment method depends on the type and stage of cancer, as well as on the purpose of the treatment. For example, chemotherapy before surgery can help shrink the tumor and make it easier to remove. After surgery, it is performed to destroy cancer cells that may have remained in the patient’s body after surgery.
Vaccine therapy is one of the most promising and rapidly developing areas in oncology. Currently, the world’s leading cancer centers are actively developing cancer vaccines, the treatment of which helps to significantly improve the results of standard therapy and reduce the risk of cancer recurrence.
MedTour strives to make innovative treatments more accessible to patients. We currently offer treatment for colorectal cancer with two types of Cancerax cancer vaccines. They have a similar principle of operation. Once ingested, the active ingredients of the drug “teach” the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells.
At the moment, vaccine therapy is carried out only in combination with standard treatment after consultation with a doctor. It is an adjuvant method of anticancer therapy that has been proven effective in clinical trials.
To learn more about the innovative method of cancer treatment with vaccines, contact the MedTour coordinating doctor in any way convenient for you.
The prognosis for colorectal cancer depends on many factors, the main one is the stage of the cancer. At an early stage, when the tumor is limited to the mucous membrane or the intestinal wall, the prognosis is usually very favorable. In this case, the chances of a full recovery are quite high.
If the neoplasm is found at later stages, when cancer cells have spread to regional lymph nodes or surrounding tissues, the prognosis is less encouraging. The spread of the tumor makes it difficult to completely remove it surgically, which negatively affects the success of treatment.
The overall five-year survival rate for colorectal cancer is 64.4%, for rectal cancer – 67%. As mentioned above, this indicator largely depends on the stage of the malignant process:
Timely detection and qualified treatment are the key to a successful cure for colorectal cancer.
The MedTour platform cooperates with the best oncology centers specializing in the diagnosis and treatment of malignant intestinal tumors. These are medical centers that have modern equipment and have access to innovative methods of therapy. Get a free consultation with a MedTour medical coordinator to learn about the best colorectal cancer treatment options available.
The MedTour platform contains information about leading doctors who specialize in the treatment of oncological diseases of the digestive system and have achieved significant success in this area. Contact us in any way convenient for you, and we will help you choose a specialist that best suits your personal needs and wishes.
Please rate the work of MedTour
