Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
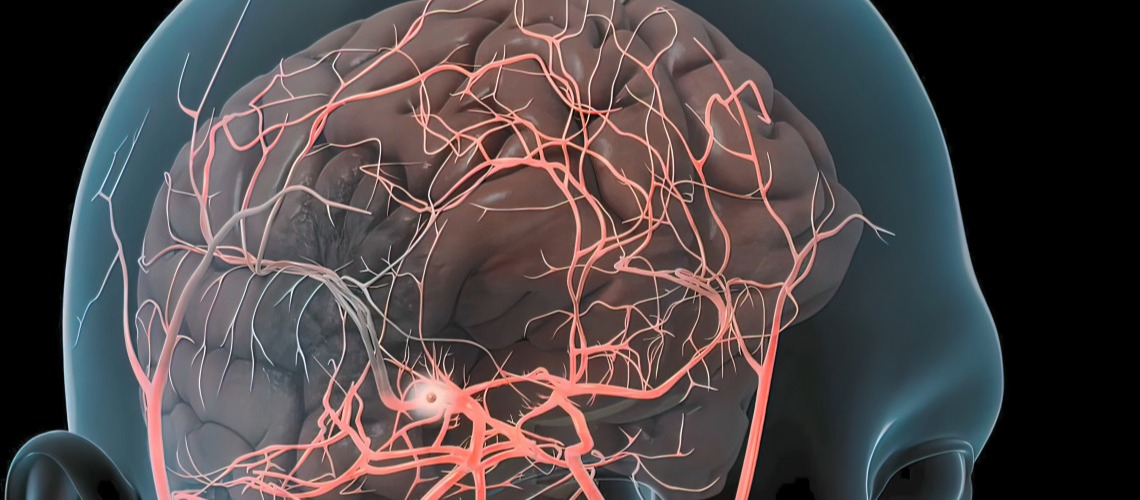
A cerebral aneurysm is a congenital or acquired pathology of cerebral vessels. Deformation of the walls of blood vessels occurs with the formation of a local area of protrusion. The danger of this condition is that even a small formation can quickly increase in size, filling with blood. In this case, the aneurysm can compress the surrounding nerves and brain tissue, and the risks of possible hemorrhage into nearby brain tissue due to a rupture of the aneurysm significantly increase.
Breast aneurysm is a common disease. For example, in the USA, approximately 3-5% of the country’s residents have such a diagnosis as “brain aneurysm”.
As a rule, aneurysms are detected in adults (middle-aged patients with a peak from 30 to 60 years), but their occurrence does not depend on age. More often this pathology is found in women.
Based on the definition given in the medical literature, a cerebral aneurysm is an abnormal condition of some vessels (such a structure can form in any vessels, for example, the neck, spinal cord, etc., but now we are talking about the vessels of the brain). Externally, it manifests itself in the form of focal expansions of the lumen of an artery or other vessel in the head, and may also be accompanied by a pathological protrusion of one of the vascular walls.
Aneurysm is one of the most common causes of subarachnoid or intracerebral hemorrhage. A prerequisite for this is that the cause of such a release of blood is not a head injury. As a result of hemorrhage, there is a threat to a person’s health, and often to life. Timely diagnosis, followed by surgical or conservative treatment of cerebral aneurysm, is one of the most important factors that can significantly prevent hemorrhagic (manifested by bleeding into adjacent tissues) stroke and serious neurological disorders. This also makes it possible to significantly reduce the risks of death and profound disability for patients.
Today, close attention of scientists is focused on studying the causes that contribute to the occurrence of vascular aneurysm. For now, it is impossible to name with absolute certainty the factors that are guaranteed to cause this pathology.
However, doctors identify causes that may contribute to the development of a cerebral aneurysm. By assessing all possible risk factors, they can be divided into two main subgroups that require close attention: congenital (internal) and acquired (external).
Congenital factors for the occurrence of aneurysms in the brain include:
Acquired factors that can cause a cerebral aneurysm include the following:
Also, the risks of developing the disease are constant stress and unregulated excessive physical activity, which can increase blood pressure and weaken the walls of blood vessels.
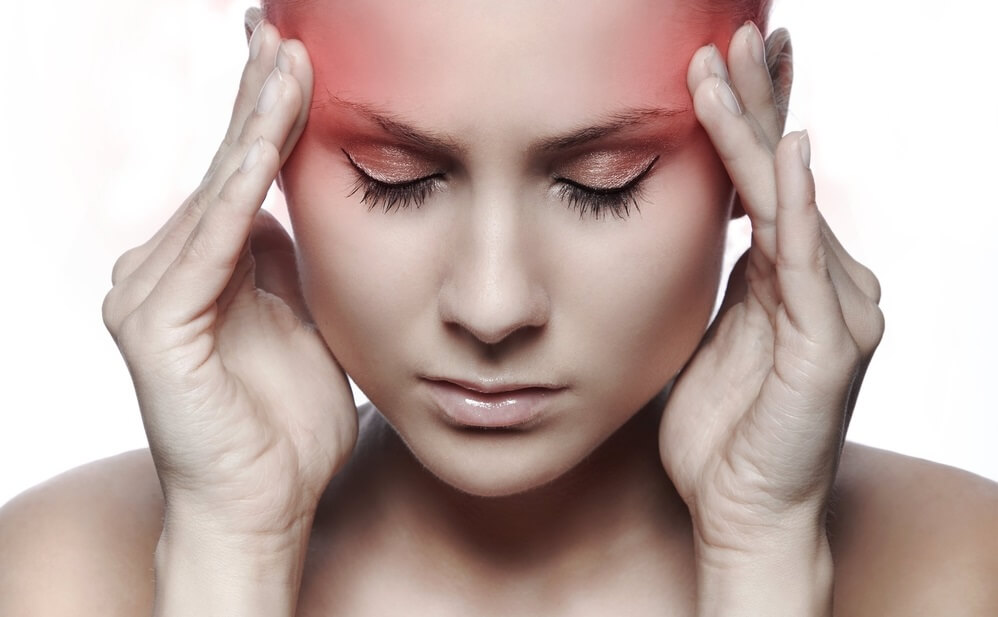

Taking into account the frequency of occurrence of certain symptoms, it should be noted that in the vast majority of all identified cases, brain aneurysm has no manifestations at the initial stage. As a result, the pathology of the vessels of the head in the so-called pre-hemorrhagic period (when there are no clear symptoms) is detected by chance.
When cerebral aneurysms appear, their main symptoms directly depend on where exactly the pathological focus is localized, as well as on its volume.
The main symptoms that suggest the occurrence of a cerebral aneurysm appear only after its growth begins, when the gradually increasing size of the tumor puts pressure on adjacent structures. The most common symptoms that occur are:
In this case, doctors often distinguish two options for the development of cerebral aneurysm:
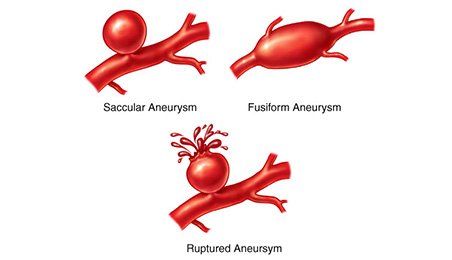
Cerebral artery aneurysms come in different types, depending on the method of classification.
Doctors classify aneurysms based on their shape:
By the number of chamber:
According to the size of the aneurysm, there are:
Aneurysms are classified according to their location:
Saccular aneurysms, up to 2.5 mm in size, are more common; sometimes a “cluster-shaped” aneurysm is diagnosed when several sections of a vessel with thinned walls protrude at once.
Headaches have different localizations depending on where exactly the aneurysm is located, what size it is, and what nerves and brain tissue it compresses.
Often, painful sensations are concentrated in the orbital area, around the eye, and also in the forehead area.
The headache can be of a migraine nature, while a few days before the rupture of the aneurysm, “warning” or “signal” pains appear; they are more intense and difficult to control with medication.
When an aneurysm ruptures, a sharp headache appears, as if after a strong blow, and it intensifies many times over compared to the pain that was observed previously.
In addition to headaches, a variety of neurological symptoms are sometimes observed with an aneurysm: a feeling of numbness or even paralysis of part of the face, weakness, double vision, blurred vision, darkening of the eyes, tinnitus, speech disturbances and movement disorders of varying degrees of manifestation may appear – from invisible to very strong and expressive.
There are cases when a brain aneurysm does not require urgent surgical intervention.
This usually applies to cases where the brain aneurysm has not yet ruptured. Then the operation may not be performed if the size of the detected pathology is very small, and also if the patient has a low risk of bleeding, or there are significant contraindications to the operation due to possible side effects. In this case, doctors recommend regular observations to assess the patient’s condition over time.
The attending physician must weigh and inform the patient of the risks accompanying the operation or the choice of conservative treatment.
The possibility of treating an aneurysm without surgery directly depends on the location of the pathology of the brain vessels, its size, as well as the symptoms and general health of the patients.
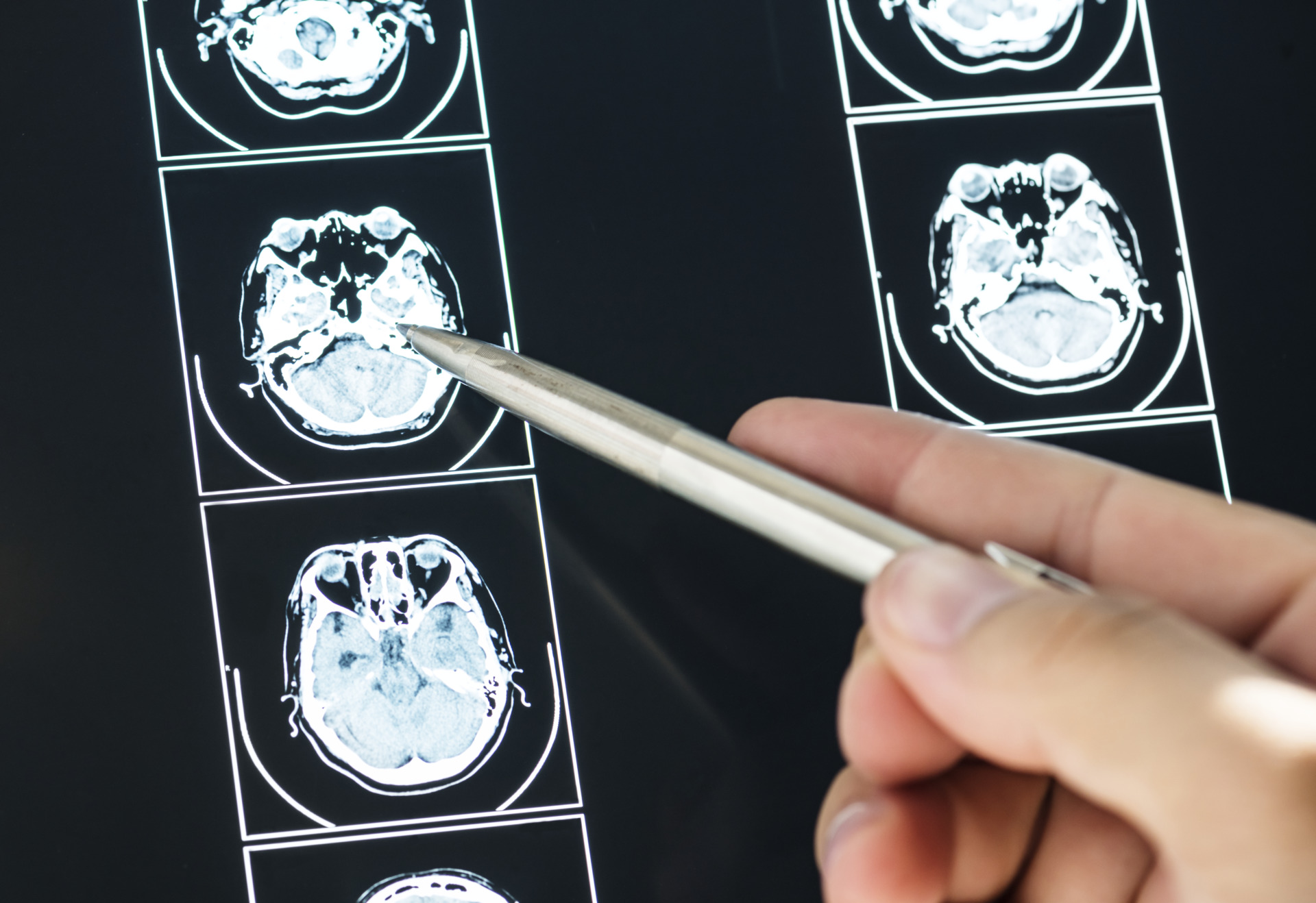
Since an aneurysm does not manifest itself in any way at an early stage, most often diagnostic measures are carried out after its rupture. For diagnosis, a neurological examination and medical history are used, but the main research methods are instrumental:
Also, if hemorrhage is suspected, a laboratory analysis of cerebrospinal fluid may be performed. It will help identify a ruptured aneurysm, as well as determine whether it was caused by an infection and whether antibiotics need to be used for treatment.
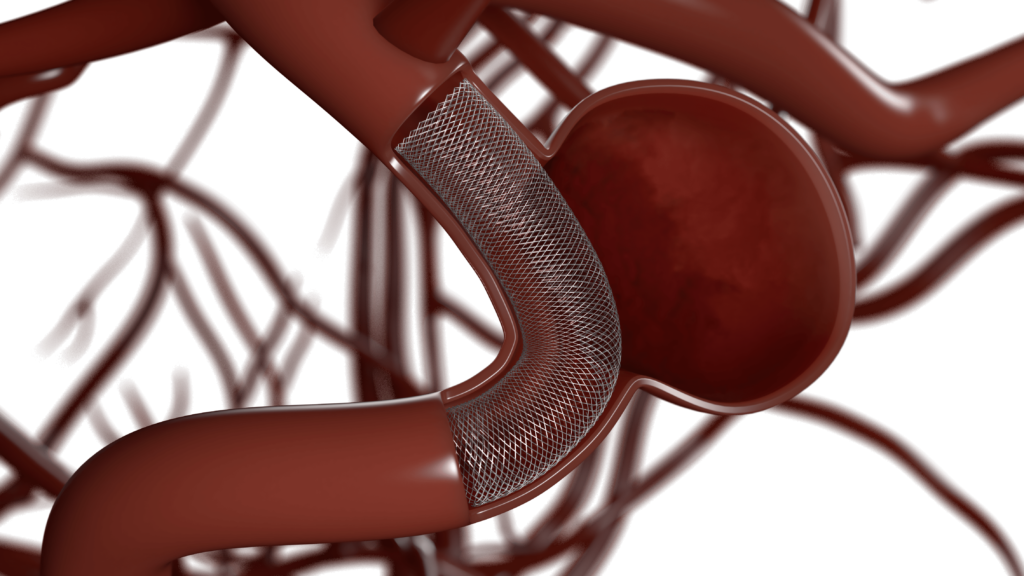
Determining the treatment option for a cerebral aneurysm largely depends on the stage of the disease:
If a cerebral aneurysm is detected at the pre-hemorrhagic stage, dynamic monitoring of the patient is possible with serial visualization of the aneurysm using instrumental methods.
Interventional therapy is indicated in cases where a rupture has occurred, with large aneurysms that give worsening symptoms.
Radical methods for treating aneurysms include various types of surgical interventions.
There are several types of surgical interventions to remove aneurysms.
Endovascular surgery may be indicated, for example, if the aneurysm is located in the vertebrobasilar region, as well as if symptoms of aneurysm rupture appear, such as bleeding in the brain, compression of adjacent tissues, etc. In this case, stenting or endovascular occlusion (exclusion of the vessel from the bloodstream) can be performed.
Surgical removal of a brain aneurysm can be an open operation, where surgical access is provided through incisions. One of these operations is vessel clipping (a special titanium clip is applied to the vessels). The main indication for surgical intervention is a ruptured aneurysm, which requires emergency care to minimize the consequences of hemorrhage.
Prices for surgery to remove a brain aneurysm directly depend on the type of aneurysm, its size and location, as well as on the choice of the method of performing the operation and the specific clinic.
MedTour company cooperates with the world’s leading medical centers that specialize in the treatment of aneurysms and overcoming its consequences.
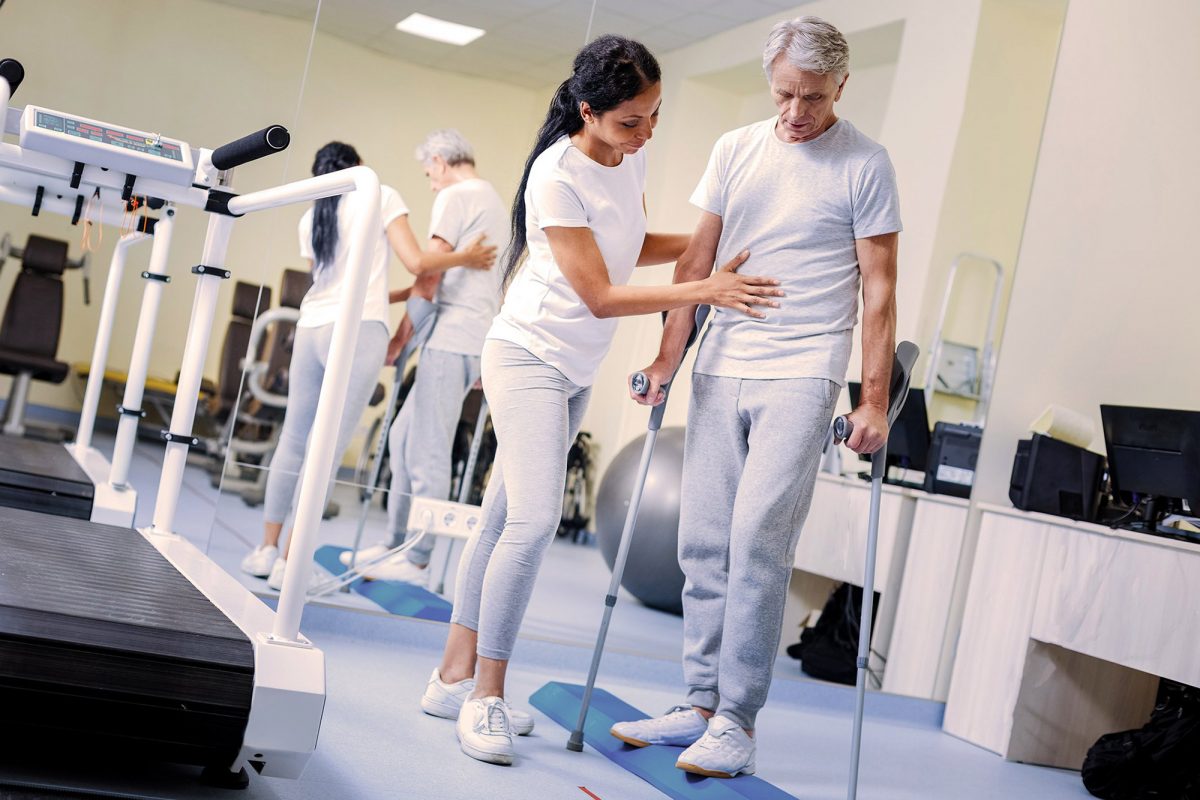

Rehabilitation after removal of an aneurysm is an individual process that largely depends on the patient’s health status. After the operation, patients may remain in the clinic for several days or weeks under the supervision of a doctor, during which specialists monitor the patient, perform dressings and assess the patient’s general condition.
If a patient has persistent neurological disorders after treatment, doctors must develop a rehabilitation plan that improves the condition. In this case, rehabilitation may include exercise therapy, physiotherapy, drug treatment, therapeutic massages and sanatorium-resort rehabilitation procedures.
It should be remembered that a brain aneurysm is a fairly serious disease that can affect a person’s life and health. Due to the fact that the pathology does not manifest itself in any way over a long period, its detection is most often an accidental diagnostic finding, which subsequently necessarily requires close monitoring, and in some cases, surgical intervention.
After a rupture of an aneurysm, treatment is mandatory, since otherwise there is a high risk of repeated hemorrhage in the brain, which can lead to disability or even death.
Unfortunately, at the moment there is no effective way to prevent cerebral aneurysm. However, if there are cases of aneurysm in the family history (especially in first-degree relatives), it is recommended to undergo an examination and minimize the risks of developing the disease (control of blood pressure, elimination of bad habits, prevention of atherosclerosis, reduction of stress levels and dosed physical activity are required)
At your request, MedTour specialists will help you find a clinic for diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation after removal of a cerebral aneurysm.
It is important to note that a brain aneurysm is the same case that is also called a “time bomb”, and therefore it requires urgent treatment.
Thanks to many years of experience and close cooperation with leading clinics, we will be able to select the optimal solution that will help you receive qualified care of the highest level in the shortest possible time.
A disease such as cerebral aneurysm requires the close attention of the following specialists: a neurologist or neurosurgeon. If you experience more than one and frequently occurring symptom that may be caused by the presence of an aneurysm, or if you are in a high-risk group (complicated family history, congenital risk factors, brain injuries), be sure to undergo an examination, because the earlier an aneurysm is detected, the greater the chance of a favorable outcome.
Please rate the work of MedTour
