Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
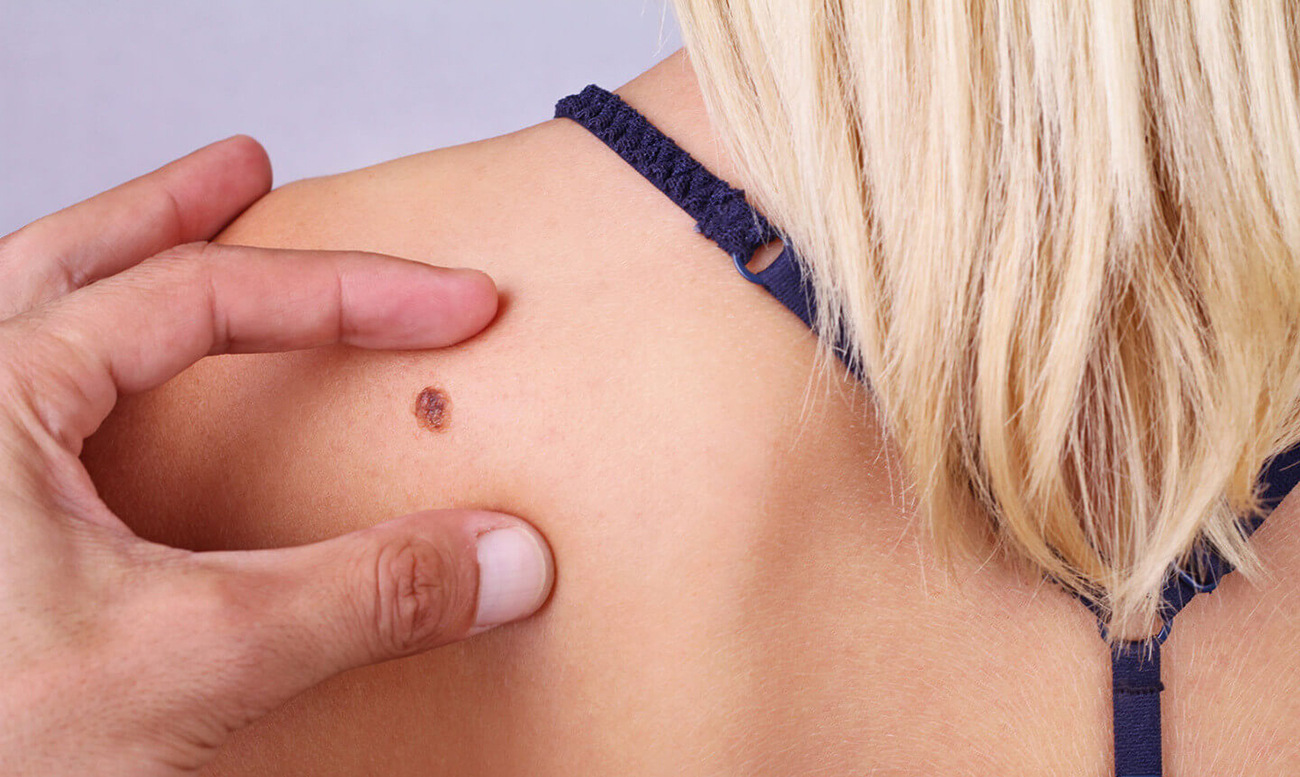
Basalioma is a type of skin cancer that develops from cells of the basal layer of the epithelium. Another name for this disease is basal cell carcinoma or basal cell skin cancer. According to statistics, this is the most common malignant disease. Of all skin malignant diseases, it accounts for about 75%. Typically, such a tumor appears in old age, but basal cell carcinoma can also be found in children. More often in fair-skinned and fair-haired people, since their skin is more sensitive to ultraviolet radiation.
Most often, basal cell carcinoma appears on the face in the area of the wings of the nose, temples, nasolabial folds, forehead, and cheeks. Basalioma of the scalp and basalioma on the eyelid may occur. Less commonly, it occurs on the neck, body, arms or legs. The tumor has a low degree of aggressiveness, grows slowly and practically does not metastasize. However, in advanced cases, it can cover large areas of the skin, grow into adjacent tissues and even destroy bone structures. Correctly selected treatment allows in most cases to completely get rid of the pathology. And even if a relapse occurs, it usually responds well to therapy.
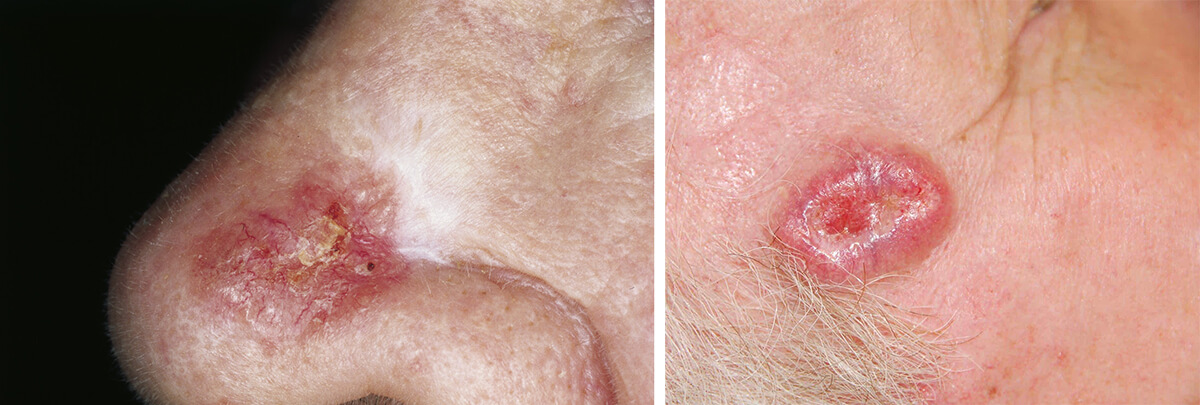
The main cause of basal cell skin cancer is exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the skin. Most often it is caused by prolonged exposure to the street under the active sun. UV rays provoke the occurrence of mutations in the basal layer of the skin, resulting in abnormal cells that begin to multiply uncontrollably.
Factors that provoke the development of this pathology include:
The likelihood of developing basal cell carcinoma also increases when the immune system is weakened. This can happen, for example, when taking immunosuppressive drugs.
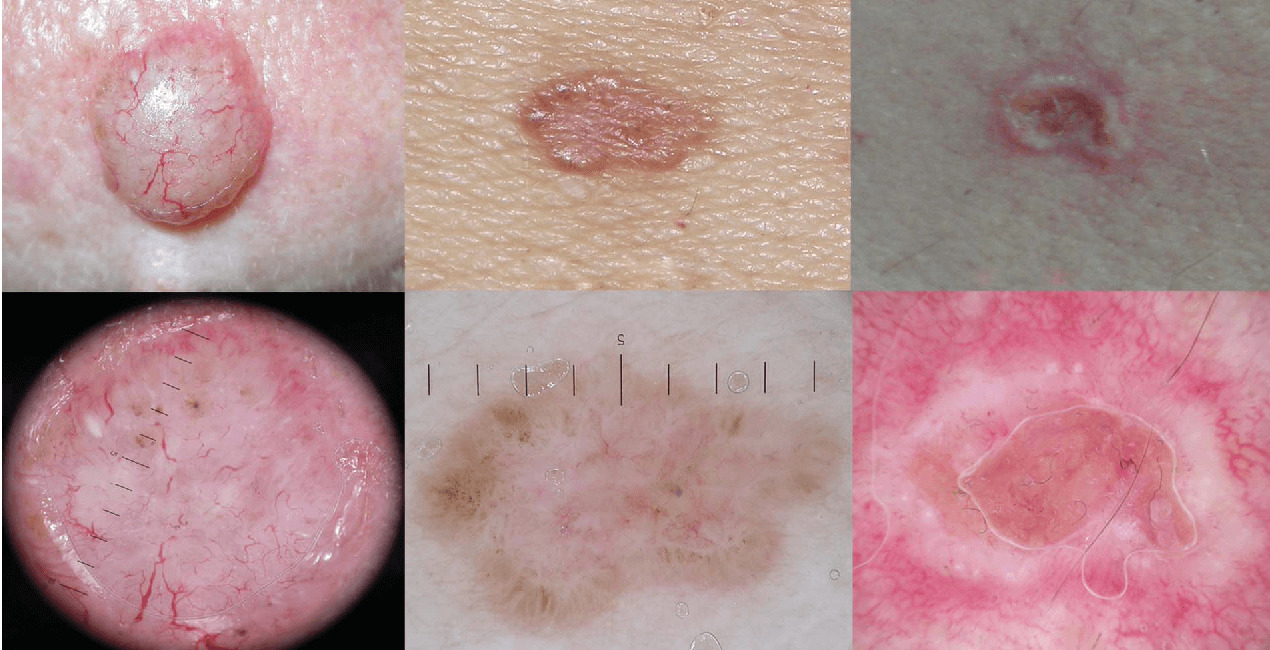
There are several types of basal cell carcinomas, the most common include:
The appearance of basal cell skin cancer may vary depending on the type. Most often, the initial stage of basalioma looks like a small nodule up to 4 millimeters in diameter, which can be of different colors, usually reddish or pinkish. It can have a shiny surface, convex or flat. At first it resembles a regular pimple, but over time it acquires the distinctive features of a neoplasm.
As basal cell carcinoma develops, it begins to grow laterally. It can become crusty, ulcerate, bleed, or peel off. At this stage, a person usually realizes that this is not an ordinary pimple, but some kind of skin problem, and consults a doctor.
If the tumor is actively growing, itching and pain may also occur.
In severe and advanced forms, the disease grows into the subcutaneous tissues, involves tendons, bones, and the process may involve the ears, brain, and eyes.
There are four stages of basalioma:
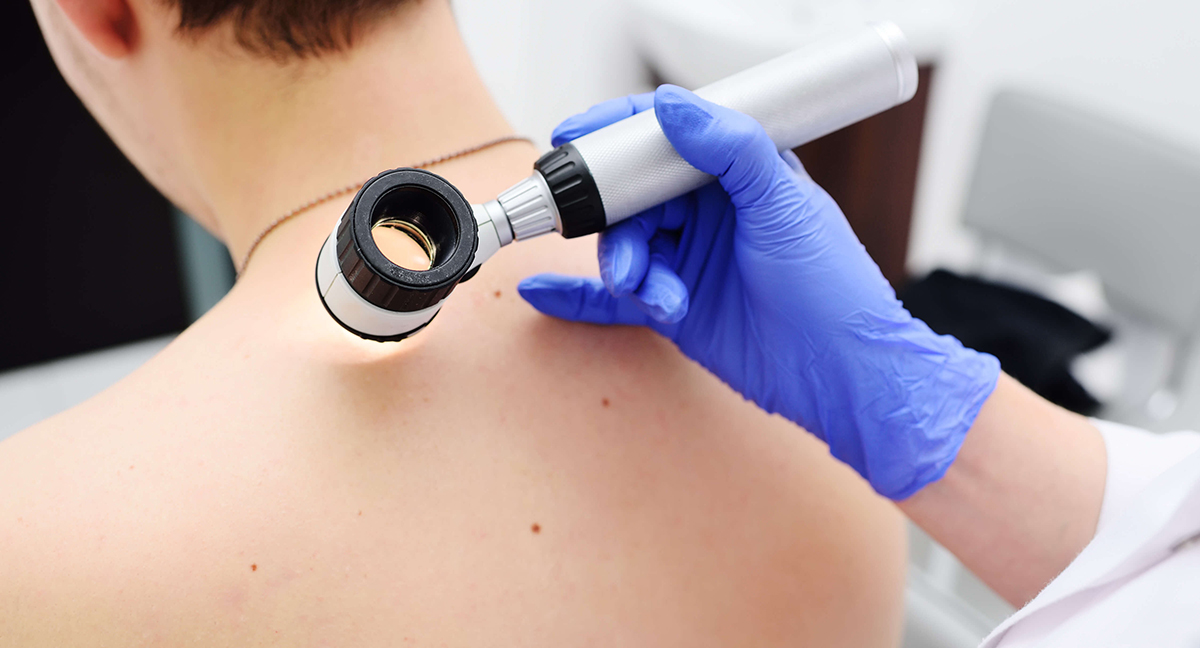
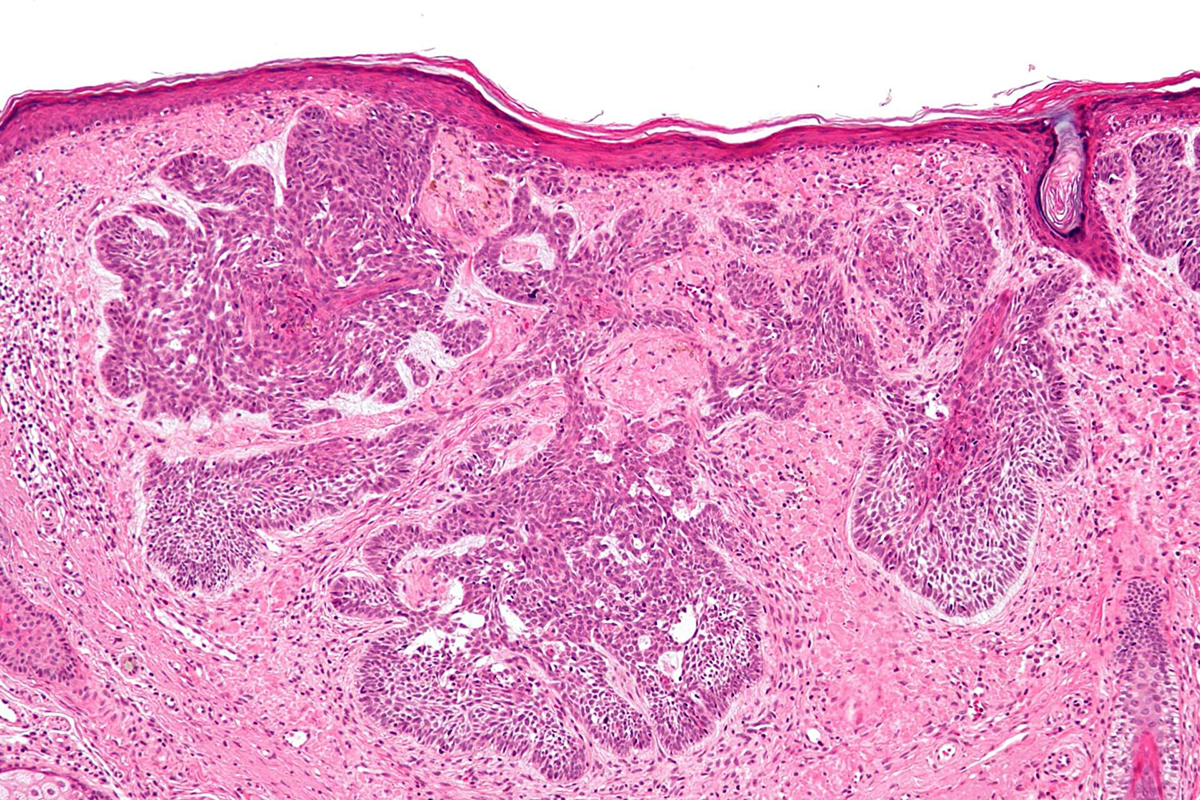
If suspicious growths appear on the skin, it is necessary to contact a dermatologist as soon as possible. Usually, a doctor determines basal cell skin cancer by its external characteristics, and for this it is enough to conduct a dermatoscopy. Using a special dermatoscope device, the doctor examines the skin tumor, and this allows to carefully examine the tumor, see its structural features and make a diagnosis with a probability of more than 80%. However, cytological or histological examination may be required to definitively confirm the diagnosis. Using histology, the doctor accurately determines the type of cells and diagnoses the type of tumor. For histological analysis, a small fragment of tissue is pinched off from the neoplasm, which is then examined in the laboratory.
In advanced cases, in order to determine how damaged nearby tissues are, doctors may prescribe an X-ray, computed tomography or MRI.
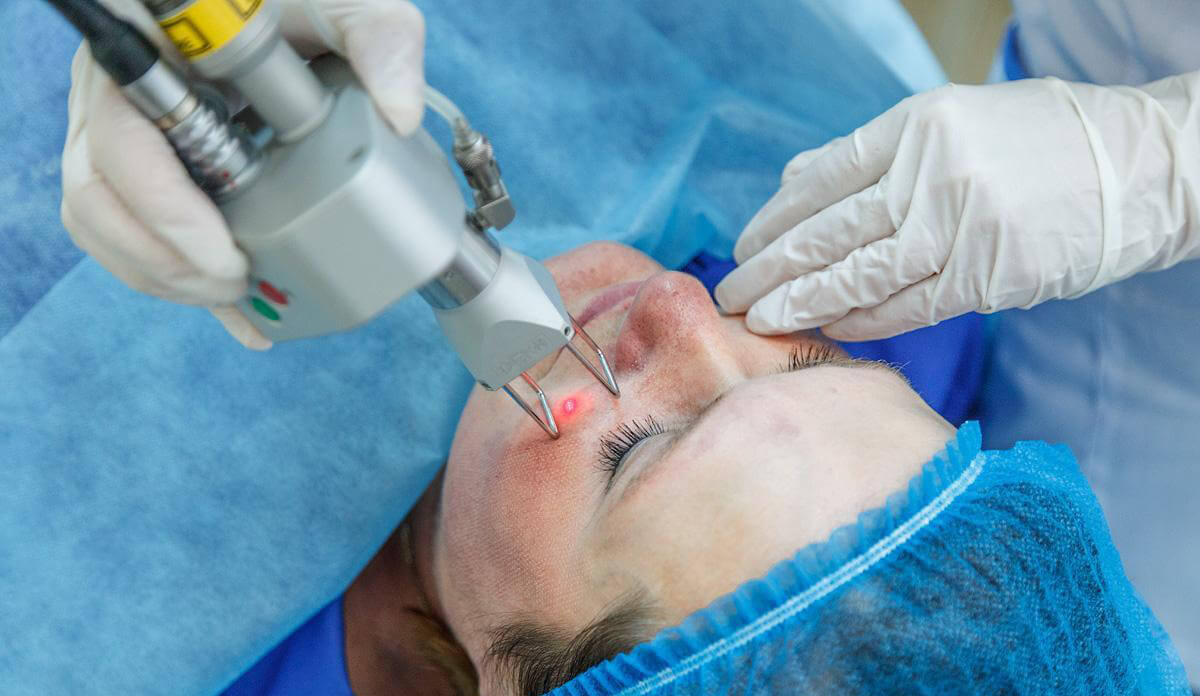
Today, there are various ways to treat basalioma. Doctors select tactics to combat the disease individually, depending on the location of the tumor, its size, histological subtype, and the degree of involvement of surrounding tissues.
Surgical removal of basal cell carcinoma is performed if gentler methods are not suitable.
Traditional surgery involves removing basal cell carcinoma using a scalpel. Before the procedure, local anesthesia is performed – the doctor injects the operation area with an anesthetic. During surgery, the doctor completely removes the tumor and a small area of healthy tissue (about 5 mm) from all sides. This is necessary so that there are no cancer cells left from which carcinoma could grow again. After which the surgeon sews the edges.
Curettage and fulguration are another type of surgical intervention. In this case, the doctor first scrapes out the tumor completely using a curette. And then treats the operation area using an electrode.
Mohs surgical removal is a technique in which removal is carried out under microscopic control. In this case, the tissues adjacent to the tumor are excised in small fragments and immediately undergo microscopic control. The procedure is repeated until there are no abnormal cells in the samples. This operation may take longer, but its advantage is that minimal healthy tissue will be removed.
In most cases, the prognosis for basal cell carcinoma is positive. Treatment allows the tumor to be completely removed. Approximately 25% of cases may recur within five years, so those diagnosed with this disease should be examined annually by a dermatologist after recovery.
Recurrent tumors also respond well to treatment; in most cases, they do not pose a threat to life and do not affect its duration. A threat to life can arise only in the later stages, when cancer cells grow into the bones, eyes, and meninges. Therefore, it is very important to promptly diagnose and properly treat skin basal cell carcinoma. The MedTour coordinator will help you get to a clinic where the best oncologists-dermatologists consult and choose the optimal treatment taking into account the characteristics of your disease.
To prevent the occurrence of basal cell carcinoma, doctors recommend:
If a person has already had basal cell carcinoma, they should be checked regularly by a doctor after treatment. Also, a good preventive method would be the use of a cancer vaccine, which will protect against relapse of basal cell carcinoma.
Interested in learning more about how vaccines can help fight cancer? The MedTour coordinator will give you a free consultation, tell you about the principles of vaccination, the opportunities it provides, and the clinics where it can be done.
Despite the fact that this type of cancer is not the most aggressive, it is better to treat it in good clinics that use modern equipment and the latest techniques for diagnosing and treating skin cancer. The MedTour platform presents leading medical institutions for the treatment of basal cell carcinoma from around the world: Germany, Turkey, Israel, Italy, Georgia, South Korea and others. We cooperate with these clinics and will help you organize a trip to them for treatment.
You can learn about treatment options for basal cell skin cancer in different countries, the cost of various types of therapy and other nuances of traveling abroad for treatment from our coordinating doctor. Call us or fill out the contact form to get answers to your questions.
MedTour works with the best doctors in the field of treatment of malignant skin diseases. We will help you find an experienced dermatologist-oncologist who will select the most appropriate treatment so that you can get rid of basal cell carcinoma as quickly as possible.
Would you like to know more? Leave a request on our website. The MedTour coordinator doctor will contact you, provide free advice on all current issues and help you choose a good specialist.
Please rate the work of MedTour
