Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
According to statistics, about 1.6 million people worldwide suffer from ulcerative colitis. Incidence rates are also higher in the group of people aged 15 to 30 years. Despite significant progress in the treatment of ulcerative colitis, this disease is still considered incurable. Modern therapeutic techniques are aimed at reducing the severity of symptoms and improving the quality of life of patients, but do not affect the direct cause of the disease. Therefore, there is currently an active search for new, effective and safe treatment strategies for ulcerative colitis, and stem cell therapy is showing promising results.
UC is one of the two major inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), along with Crohn’s disease (CD). Unlike Crohn’s disease, which can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, ulcerative colitis usually affects only the colon. It is a lifelong condition that is associated with serious emotional and social consequences for patients.
The exact causes of ulcerative colitis are unknown. It is believed to be an autoimmune disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy intestinal cells and tissues.
Scientists suggest that genetics is one of the significant risk factors for developing the disease. People who have a first-degree relative (i.e. sibling, child, parent) with ulcerative colitis are more likely to develop this condition. In recent years, researchers have identified about 30 genes that may increase susceptibility to the disease.
The first sign of ulcerative colitis may be blood in the stool, which usually indicates inflammation of the colon. You may also experience changes in stool frequency and texture, abdominal pain, decreased appetite and weight, fatigue and weakness. In addition, signs of UC may include: decreased body temperature, increased sweating. These manifestations may be associated with inflammation and changes in the functioning of the body’s immune system in ulcerative colitis.

The most common symptoms of the disease are episodes of bloody diarrhea, pain and cramping in the lower abdomen, and a frequent urge to defecate. The stool is loose and often contains mucus or pus. Other manifestations of ulcerative colitis are:
Symptoms vary in frequency and severity. This is directly related to how affected the colon is.
Possible complications of ulcerative colitis include:
Patients who have extensive bowel disease for a long time also have an increased risk of developing colorectal cancer.
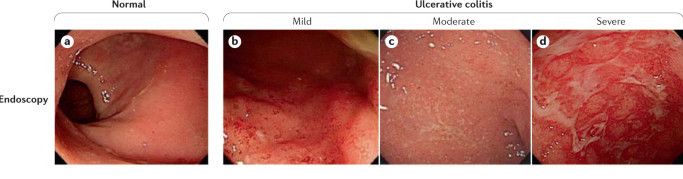
Doctors classify UC according to endoscopic activity:
The severity of ulcerative colitis can be classified as follows:
UC is also characterized by alternating periods of exacerbation and remission.
Typical signs of exacerbation of the disease are:
Exacerbation can be caused by taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics and antipyretics. Other possible reasons for worsening the severity of symptoms are: severe stress, drinking milk, gastrointestinal infections, antibacterial therapy, abrupt cessation of smoking.
A diagnostic examination for suspected ulcerative colitis includes the following laboratory and instrumental studies:
Comprehensive diagnostics allows not only to make the correct diagnosis, but also to determine the severity of UC, which helps to choose the right treatment.
Therapeutic tactics usually involve the use of anti-inflammatory drugs. These medications reduce inflammation in the colon and rectum, leading to relief of symptoms.
When ulcerative colitis worsens, doctors prescribe corticosteroid medications in the form of tablets or rectal suppositories. Due to side effects, corticosteroids used to treat ulcerative colitis should not be used long-term. For severe exacerbations, the patient is hospitalized and corticosteroids are administered intravenously.
In addition, drug treatment for ulcerative colitis includes taking immunosuppressants, drugs that suppress the function of the immune system. They help reduce the severity of the disease, but at the same time make the patient’s body more vulnerable to infections and other diseases.
What are the disadvantages of standard treatment for UC?
Studies have shown that corticosteroid use is associated with weight gain, hyperglycemia, skin lesions, osteoporosis, adrenal insufficiency, and an increased risk of opportunistic infections, especially when combined with other immunosuppressants. These side effects cause nearly a quarter of patients with ulcerative colitis to stop treatment.
Thus, standard approaches are associated with a number of disadvantages. Drug therapy is associated with serious adverse reactions and does not always avoid exacerbations of the disease. In addition, medications only reduce symptoms, but do not cure ulcerative colitis. Trying to solve this problem, scientists are actively looking for alternative approaches in the treatment of ulcerative colitis, and cell therapy is one of the most promising areas in this area.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are one of the most popular multipotent stem cells that have been widely studied over the past few decades. Due to their hypoimmunogenic and immunoregulatory properties, MSCs have shown therapeutic effects in various inflammatory diseases, including ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.
Mesenchymal stem cells are easily isolated from a patient’s bone marrow, adipose tissue, and blood. Studies have shown that they can regulate the innate and adaptive immune response by releasing various mediators such as: immunosuppressive molecules, growth factors, exosomes, chemokines, complement components and multiple metabolites. Once in the inflammatory environment, mediators contribute to the restoration and regeneration of damaged tissues.
A large number of studies have been conducted, both in animal models and in humans. Their review shows that MSC therapy achieves greater therapeutic effects in ulcerative colitis than traditional treatments. An important fact is that when tested on humans, cell therapy did not lead to a single serious side effect.
How do stem cells help with ulcerative colitis?
Stem cell infusions introduce millions of health-promoting and immune-boosting cells into the body. Stem cells respond to cytokine signals (cellular messengers) from damaged tissue, so in ulcerative colitis they migrate to the colon tissue. There they reduce inflammation and facilitate healing and recovery.
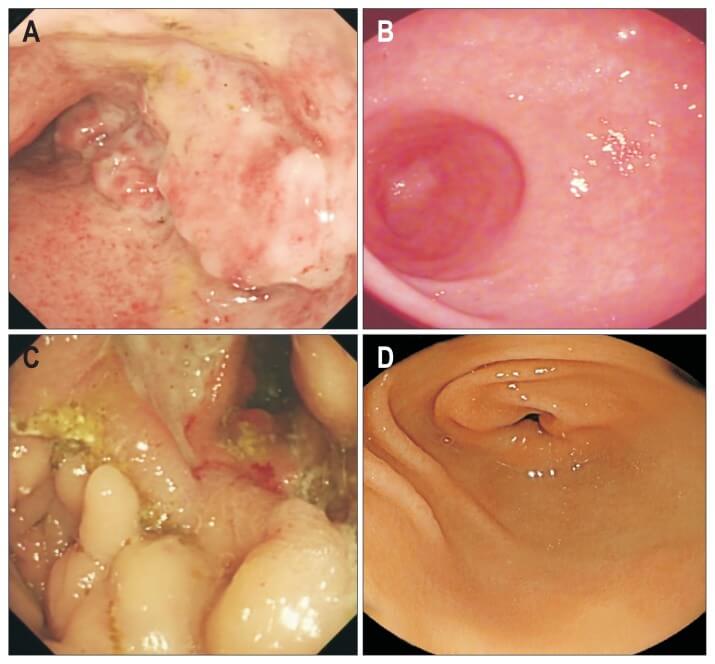
The photo shows endoscopic findings of a patient with inflammatory bowel disease before and 12 months after the patient received stem cell treatment. A significant reduction in inflammation of the colon mucosa can be noted. This, in turn, leads to a reduction in the symptoms of the disease.
What results can you expect?
Much depends on the type, shape and severity of ulcerative colitis. Research shows that cell therapy can improve patient well-being just a few weeks after MSC injections. This translates into increased energy and endurance. Improvement in the morphological characteristics of the intestinal mucosa and relief of specific symptoms occurs 3-12 months after cell therapy.
MedTour: we will help organize stem cell treatment for ulcerative colitis!
Currently, cell technologies are just beginning to develop rapidly. Therefore, it is difficult for patients to understand the features of the new treatment, as well as find a suitable medical center and qualified specialists. MedTour company cooperates with the best regenerative medicine clinics around the world. The impressive results of cell-based treatment suggest that this technology will be widely used in the future.
If you would like to learn more about stem cell treatment for ulcerative colitis, please call the phone number listed on the website or fill out the feedback form. The MedTour medical coordinator will answer all your questions and help you choose the best clinic and doctor.
There are several prevention principles that can reduce the risk of developing the disease and prevent its exacerbation.
The first thing to consider is proper nutrition. People who are at risk for the disease should avoid foods that may trigger a flare-up, such as milk, spicy foods, alcohol, caffeine, artificial additives, and fast food. The diet should be rich in fiber, fresh vegetables and fruits.
Patients with ulcerative colitis should avoid stress. It is one of the factors that can cause an exacerbation of the disease. Therefore, it is important to learn how to effectively cope with stress, for example, through psychotherapy, meditation, yoga, deep breathing, regular rest and sleep.
It is also important to undergo regular examinations with a gastroenterologist. The doctor will tell you what changes need to be made to your lifestyle to minimize the risk of the disease progressing to the acute phase.

According to the general recommendations of gastroenterologists, patients with UC need to:
The doctor will give more detailed recommendations after studying the medical history and diagnostic examination.
The life expectancy of a person with ulcerative colitis depends on many factors, such as the severity of the disease, the presence of complications, age, general health and appropriate treatment.
For most patients, life expectancy is not significantly different from that in the general population. However, some patients with severe ulcerative colitis or complications (such as intestinal obstruction, bleeding, or cancer) may have a less favorable prognosis.
It is important to note that modern treatments, such as new drugs, immunotherapy, and cell technologies, are helping to improve the prognosis for patients with UC.
MedTour company cooperates with the best clinics in the world that treat inflammatory bowel diseases. Currently, there is a unique opportunity to treat the disease using an innovative method – using cell technologies. Contact our medical coordinator for a free consultation. We will help you choose the clinic and doctor that best suits your personal needs.
Gastroenterologists treat inflammatory bowel diseases. MedTour company cooperates with the best specialists in this field from the most famous and prestigious clinics in the world. If you are interested in stem cell treatment for ulcerative colitis, you can consult online with Andriy Kovalchuk, surgeon, candidate of medical sciences, biotechnologist, specialist in the field of regenerative medicine.
Is it possible to completely recover from ulcerative colitis?
Unfortunately, standard methods of therapy can only reduce the severity of the symptoms of the disease, but not cure it completely. However, innovative techniques such as cell therapy offer hope for patients with ulcerative colitis. Stem cells promote the regeneration of damaged colon tissue and also reduce the reactivity of the immune system, affecting the immediate cause of the disease. To learn more about the new treatment method, get a free consultation with the MedTour coordinating doctor.
How do people live with ulcerative colitis?
Symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease, such as diarrhea, blood and mucus in the stool, severe abdominal pain, constant weakness and fatigue, significantly reduce the quality of life of patients. Drug therapy helps reduce the symptoms of the disease, but is often accompanied by side effects. An alternative method is cell therapy. Stem cell administration helps reduce inflammation and the body’s immune response by targeting the underlying causes of ulcerative colitis. All this leads to a persistent reduction in the severity of symptoms and an improvement in the quality of life of patients. Find out more about the new therapy method from the MedTour coordinator.
How to restore the intestinal mucosa using folk remedies?
Unfortunately, traditional methods are poorly effective for ulcerative colitis. They may help repair the intestinal lining, but have no effect on the immune system, which attacks colon cells. A new stem cell treatment simultaneously reduces inflammation and normalizes immune function, allowing the intestinal lining to successfully repair itself. Find out more about innovative treatment from the MedTour coordinator.
Please rate the work of MedTour
