Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
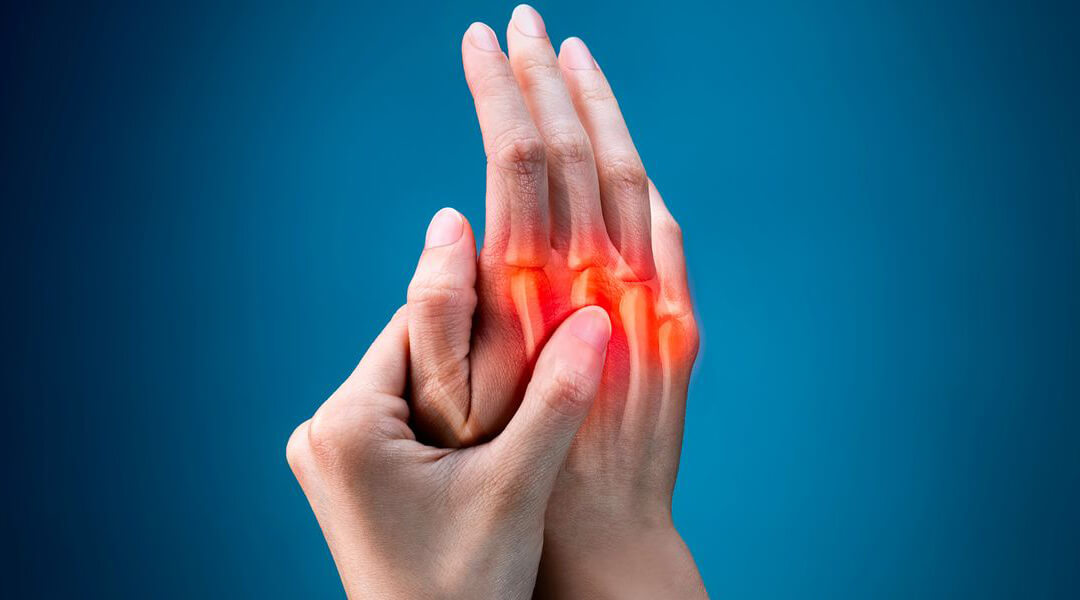
Rheumatoid polyarthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease that is characterized by the appearance of inflammatory processes in the joints, which eventually leads to the degradation of cartilage and bone tissue. Most often, the hands, feet, wrists, knees, and elbows are affected. Usually there is a symmetrical lesion of the joints. With polyarthritis, 4 or more joints are involved in the inflammatory process.
Doctors distinguish several forms of the disease:
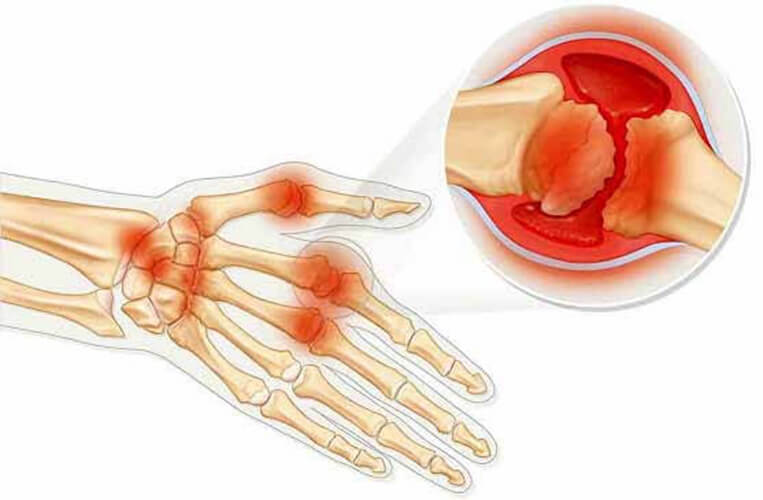
This disease occurs when cells of the immune system begin to attack their own tissues. Factors that can trigger an excessive immune response include:
Characteristic signs of the disease:
The temperature may rise: it can be subfebrile in the chronic course of the disease or rise to 38 degrees in the acute phase of the disease. Muscle pain may also occur, characteristic subcutaneous rheumatoid nodules form, and additional symptoms appear that indicate inflammation in other organs. In the later stages, characteristic deformities of the joints appear.
In fact, rheumatoid arthritis and polyarthritis are the same disease. Arthritis affects one or more joints. They say about polyarthritis when a large number of joints are involved in the process.
Polyarthritis often occurs with inflammation of the internal organs. May be affected:
This is a serious disease that can lead to many complications and significantly worsen well-being. To prevent this, when symptoms of arthritis appear, you need to consult a doctor, undergo an examination and choose an adequate treatment.
To diagnose arthritis, doctors use instrumental and laboratory methods.
Laboratory studies include:
Of the methods of visual diagnostics, ultrasound, radiography, CT, MRI of the joints are used. Also, the doctor may prescribe additional examinations to identify complications and conduct differential diagnosis.
Treatment of rheumatoid polyarthritis involves an integrated approach that includes:
Treatment is selected individually depending on the characteristics of the condition and the stage of the disease. The doctor may prescribe antirheumatic drugs, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, hormonal drugs and other medications, recommend a diet, and prescribe certain physiotherapy.
In later stages, surgery may be required. The need for it arises with deformities of the joints, a significant limitation of their mobility, necrosis and other serious lesions. Operative orthopedic treatment may involve the removal of the synovial membrane of the joint (the inner layer of the joint bag), arthroplasty, endoprosthesis and other types of surgery.
Modern medicine is constantly looking for and introducing new more effective methods of treatment. Thanks to numerous studies, stem cells have been used as the most promising methods of therapy for rheumatoid arthritis in recent years.
Mesenchymal stem cells are cells that have the unique ability to differentiate into any cell type in the body. In arthritis, there is chronic inflammation in the joints, cartilage and bone tissues are destroyed. The use of stem cells allows the body to start regeneration processes in the affected areas. Their use gives an anti-inflammatory effect, pain decreases, processes of restoration of damaged tissues are underway, and joint mobility improves. Also, cell therapy has an immunomodulatory effect and helps to reduce the immune response.
Stem cells are used in two ways:
Treatment using cell therapy shows promising results, allows the body to activate regeneration processes, improve the functioning of the immune system and significantly improve the quality of life of patients.
To choose a good clinic and get treatment from leading specialists in the treatment of joints, you can contact the MedTour company.
You can get arthritis treatment with cell therapy at Dr. Andriy Kovalchuk. Andriy Kovalchuk is a surgeon, candidate of medical sciences, a doctor who treats various diseases with the help of mesenchymal stem cells. Therapy of immune diseases, including arthritis, is just in the area of attention and competence of the doctor.
You have the opportunity to have an online consultation with Dr. Kovalchuk!
Can rheumatoid polyarthritis be cured?
To date, there is no therapy that would completely cure this disease. But the right treatment can slow down the progression of the disease and stop the destruction of the joints, remove pain and improve overall well-being.
Which doctor treats rheumatoid polyarthritis?
If you suspect this disease, you need to contact a rheumatologist. A doctor of this specialization will help to accurately diagnose and choose the most effective treatment.
How long do people live with rheumatoid arthritis?
It is believed that the presence of this disease shortens life by 3-10 years, depending on the severity of the course. However, the use of modern methods of treatment, such as cell therapy, allows the body to stop the destruction of joint tissues and take control of the state of health.
What results can be achieved with stem cell treatment?
Regenerative cell therapy allows not only to slow down the course of the disease, but also launches recovery processes. To date, this is the only method by which it is possible to activate the regeneration of damaged joint tissues. The use of stem cells for arthritis can significantly improve the condition of the joint, delay or avoid joint replacement surgery.
Please rate the work of MedTour
