Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
Ovarian cancer is a malignant tumor that most commonly arises from the epithelial tissue of the ovary. The disease develops against the background of borderline (precancerous) or benign neoplasms. According to worldwide statistics, mortality from ovarian cancer exceeds the total number of deaths from cervical and uterine cancer. This is associated with a high risk of ascites (accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity) and metastases to distant organs.
Scientifically (according to research from the US National Cancer Institute), ovarian cancer begins to develop in the cells of the fallopian tubes. These abnormal cells are precursors to malignant tumors. Over the years, this leads to ovarian cancer.
Scientists still do not know what exactly causes the transformation of mutated cells from the fallopian tubes into a malignant ovarian tumor.
What can cause ovarian cancer:
Women who have a family history of ovarian cancer or certain gene changes (such as BRCA1 or BRCA2) are at higher risk than women who do not have such relationships.
In the early stages, ovarian cancer is asymptomatic. Women experience severe discomfort when the disease reaches stage 3-4.
What are the symptoms of ovarian cancer:
In patients with ovarian cancer, symptoms are active when the process is widespread. Most often, this is accompanied by unreasonable weight loss, general malaise, weakness, and fever.
At stage 4 ovarian cancer, the patient has fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity. At the same time, pain is expressed not only in the abdomen, but also in the back at the slightest load.
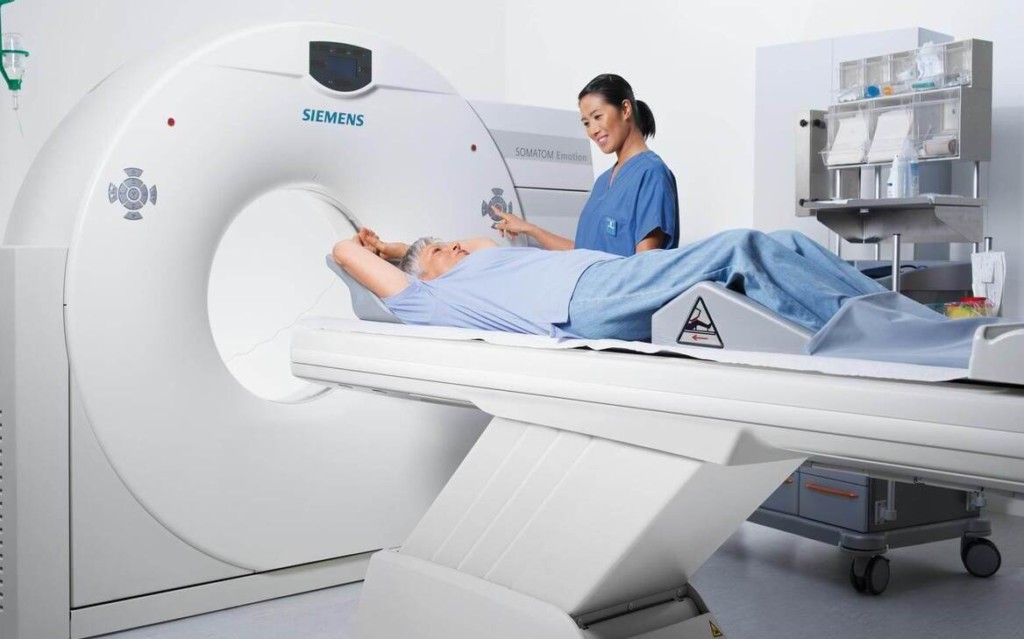
The diagnosis of ovarian cancer should begin with the consultation of a gynecologist. The doctor conducts a rectovaginal examination and palpation of the abdomen, which helps to suggest the presence of pathology.
In specialized clinics, doctors carry out comprehensive diagnostics, which includes:
How to detect early ovarian cancer?
Diagnostics should include all necessary studies that are recommended by the World Health Organization. In clinics abroad, patients undergo all instrumental and laboratory examinations, including PET-CT.
Examples of the cost of PET-CT for ovarian cancer in clinics around the world:
Ovarian cancer responds well to treatment if the patient is diagnosed on time. A timely visit to an oncologist and the correct treatment tactics give a favorable prognosis for a life expectancy of 5 years and even a complete cure.
The prognosis for survival largely depends on the type of ovarian cancer, the general condition of the patient and concomitant diseases. The highest 5-year survival rate is characteristic for mucinous tumors – 68%. With clear cell type – 60%, with endometrioid and serous cancer – 41%.
The 5-year survival rate for ovarian cancer is higher in younger women. Patients under 35 years old pass the five-year milestone in 80% of cases, over 65 years old this figure is about 40%.
Average statistics of five-year survival rate during treatment:
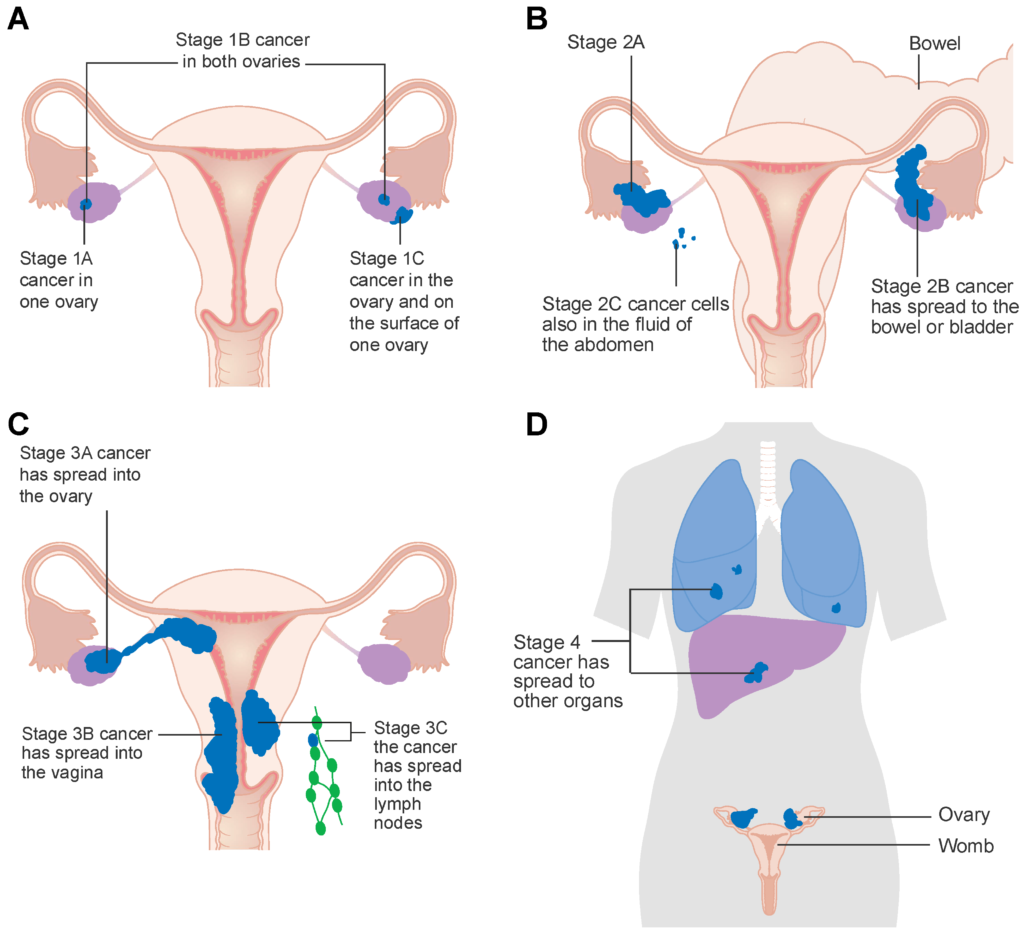
Doctors determine the stage of ovarian cancer based on the size of the tumor and the extent to which it has spread to nearby organs and distant structures.
Each stage of the disease is characterized by:
Doctors determine primary, secondary, or metastatic ovarian involvement. Primary cancer develops directly in the glandular tissue. Secondary cancer develops in teratoid, serous and pseudomucinous ovarian cysts. Metastatic cancer is characterized by spread to neighboring and distant organs through the blood and lymph.
Ovarian cancer is classified into two types: epithelial and non-epithelial tumors.
Malignant epithelial tumors develop from epithelial cells that cover the outside of the ovaries. They are divided into kinds:
Non-epithelial ovarian cancers:
Ovarian cancer can have a variety of histological structures. About 80% of ovarian cancers originate in the epithelium, and about 10% are invasive mucus-forming carcinomas.
The type and kind of tumor affects how quickly ovarian cancer develops and what the patient’s prognosis is. Rare cancers are more difficult to treat. In this case, it is necessary to seek medical help from an experienced oncologist who has clinical experience in the treatment of such malignant neoplasms.
Surgery combined with postoperative chemotherapy is the leading treatment for ovarian cancer. In some cases, chemotherapy is used in the preoperative period to reduce the manifestation of the disease.
Whether ovarian cancer can be completely cured will depend on the patient’s individual diagnostic results and the cancer’s sensitivity to therapy.
The main indicators that doctors rely on when choosing a treatment regimen:
Key treatments for ovarian cancer:
In modern clinics where ovarian cancer is treated according to international protocols, doctors use the latest equipment. Such equipment makes it possible to efficiently and with the least traumatism carry out operations and therapeutic procedures for patients with ovarian cancer.
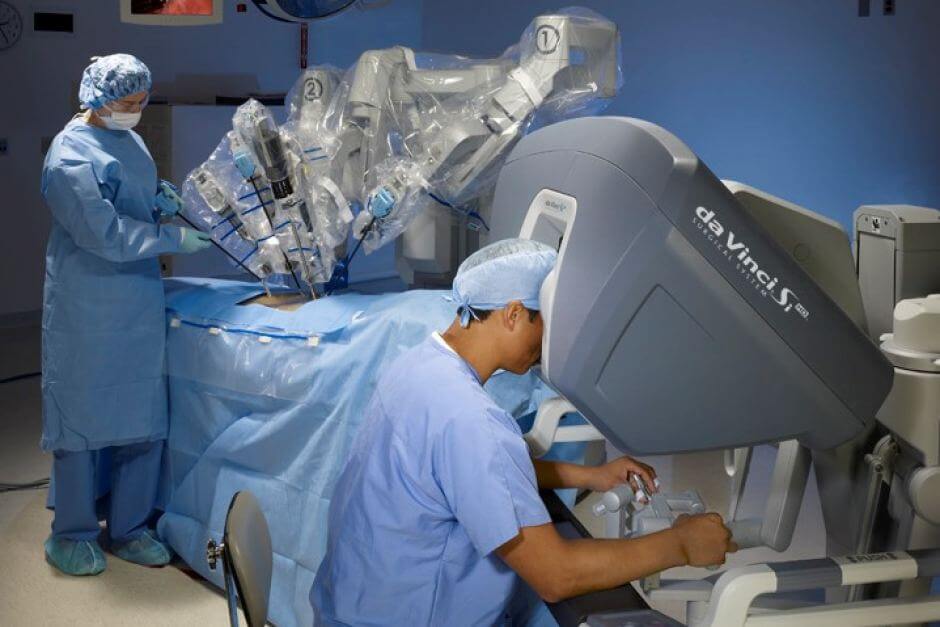
Operations to remove ovarian cancer on a Da Vinci robot
Robotic operations allow surgical treatment of malignant tumors without large incisions compared to abdominal operations. This is important from an aesthetic point of view, as large scars are not left on the patient’s body.
Benefits of Da Vinci surgery:
Radiosurgery for the treatment of ovarian cancer with CyberKnife
The peculiarity of this treatment lies in the precise effect on cancerous tissues. At the same time, the patient does not experience discomfort and does not need long-term hospitalization. The CyberKnife robotic installation can be used by doctors as an alternative to surgical intervention for certain types and stages of ovarian cancer.
Advantages of CyberKnife irradiation:
Radiosurgical treatment of ovarian cancer with the Gamma Knife
Using the Gamma Knife device, oncologists irradiate metastases that have spread to the brain. The therapy is effective for hard-to-reach tumors in the ovaries, which cause complications in distant structures of the body.
Advantages of Gamma Knife irradiation:
The formation of the final cost of ovarian cancer treatment will be influenced by a number of factors related to both the patient’s condition and the pricing policy of a particular clinic. The main criteria for pricing:
The cost of a course of chemotherapy in leading clinics in the world varies on average from $300 to $1 600. The price of drugs in Europe and Turkey is the same, but the cost of the therapy itself will depend on the form of the drug (pills, injections, etc.) and the composition of the formula (for each stage and certain medications are suitable for the type of cancer). If the patient needs intravenous administration of chemotherapy drugs, the clinic may include staff services and the length of stay in the ward in the cost of treatment.
If a patient is considering the option of surgical treatment of a tumor on a Da Vinci robot, then Ukraine comes to the fore in terms of price-quality ratio. The cost of a robotic operation will be about $10 000. Turkish clinics offer operations on the Da Vinci robot at a price of $18 000. This is due to the extensive clinical experience of specialists and work on the latest generation installations. It is also worth considering the additional costs of travel and accommodation in the country.
A woman should immediately consult a doctor if she has:
The most popular destinations for the treatment of cancer among medical tourists are Turkey, Israel, South Korea and European countries.
In the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, in terms of accessibility to the country and value for money, the priority remains clinics for the treatment of ovarian cancer in Turkey and Ukraine, where women are successfully treated for ovarian cancer.
Laboratory diagnostics based on modern medical centers offers a wide range of studies for the diagnosis of ovarian cancer: tumor markers, genetic testing, complete blood count and biochemistry.
According to individual medical indications, surgeons perform the following types of surgery to treat ovarian cancer:
The cause of recurrence of ovarian cancer is metastases, which can persist inside the body. After treatment, relapse is triggered by certain factors that affect metastases. They are the reasons why the disease returns.
Recurrence of ovarian cancer can be prevented if the patient is attentive to any changes in well-being. In this case, it is necessary to immediately contact an oncologist and undergo repeated examinations.
General tips to help reduce the risk of ovarian cancer recurrence:
In some cases, oncologists recommend that patients undergo mammological screening once a year. In a number of countries, the consultation of a mammologist is included in the diagnostic protocols for the prevention of ovarian cancer and its recurrence.
Women who are diagnosed with obesity, diabetes mellitus, thyroid pathology are more prone to the formation of benign and malignant ovarian tumors.
At different stages, ovarian cancer is characterized by nonspecific manifestations and is often disguised as a different disease. Sometimes doctors make a preliminary false diagnosis due to similar symptoms. Insufficiently qualified doctors confuse diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and urinary system with ovarian cancer.
A woman should immediately consult a doctor if she has:
The most popular destinations for the treatment of cancer among medical tourists are Turkey, Israel, South Korea and European countries.
In the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, in terms of accessibility to the country and value for money, the priority remains clinics for the treatment of ovarian cancer in Turkey and Ukraine, where women are successfully treated for ovarian cancer.
Laboratory diagnostics based on modern medical centers offers a wide range of studies for the diagnosis of ovarian cancer: tumor markers, genetic testing, complete blood count and biochemistry.
According to individual medical indications, surgeons perform the following types of surgery to treat ovarian cancer:
The cause of recurrence of ovarian cancer is metastases, which can persist inside the body. After treatment, relapse is triggered by certain factors that affect metastases. They are the reasons why the disease returns.
Recurrence of ovarian cancer can be prevented if the patient is attentive to any changes in well-being. In this case, it is necessary to immediately contact an oncologist and undergo repeated examinations.
General tips to help reduce the risk of ovarian cancer recurrence:
In some cases, oncologists recommend that patients undergo mammological screening once a year. In a number of countries, the consultation of a mammologist is included in the diagnostic protocols for the prevention of ovarian cancer and its recurrence.
Women who are diagnosed with obesity, diabetes mellitus, thyroid pathology are more prone to the formation of benign and malignant ovarian tumors.
At different stages, ovarian cancer is characterized by nonspecific manifestations and is often disguised as a different disease. Sometimes doctors make a preliminary false diagnosis due to similar symptoms. Insufficiently qualified doctors confuse diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and urinary system with ovarian cancer.
Please rate the work of MedTour
