Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
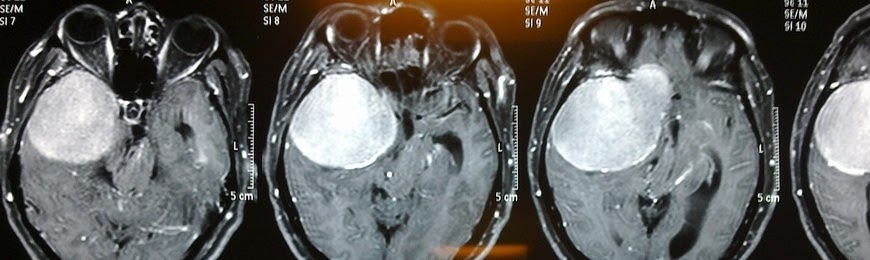
Meningioma is a benign tumor of the brain and spinal cord. The tumor arises in one of the meninges – the arachnoid. These membranes are the layer between the brain and the skull. They act as a scaffold for arteries and veins, and are involved in the normal circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. Meningioma increases intracranial pressure and compresses the centers of the brain, leading to disability.
Scientists have not found reliable reasons for the development of meningioma. It is believed that changes in the work of some genes and hormones can lead to uncontrolled multiplication of meninges cells. Genetic changes can be inherited from relatives or acquired over the course of life.
Doctors have identified risk factors that can lead to the development of the disease:
This does not mean that a person with a risk factor will necessarily get sick over time, but the likelihood of getting the disease increases.
Meningioma is characterized by asymptomatic onset and growth. In the initial stages, the patient may not be bothered by anything. Symptoms appear gradually, but sometimes the patient needs urgent help. The nature of the symptoms depends on the size and location of the tumor in the brain or spinal cord. The patient may have the following complaints:
Meningioma can be discovered incidentally when other conditions are diagnosed, for example, with a head injury or during a preventive examination. This is due to the asymptomatic course of the tumor, if the important centers of the brain are not affected.
Doctor’s consultation
The doctor should familiarize himself with the patient’s medical history, collect a detailed history and clarify the onset and nature of the symptoms. For an accurate diagnosis, it may be necessary to consult several specialists: a neurosurgeon, ophthalmologist, endocrinologist, neurologist.
The doctor can test hearing, memory, reflexes and visual acuity. This is necessary to clarify the possible localization of the meningioma.
Radiological examination
CT (Computed tomography)
The tomograph examines the penetration and attenuation of X-rays. Unlike radiography, CT provides images after complex computer processing. This makes it possible to explore the internal structure of a person in layers. In some cases, for a clearer visualization of the meningioma, an iodine-containing dye is injected into the patient.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
The method is based on measuring the difference in magnetic fields in certain tissues. It allows the doctor to obtain high-quality images of all brain structures and meningiomas. Radiological tests allow doctors to distinguish benign growths from cancer. The pictures show whether the tumor grows into adjacent tissues and organs or is located separately.
Biopsy
If the tumor is removed, its samples are sent to the pathohistological laboratory for further examination. Fabric samples are treated with special dyes and placed on glass. Thus, specialists prepare a micropreparation for examination under a microscope.
A biopsy provides information about tumor cells, their degree of malignancy. Based on the results of the biopsy, doctors decide if additional treatments are needed besides surgery.
Examples of the cost of diagnosing meningioma in clinics around the world:
Life expectancy with a diagnosis of meningioma depends on the age of the patient, the size of the tumor, its location in relation to the structures of the brain, and the degree of malignancy. Life expectancy is higher in patients with meningioma at a young age, compared with patients in older age groups.
Surgical treatment for a non-malignant form of meningioma provides a longer life expectancy: 96% for spinal forms and 83% for meningiomas of the meninges. The five-year survival rate in patients with anaplastic (second degree) and malignant (third degree) meningioma is 63.8%.
Experienced doctors use the World Health Organization (WHO) tumor classification. It is based on the division of tumors depending on the cellular structure, which is visible under a microscope:
Dividing meningiomas into three classes allows the doctor to predict the rate of growth and the likelihood of recurrence based on past experience.
Another classification of meningiomas is based on the location of the tumor relative to the brain and nearby anatomical structures of the central nervous system. This classification is important when planning the surgery to remove the tumor.
When drawing up a treatment plan, doctors take into account the following factors:
If the tumor actively grows or causes acute symptoms, the patient will be offered options for surgical removal of the meningioma. The following methods of surgical treatment of meningioma are available abroad:
As a rule, a craniotomy is performed – a small window is made on the skull through which all surgical manipulations are performed and the neoplasm is removed. The incision is made along the hairline, so after healing, no traces of the operation are visible.
In some cases, endoscopic removal of the tumor through the nose and sinuses is possible if the tumor is small and located in a place accessible to this technique.
Doctors try to remove the entire tumor, but sometimes this cannot be achieved due to the location of the meningioma near important centers of the brain and spinal cord. In these cases, the patient undergoes additional treatment – radio- or chemotherapy.
If the tumor has been completely removed and the biopsy results show that the cells are benign, surgery may be the only treatment.
How long does the operation to remove a meningioma take
Benign tumors of the central nervous system operate faster than malignant neoplasms, since the tumor does not grow into the surrounding tissues. On average, the duration of an operation to remove a meningioma is 4-6 hours. If the intervention is carried out through the sinuses (transsphenoidal approach), the operation takes 3 to 4 hours.
Examples of the cost of surgical removal of meningioma in clinics around the world:
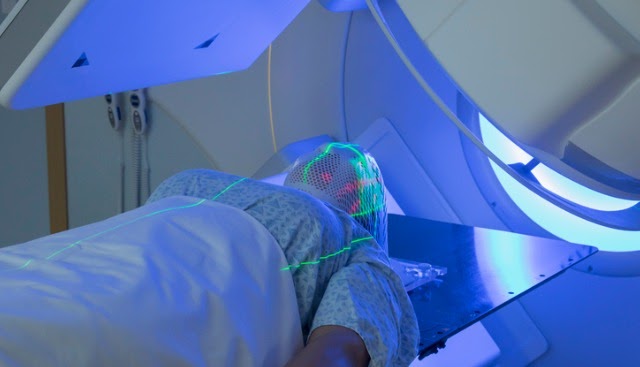
Radiation therapy is a method of treating benign and malignant neoplasms using radioactive particles directed directly to tumor cells. Radiation is generated and directed to the tumor by special devices – linear accelerators.
Radiation therapy for patients with meningioma is given in order to reduce the likelihood of recurrence and to destroy cells that could not be removed during surgery.
Modern foreign clinics can offer different options for radiation therapy:
Examples of the cost of radiation therapy for meningioma in clinics around the world:
The price will depend on the selected country, the medical center and the complex of prescribed procedures during diagnosis and treatment. Therefore, the final cost is calculated individually for each patient.
Please rate the work of MedTour
