Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
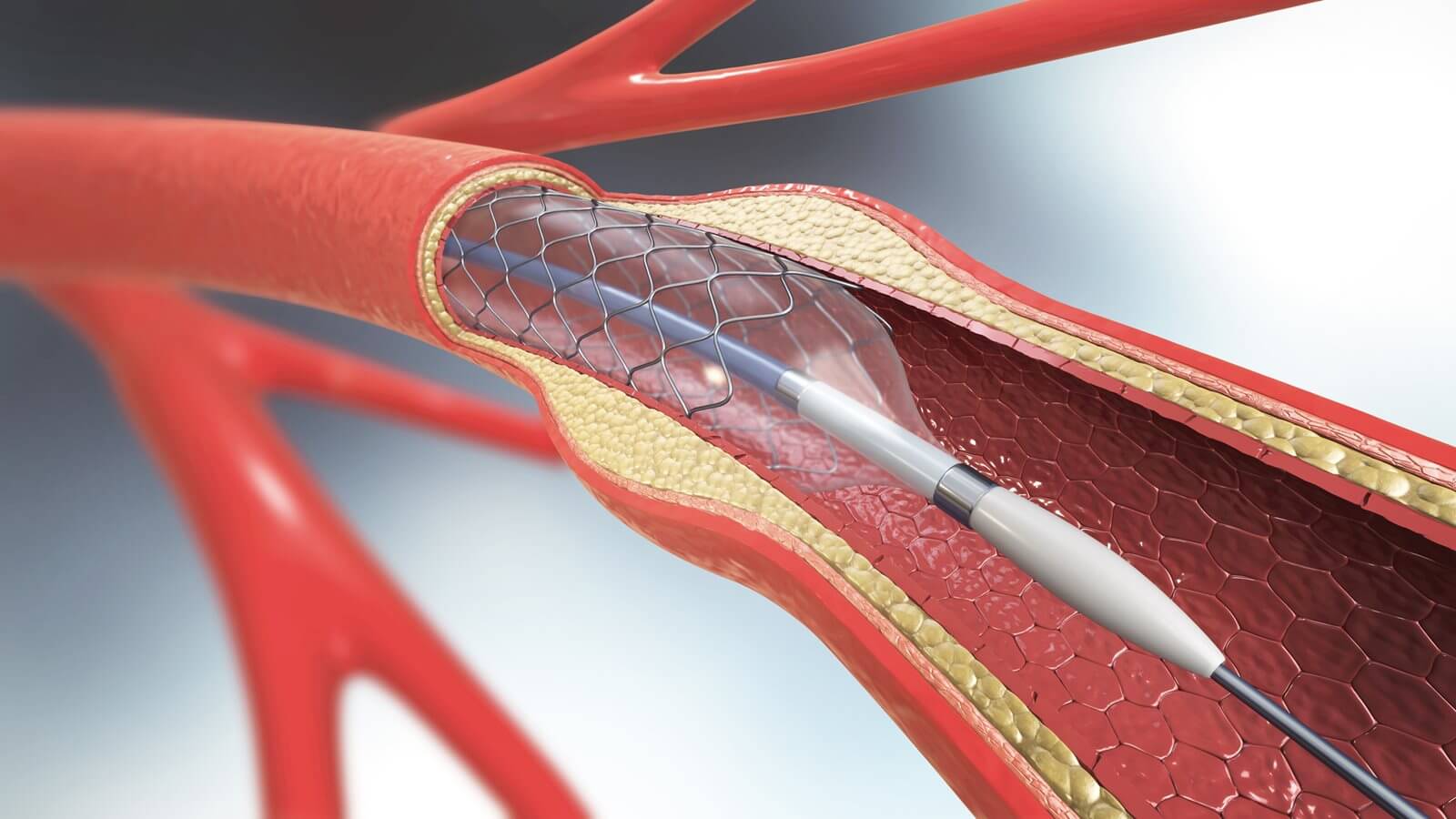
Stenting of the heart is a modern highly effective method of treatment that allows you to eliminate the narrowing of the coronary vessels and restore normal blood supply to the heart. The main reason for this narrowing is the deposition of cholesterol plaques on the walls of blood vessels. When these plaques become too large, the lumen of the vessel is noticeably narrowed. This leads to a deterioration of the blood supply to the heart, an ischemic disease occurs, a heart attack may develop, and a threat to life may arise. Cardiovascular diseases are in the first place in the world among the causes of death and disability. According to the American Heart Association, approximately
40% of the population aged 50-64 years have cholesterol plaques in the coronary arteries of the heart. Stenting allows you to solve the problem of significant blockage of blood vessels by installing a coronary stent.
This is a modern minimally invasive technique that allows you to restore normal blood flow in the coronary arteries without open heart surgery. During surgery, a stent is inserted into an artery that has been excessively narrowed. This is a special medical device that helps to expand the lumen of the vessel. The structure is a mesh cylindrical frame, which is inserted into the lumen of the coronary artery in a folded form. It is installed in the area of the pathologically altered area, and then straightens. Due to this, a normal lumen appears again between the walls of the artery, and thus the blood supply to the heart is restored.
In what cases do they put a stent
Coronary stenting is recommended if a narrowing of the artery by 60% or more is diagnosed. Before the procedure, a coronary angiography and other necessary diagnostics may be prescribed to clarify the condition. Then the cardiac surgeon analyzes the medical information and determines whether an operation is needed, and which technique will be optimal.
This procedure is a low-traumatic alternative to coronary bypass surgery. It is better tolerated and gives fewer complications, but it is up to the doctor to determine whether bypass surgery or stenting of the heart will be optimal.
Coronary stents can be divided into two main groups:
The second type of stents has a noticeable advantage, because it is covered with a special preparation, due to this, the risk of thrombosis and restenosis (repeated narrowing of the lumen) is significantly reduced.
A stent installation operation can be prescribed when:
Stenting after a heart attack, carried out in the first hours, is the most effective method to completely eliminate circulatory disorders. And the earlier it is carried out, the less the heart muscle will suffer.
Despite the fact that the operation is classified as minimally invasive, it is still a surgical intervention. Today, non-surgical methods of treating atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries are increasingly used, and one of the most promising is the use of cellular technologies.
Studies show that the use of mesenchymal stem cells allows you to start regeneration processes. Their introduction allows you to restore the structure of the walls of blood vessels, reduces the level of lipids in the blood, reduces the level of inflammation in the body.
Mesenchymal cells can be obtained from the bone marrow, adipose tissue or blood of the patient. Then they are injected back into the bloodstream and have a positive effect on the condition of the arteries.
If the narrowing of the vessel has already reached the degree when surgery is necessary, cellular regeneration therapy can be used additionally. This will improve the overall condition of the arteries and reduce the likelihood of a
recurrence of such a problem. In cases where the patient has atherosclerosis of the first or second stage, cell therapy will avoid surgery.
To learn more about the possibilities of cell therapy and get information about the best regenerative medicine clinics, contact the coordinator of the Medical Center.
The operation lasts 1-2 hours. All manipulations are carried out under the control
of X-ray equipment.
Short-term pain may occur during the procedure. This usually happens when the balloon is inflated and the blood flow through the artery stops for a while. After the balloon is blown off, the unpleasant sensations pass. If there is shortness of breath and pain after stenting, you need to contact a cardiologist as soon as possible.
After stenting of the heart vessels, rehabilitation takes place fairly quickly. Within 1-3 days, the patient is usually discharged home.
Rehabilitation after stent installation includes:
This minimally invasive operation is easily tolerated and gives a long-lasting effect, so the feedback from patients who have undergone the procedure is good. In most cases, the stent regularly serves throughout life. In rare cases, complications may occur, such as restenosis, then repeated stenting of the heart vessels may be required. If there are no complications, then the life expectancy after stenting is comparable to the life expectancy of people without
pathologies of the heart vessels.
The additional use of cell therapy will further reduce the likelihood of complications and improve the quality of life.
The cost of heart stenting depends on several parameters:
The medical coordinator of Medtour will help you calculate the approximate price.
It is possible to install a stent in the coronary arteries today in many cardiological centers in different countries of the world. Medtour will help you choose a clinic and a doctor.
You can undergo cell therapy with Dr. Andrey O. Kovalchuk, a surgeon, candidate of medical sciences. Andrey Olegovich is engaged in the treatment of various diseases with stem cells, including diseases of the cardiovascular system. There is a possibility of online consultations with Dr. Kovalchuk!
On average, stenting takes about one hour. But in some cases it may take several hours, depending on the specifics of the situation.
This surgical procedure is well tolerated and does not require a long recovery. During the first day, the patient remains in the clinic for observation. On the second or third day, if the state of health is normal, the person is discharged.
In the first 7-10 days after the stent is installed, there are strict restrictions on physical activity. Thermal procedures should also be avoided. Some restrictions on physical activity persist for 1.5 months. After stenting, it is recommended to adjust the diet and exclude some dishes and products from the menu. It is advisable to give up excessively fatty, spicy, smoked foods, reduce the amount of sweets, and minimize alcohol consumption. An
increase in the proportion of vegetables and fruits, whole grains, and products that contain unsaturated fatty acids in the diet has a positive effect on the condition of blood vessels.
Stem cell treatment reduces the concentration of fats in the blood, it helps to stop
the growth of cholesterol plaques. In addition, mesenchymal stem cells activate
cell regeneration and reduce the level of inflammation in the body. In other words,
the use of cell therapy in the early stages of atherosclerosis makes it possible to
stop the processes of vascular blockage by cholesterol plaques, and thus avoid the
need for stenting. At later stages, the use of stem cells in combination with the
installation of a stent will increase the effectiveness of treatment.
Please rate the work of MedTour
