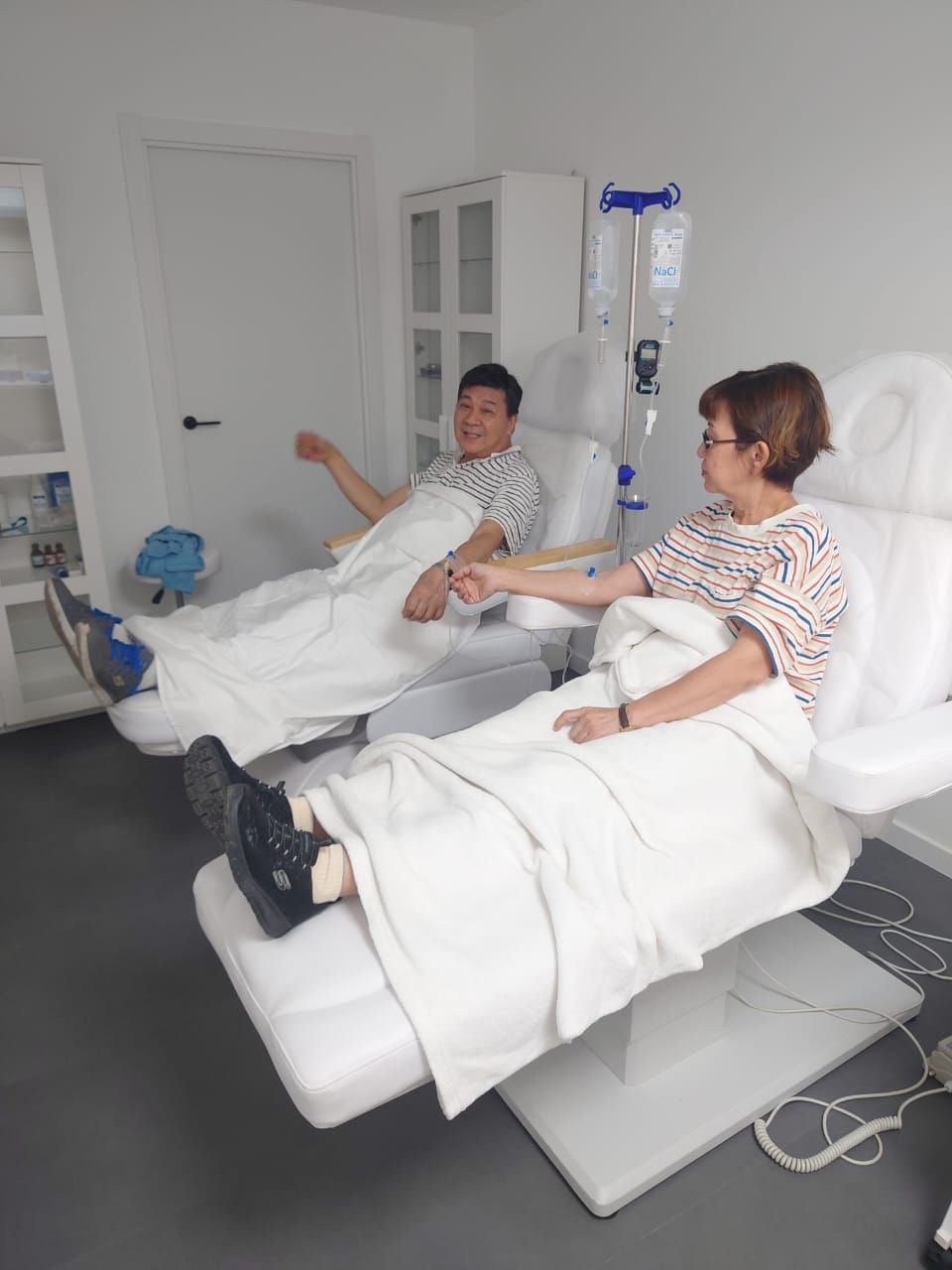
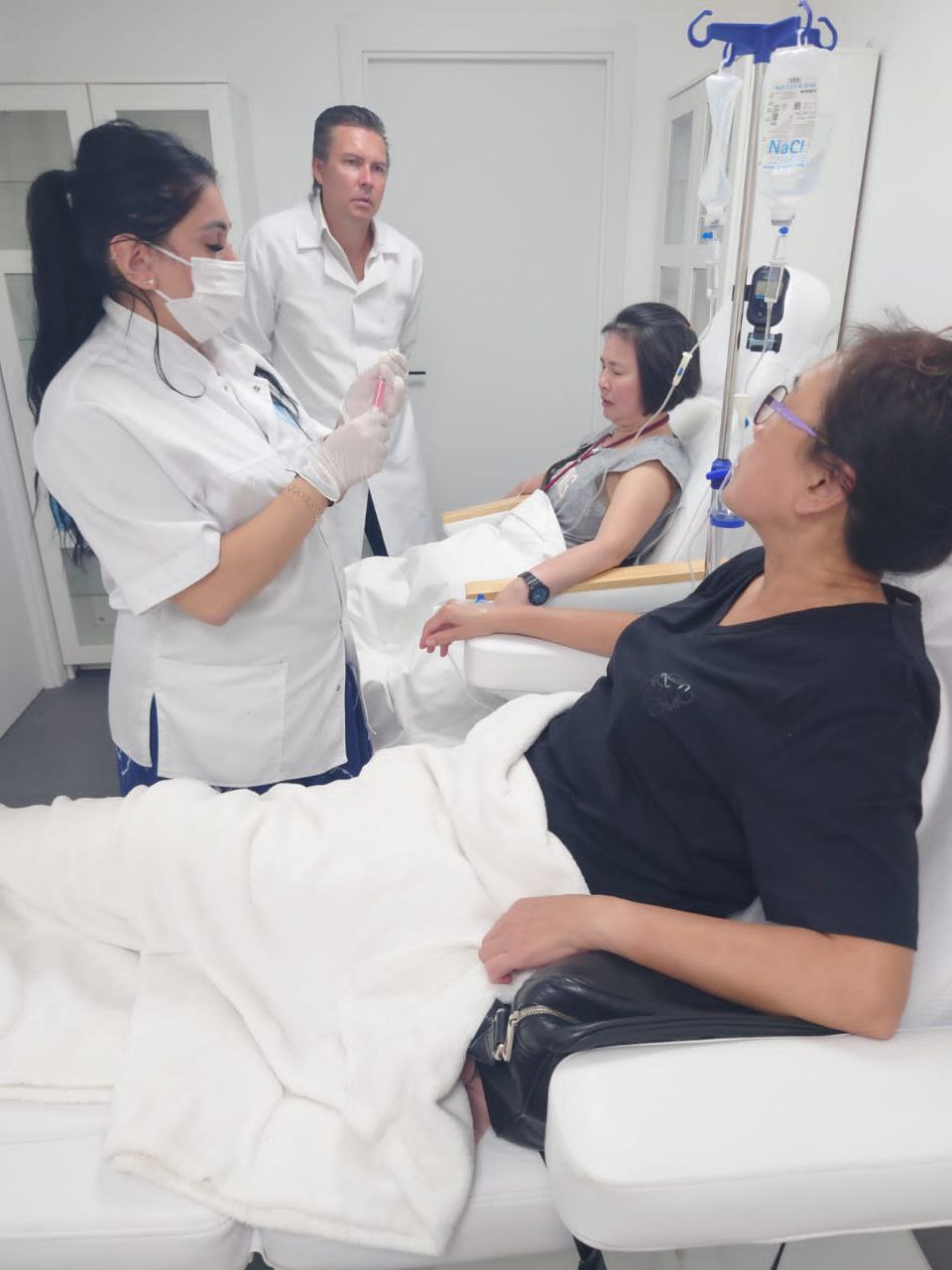
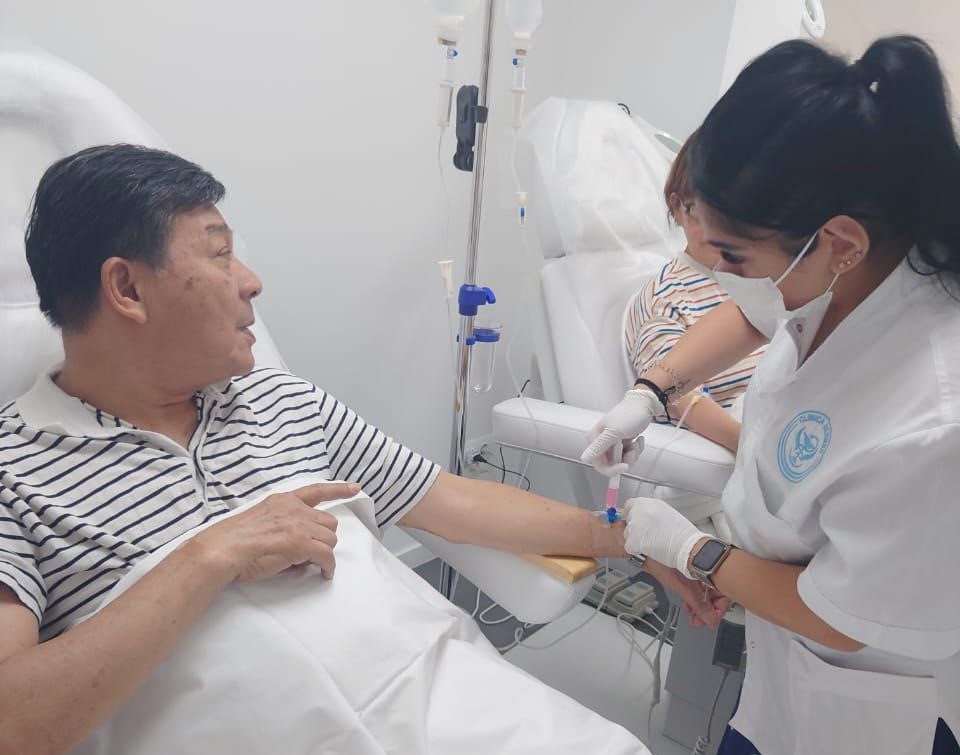
Cell therapy at the SERMED clinic (Barcelona, Spain)
The company BioPro Stem Technology & AntiAging Biotech Clinic, operating on the basis of the SERMED clinic, offers patients a unique opportunity for innovative treatment with cell therapy methods.
Anti-aging therapy with mesenchymal stem cells
One of the main goals of regenerative therapy is the fight against aging. With age, irreversible changes occur in the human body: loss of bone and muscle mass, wearout of vital systems and organs. Scientists have found that it is stem cells, as the builder of all body tissues, that make it possible to restore losses that have occurred as a result of aging at the molecular level. Once in the body, stem cells stimulate the regeneration process. Using chemical signals, damaged organs and tissues attract stem cells to repair the damage.
Penetrating into the tissues of the body, stem cells divide, reproducing young offspring. The main difference between young cells and old cells is the length of telomeres – the ends of chromosomes. The older the cell, the shorter the telomere. Stem cells have the longest telomeres. By dividing, the stem cell produces offspring from the same cells with long telomeres. They replace worn out and damaged body cells.
Anti-aging therapy involves using the body’s own stem cells. Intravenous infusions help reduce age-related changes such as memory loss, arthritis, arthrosis, kidney failure, cardiovascular diseases, hormonal deficiency and many others.
The aging process occurs at different rates in different people, so it is customary to distinguish between actual and biological age. Taking this fact into account, the clinic staff developed various options for using cells (3 specialized packages). This approach makes it possible to make treatment more personalized and select the most optimal protocol for each patient. A detailed description and cost of packages can be found above in the “Procedures and their cost” section.
Therapy with autologous mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) from blood or adipose tissue
Mesenchymal stem cells are a population of multipotent cells that can differentiate (transform) into derivatives of connective tissue, that is, cells of the heart, blood vessels, connective tissue framework of the lungs, bones, cartilage, muscles and other tissues.
How are autologous MSCs generated?
The term “autologous” means that the cells are obtained from the patient himself. To do this, the specialist takes 10 ml of venous blood or 5-7 cm3 of adipose tissue from the patient. Within 10-14 days, stem cells are isolated from the obtained samples and grown to the required quantity.
For what diseases are autologous MSCs used?
- all autoimmune diseases (type 1 diabetes, ALS, multiple sclerosis, autoimmune thyroiditis, autoimmune hepatitis, autoimmune glomerulonephritis, lupus erythematosus, psoriasis, etc.);
- cirrhosis;
- type 2 diabetes;
- degenerative joint diseases, etc.
T-cell therapy (based on CAR-T cell technology)
This is an innovative and personalized immunotherapy. The method is based on changes in antigens on the surface of autologous T-lymphocytes (cells of the immune system). Simply put, this method involves using the patient’s own immune system to fight tumor cells.
How are cells obtained for treatment?
The doctor takes 7-10 ml of venous blood from the patient. The leukocyte fraction is isolated along the density gradient. Within 3-4 days, T-lymphocytes are processed in the laboratory and the antigenic characteristics of the immune cells change.
How is T-cell therapy performed?
The resulting cells are injected into a vein. Before the injection, the specialist takes blood again to prepare the next dose of the cellular drug. The interval between injections is 7 days. Basic course – 3 injections.
For what diseases is T-cell therapy used?
- oncological diseases (leukemia, some forms of solid tumors);
- stopping tumor spread (metastasis);
- reduction in the size of a malignant neoplasm;
- prevention of metastasis.
Individual iPS cell lines
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are produced by genetic reprogramming, or “forcing” the introduction of genes into normal somatic (differentiated) human cells. That is, these cells revert back to an embryonic-like pluripotent state and can become any cell in the body, such as beta cells to treat diabetes, hepatocytes to treat cirrhosis, or neurons to treat neurological disorders.
iPS cells were first created by Professor Shinya Yamanaka’s group at Kyoto University, for which he and his team were awarded the Nobel Prize. Today this innovative treatment method is available at the SERMED clinic in Spain.
How are iPS cells produced?
The doctor takes 10 ml of venous blood from the patient. Within a week, a fraction of target cells is isolated and transduced with embryonic genes. Within a few months, a stable personal line of patient embryonic stem cells is obtained.
What diseases are iPS cells used for?
- global, at the level of the whole organism, inhibition of the aging process;
- prevention of diseases associated with old age (Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, muscular dystrophy, heart failure, atherosclerosis, hormonal deficiency, etc.);
- treatment of existing diseases of a non-infectious nature.
Artificial bone marrow
A 3D structure biocompatible with cells is created, into which the patient’s stem cells with different differentiation characteristics are populated. During the co-culture process, many cellular niches arise that are as similar as possible to natural bone marrow. These cellular conglomerates release into the liquid a huge amount of biofactors, which are as close in composition as possible to serum proteins. This serum is as close as possible to human plasma.
How are cells obtained to create artificial bone marrow?
The specialist takes 10 ml of blood from the patient. Mesenchymal stem cells are isolated in the laboratory. When growing a primary culture, the cells differentiate into three types of cells – mesenchymal, hematopoietic, and endothelial. After a month, the cells fill a 3D matrix in which they will grow. The production of biofactors is carried out continuously. It is also possible to periodically obtain a cell suspension.
What diseases are treated by creating artificial bone marrow?
- oncology (various types of leukemia);
- hematology (hematopoietic insufficiency);
- urology (compensation for the consequences of dialysis);
- toxicology (replacement therapy or plasmapheresis).
Universal stem cell therapy (Clean Line)
Gene editing of the HLA-2 complex of mesenchymal stem cells is carried out. The antigenic characteristics of histocompatibility of allogeneic (donor) stem cells change. The resulting stem cell becomes non-personalized. It loses its “individuality” and becomes invisible to the immune system of any person. Such a cell can be transplanted into any person, without the risk of rejection and destruction by the immune system.