Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
Deep brain stimulation is a revolutionary treatment for neurological and psychiatric disorders. Its essence lies in the implantation of a device that sends electrical signals to the areas of the brain responsible for motor activity. Electrodes are placed deep in the brain and connected to a neurostimulator. They send electrical impulses that regulate brain activity.
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) has been shown to significantly reduce the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease (tremor, rigidity, sluggishness, imbalance), as well as the severity of dystonia and essential tremor. Successful treatment allows patients to reduce the number of medications they take and improve their quality of life.
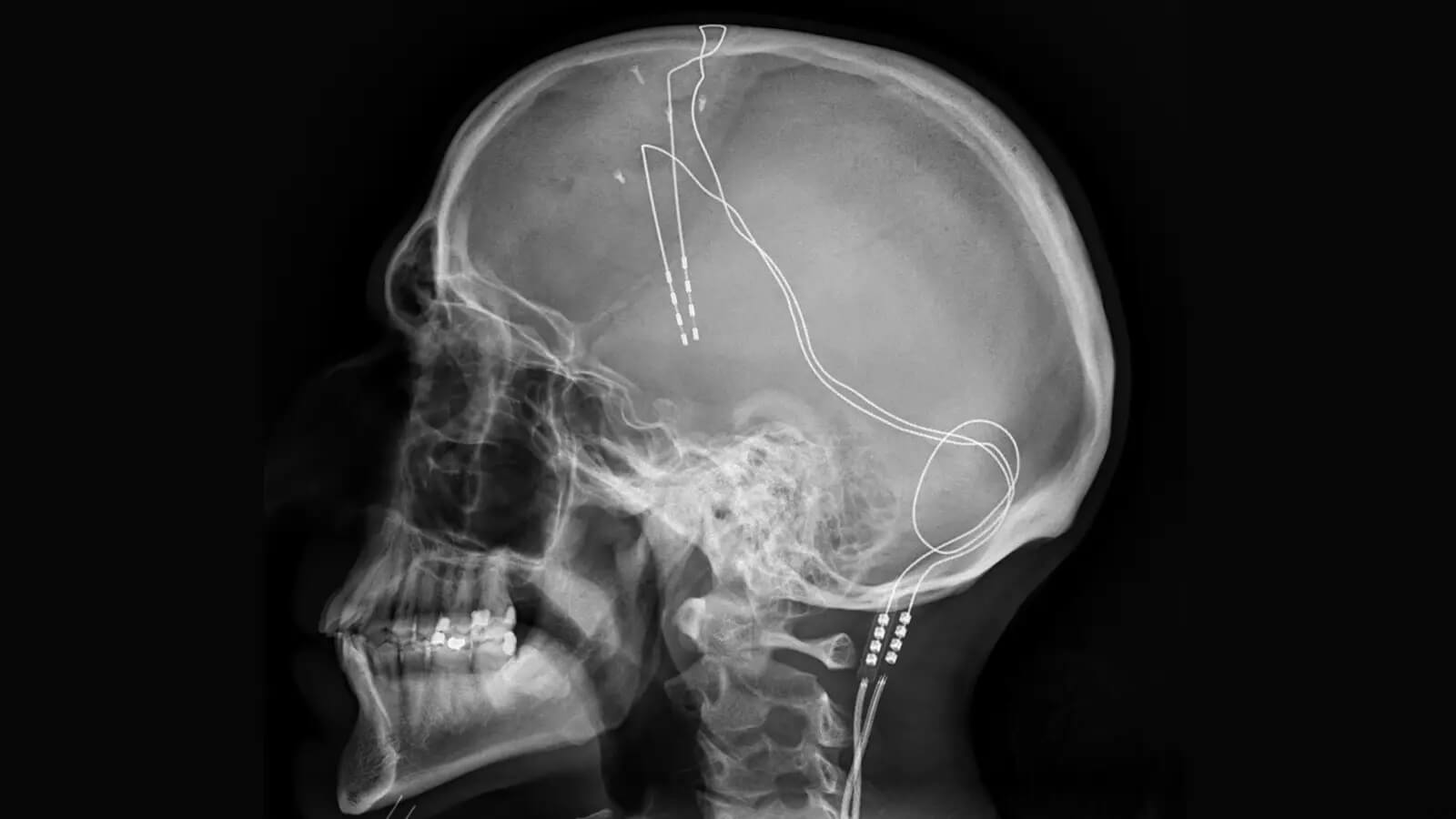
Deep brain stimulation involves the implantation of electrodes in a specific area of the brain (depending on the patient’s symptoms). The electrodes can be placed both in the right and in the left hemisphere. They are implanted through small holes in the skull. At the same time, a small neurostimulator is placed in the chest area. It is connected to the electrodes by thin wires that run under the skin. When turned on, the neurostimulator sends out electrical impulses that block erroneous nerve signals in the brain that cause tremors, stiffness, increased muscle tone, and other symptoms.
The DBS system consists of three parts implanted inside the body:
The patient can turn the DBS system on and off using the handheld controller. The neurostimulator is set up by the doctor using a wireless device (programmer). Settings can be changed as the patient’s condition changes over time.
Unlike other treatments such as pallidotomy (placement of a probe in the globus pallidus) and thalamotomy (stereotactic destruction of certain areas of the thalamus), the DBS procedure does not damage brain tissue. Thus, if more effective treatments are developed in the future, the neurostimulator can be removed without harm to the patient.
A doctor may recommend a DBS procedure if the patient has one or more of the following conditions:
Deep brain stimulation is not suitable for patients with severe untreated depression, severe dementia, or symptoms that are not typical of Parkinson’s disease.
Deep brain stimulation can reduce symptoms caused by conditions such as:
The effectiveness of DBS in the treatment of a number of other diseases and conditions, such as Alzheimer’s disease, Tourette’s syndrome, anorexia nervosa, restless legs syndrome, etc., is currently being studied. But so far, the therapy is experimental.
Before the appointment of the operation, the patient’s condition is assessed by a group of specialists, including a neurologist, a neuropsychologist and a neurosurgeon. They test thinking and memory, as well as the general health of the patient. In addition, doctors evaluate his movements (walking, getting up from a chair, tapping his fingers) with and without medication. In patients with parkinsonism, symptoms will be classified according to the Uniform Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS).
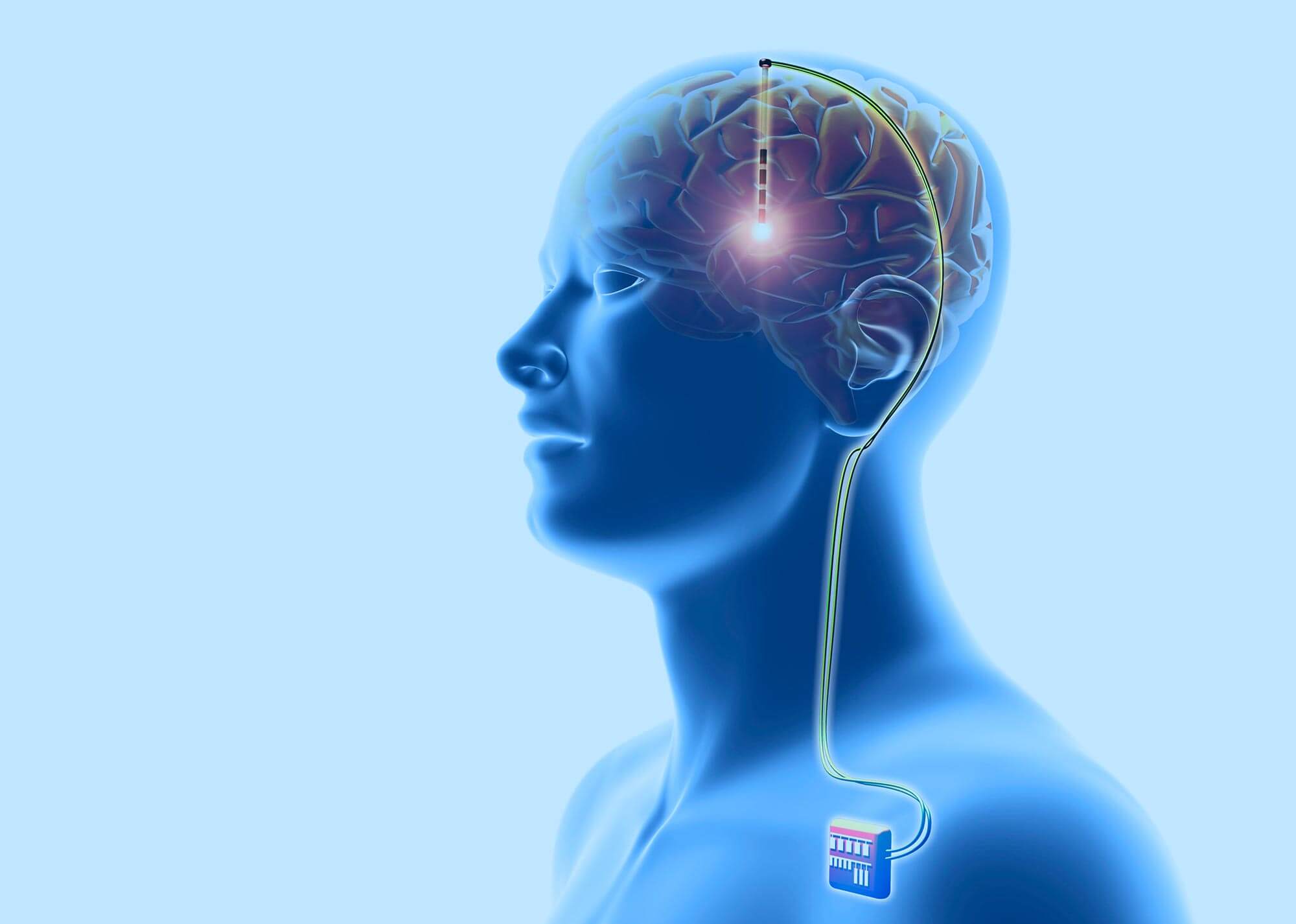
During the first operation, surgeons implant electrodes in specific areas of the brain. For the correct positioning of the devices, MRI mapping of the brain is preliminarily performed. During surgery, the patient will remain awake and answer questions from the neurologist and other members of the medical team. This is to ensure that clinicians are confident in the correct placement of the electrodes. In some clinics, a speech therapist is present at the operation. One possible side effect of DBS is speech impairment. The speech pathologist will ensure that this does not happen. The operation takes about an hour. Most patients are discharged the very next day.
During the second operation, surgeons place a neurostimulator under the skin in the chest area near the collarbone. It will be connected to the electrodes implanted in the first stage. The surgery is performed under general anesthesia. It is usually well tolerated by patients and performed on an outpatient basis.
At the final stage of the procedure, the neurologist will set up the neurostimulator using a wireless programmer. This process is individual for each patient. Most people who have undergone deep brain stimulation surgery experience a significant improvement within a few days after the procedure.
Sign up for a procedure deep Brain Stimulation
Fill in your details and our medical coordinator will contact you for a consultation
Pay for the ProcedurePossible side effects of the DBS procedure include:
Some side effects may be due to improper setting of the neurostimulator. They will pass after the doctor selects the optimal mode of operation.
How should a patient use the DBS system?
People with Parkinson’s disease or dystonia are advised to leave the neurostimulator on at all times. The exception is the passage of diagnostic or medical procedures. Patients with essential tremor who have electrodes placed in the ventrolateral nucleus of the thalamus can turn the neurostimulator on or off depending on when they need to control the tremor. Many people turn it on in the morning after waking up and turn it off at night.
How effective is deep brain stimulation treatment?
Much depends on the individual characteristics of the patient. But in most cases, the DBS procedure can significantly reduce the severity of symptoms and improve the quality of life of a person. It helps to cope with such manifestations of the disease as tremor, involuntary movements (dyskinesia), stiffness or slowness of movement.
How long does the effect last after the DBS procedure?
For most people, a positive result of treatment lasts for many years. A study published in “JAMA Neurology” in 2011 found that Parkinson’s patients still saw significant improvement 10 years after the DBS procedure.
How is recovery after deep brain stimulation surgery?
Patients are usually discharged after 1-2 days. Most of them can return to normal activities after 2 weeks. The stitches are removed one week after the operation. At the same stage, the neurostimulator is adjusted. Patients are advised to avoid physical activity during the first month after surgery. Finding the optimal settings for the neurostimulator and adjusting the dosage of the medications taken can take from several weeks to a couple of months.
Can I do an MRI with the DBS neurostimulator?
If medically indicated, an MRI can be done. In some cases, doctors advise performing the procedure on a device with a lower magnetic field (1.5 T). As a rule, the neurostimulator is turned off during an MRI, and turned on at the end of the procedure.
Can home appliances interfere with the DBS neurostimulator?
Most household appliances such as telephones, microwave ovens, and computers do not interfere with the operation of the neurostimulator. Older generation DBS systems were prone to accidentally turning off or on due to nearby magnets, including small fridge magnets. However, this does not happen with modern neurostimulators. However, patients are advised to carry the programmer with them to ensure that the neurostimulator is turned on.
What does it take to have deep brain stimulation surgery?
Fill out a special online form or call any of the phone numbers listed on the site. In the near future, medical coordinators of MedTour will contact you and provide all the necessary information. They will help you choose the doctor and clinic that best suits your disease and individual needs. MedTour services are free. The patient pays the cost of the operation at the cash desk of the selected clinic.
We are always happy to help you. Write your question by filling out the form. We are happy to answer all your questions.
Please rate the work of MedTour
