Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
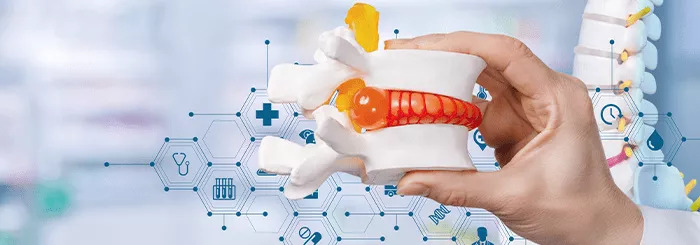
Disc degeneration is a common disease that progresses with age. Stem cell therapy is a new treatment option for patients with persistent severe back pain that can be considered as an effective alternative to chronic medication and surgery.
The essence of the method is the introduction of stem cells into the area of the affected intervertebral disc. There is clinical evidence that the therapy helps relieve pain, halt the progression of the degenerative process, and maintain normal spinal function.
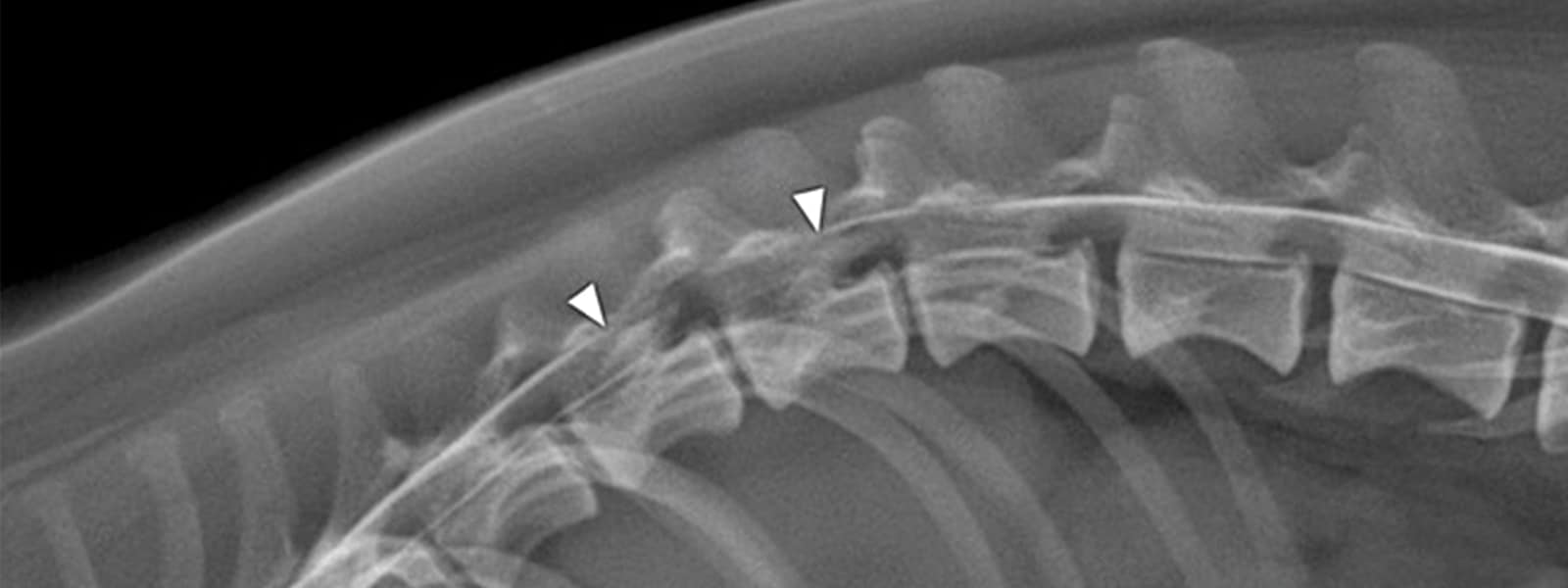
The intervertebral discs are structures located between the vertebrae, the main function of which is to cushion the spine from the load caused by gravity and physical activity. The discs absorb the shock wave and protect the bones of the spine from wear and stress.
Each intervertebral disc consists of a tough outer layer (annulus fibrosus) and a soft center (nucleus pulposus). When a person is born, his intervertebral discs are 80% water. With age, they gradually lose fluid, fibrous tissue becomes more fragile.
Gradual wear of the disc and injury can lead to rupture of its outer layer. The internal jelly-like mass bulges out and presses on nearby nerves, causing severe pain. In addition, there are proteins in the nucleus pulposus, which, when they enter the surrounding tissues, cause swelling and inflammation. Symptoms of the disease depend on the location of the hernia. These can be: pain, numbness, tingling, weakness in the back, arms and legs.
Intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) affects more than 70% of adults under the age of 50 and more than 90% of people over 50 years of age. Although sometimes the disease is asymptomatic, discogenic pain accounts for up to 80% of all patient complaints. With the accelerated aging of the population, the incidence of TIR continues to skyrocket.
Currently, for the treatment of IDD, most patients use conservative therapy for pain relief, as well as various drugs such as steroids and local anesthetics. When these methods fail, surgery is the last hope for patients to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life. However, it is associated with a number of significant drawbacks. Surgery does not help to restore the height of the intervertebral disc, does not stop the progression of the degenerative process, and also has a high risk of various intraoperative and postoperative complications.
The development of the field of regenerative medicine has made it possible to find a solution to this problem. Stem cell therapy is a minimally invasive alternative to surgery. The risk of side effects and complications of cell therapy is very low. Most patients can return to normal activities just a few days after the stem cell injection.
Compared to standard methods, regenerative stem cell therapy has a number of undoubted advantages:
The effectiveness of stem cell therapy for a herniated disc has been proven in clinical trials. One of them was conducted by American scientists. The study involved 33 people with chronic back pain caused by herniated discs in the lumbar region.
The results showed that cell therapy resulted in significant changes in the NPRS pain score at 3, 36, 48, 60 and 72 months after treatment. On average, patients reported a 60% improvement in their condition 3 years after stem cell injection. 20 patients underwent MRI after treatment. In 85% of them, a decrease in disc herniation by an average of 23% was noted.
For regenerative therapy, own and donor cells can be used. To obtain their own stem cells, health workers take blood or a small amount of adipose tissue from the patient using lipoaspiration. After taking the biomaterial, the stem cells are scaled and cultured. They then multiply over several weeks. As a rule, preparation of cells takes from 14 to 21 days.
When using a donor biomaterial, a biotechnologist, as prescribed by a doctor, selects a suitable sample in a cryobank. All donor cells undergo rigorous safety controls. In the case of using donor cells, the patient does not need a waiting period. Treatment can be carried out immediately after the diagnostic examination and drug preparation.
Regenerative therapy includes the following steps:
Final consultation with a doctor. The patient will receive a medical report on the treatment performed and medical recommendations.
What are stem cells?
These are undifferentiated cells that are present throughout the human body and can transform into a specialized cell type depending on where they are found. When they enter the area of the affected intervertebral disc, stem cells turn into connective tissue, bone and cartilage, replacing damaged cells.
Is cell therapy effective in the treatment of herniated discs?
Regenerative therapy is an effective minimally invasive treatment for patients suffering from a herniated disc and contraindicated for surgery. The introduction of stem cells allows the body to normalize the content of fluid, trace elements and amino acids in the nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus, which makes it possible to restore the shock-absorbing ability of the intervertebral disc, as well as stop chronic pain syndrome.
Are there any side effects of stem cell treatment for a herniated disc?
Cell therapy is a relatively safe procedure. When using your own stem cells, the rejection reaction is reduced to zero. Patients may experience redness, pain, and slight swelling at the injection site, which resolve on their own after a few days.
These are undifferentiated cells that are present throughout the human body and can transform into a specialized cell type depending on where they are found. When they enter the area of the affected intervertebral disc, stem cells turn into connective tissue, bone and cartilage, replacing damaged cells.
Regenerative therapy is an effective minimally invasive treatment for patients suffering from a herniated disc and contraindicated for surgery. The introduction of stem cells allows the body to normalize the content of fluid, trace elements and amino acids in the nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus, which makes it possible to restore the shock-absorbing ability of the intervertebral disc, as well as stop chronic pain syndrome.
Cell therapy is a relatively safe procedure. When using your own stem cells, the rejection reaction is reduced to zero. Patients may experience redness, pain, and slight swelling at the injection site, which resolve on their own after a few days.
Please rate the work of MedTour
