Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
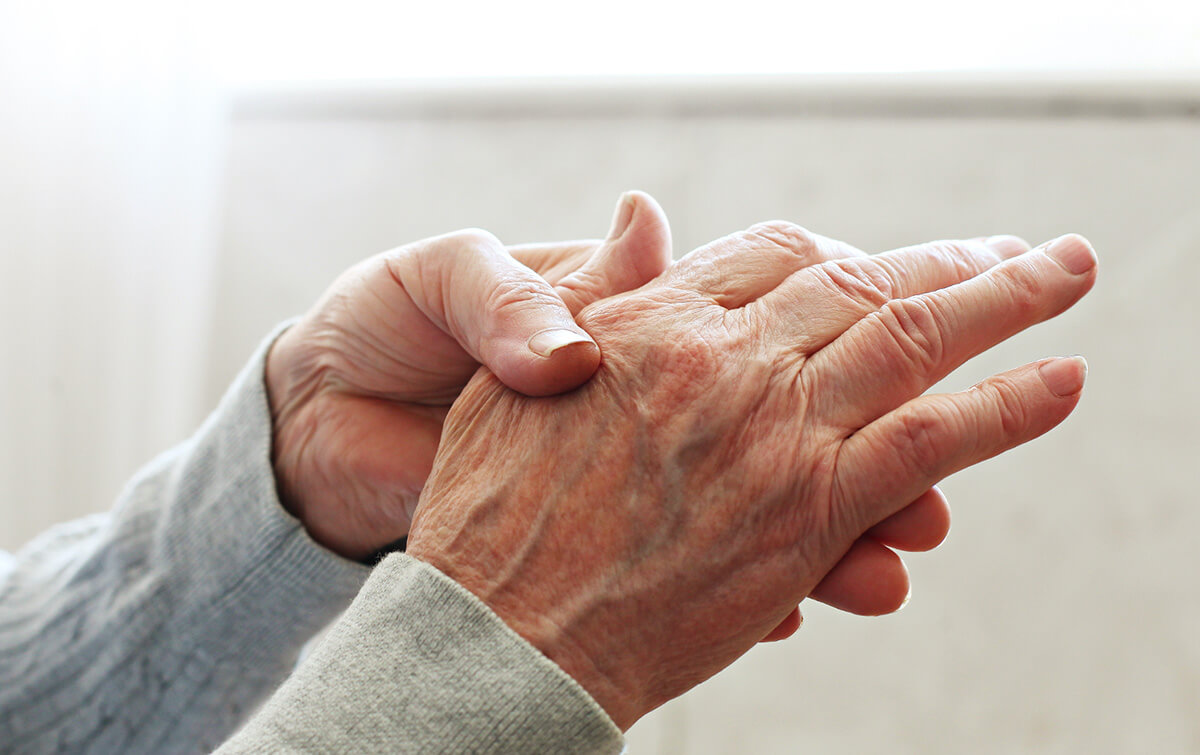

Systemic scleroderma, or systemic sclerosis (SS) is an autoimmune pathology that affects the skin, musculoskeletal system, various internal organs and blood vessels. Pathology is accompanied by excessive growth of connective tissue and disruption of the internal organs. According to statistics, about 1 per 10,000 people in the world suffer from this disease. Most often, systemic scleroderma is diagnosed in adults. It usually occurs between the ages of 20 and 50, and is 4 times more common in women than in men. For children, this disease is rare, but juvenile scleroderma also occurs.
This systemic disease can significantly impair the quality of life, lead to the development of quite serious complications and even death. Systemic scleroderma is difficult to treat, especially when it comes to the severe course of the disease. However, the introduction of new techniques, such as cell therapy, opens up new possibilities for effectively combating this pathology.
Systemic scleroderma is a disease in which diffuse fibrosis develops. With SS, collagen and other connective tissue proteins are too actively produced, fibrous tissue begins to grow excessively in various tissues and organs of the body. This leads to the fact that the area affected by fibrosis becomes less elastic, the ability of the affected area to fully perform its functions is impaired. Most often, there is damage to the skin, blood vessels, joints, as well as the heart, lungs, kidneys, and digestive organs.
Doctors distinguish two main forms of the disease:
In turn, systemic scleroderma is divided into:
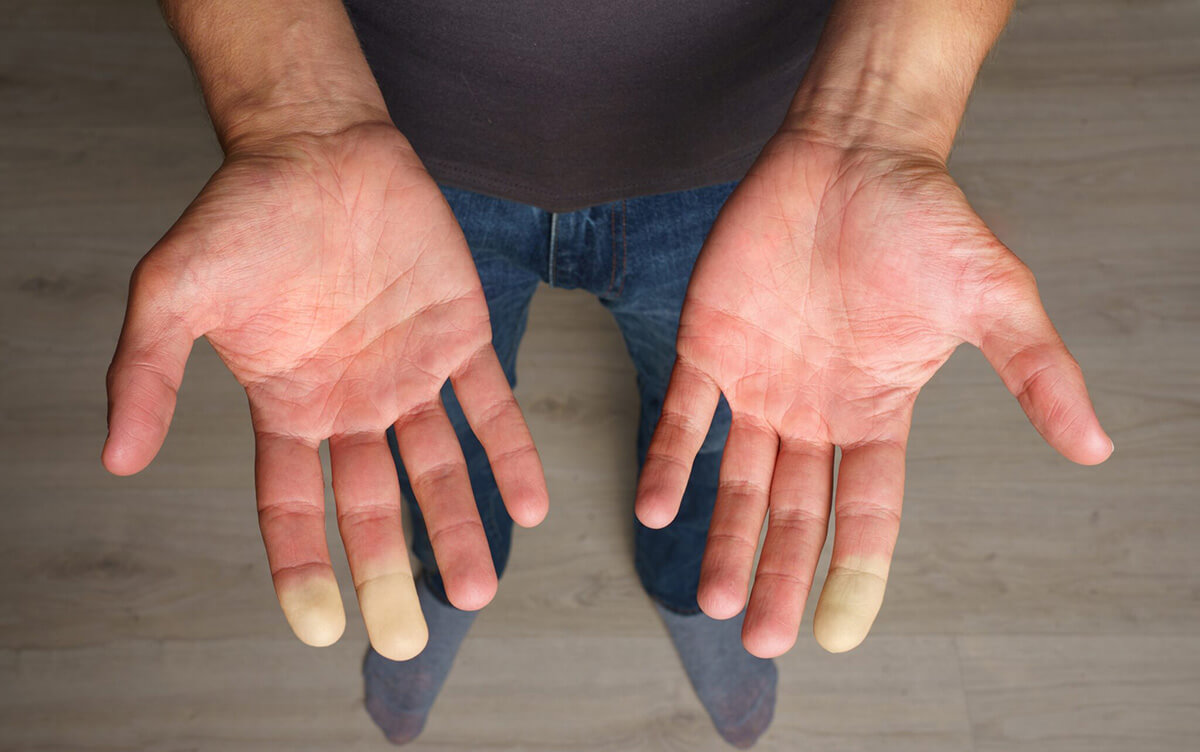

Symptoms of systemic scleroderma are quite diverse. Most often, the first sign is the appearance of Raynaud’s syndrome. Raynaud’s syndrome is a condition when the fingers become very cold, turn pale or red, become numb in response to cold or stress. Also a characteristic symptom of SS is severe swelling of the fingers. Later, symptoms of the digestive system, musculoskeletal system, etc. may be connected.
Characteristic signs of systemic scleroderma:
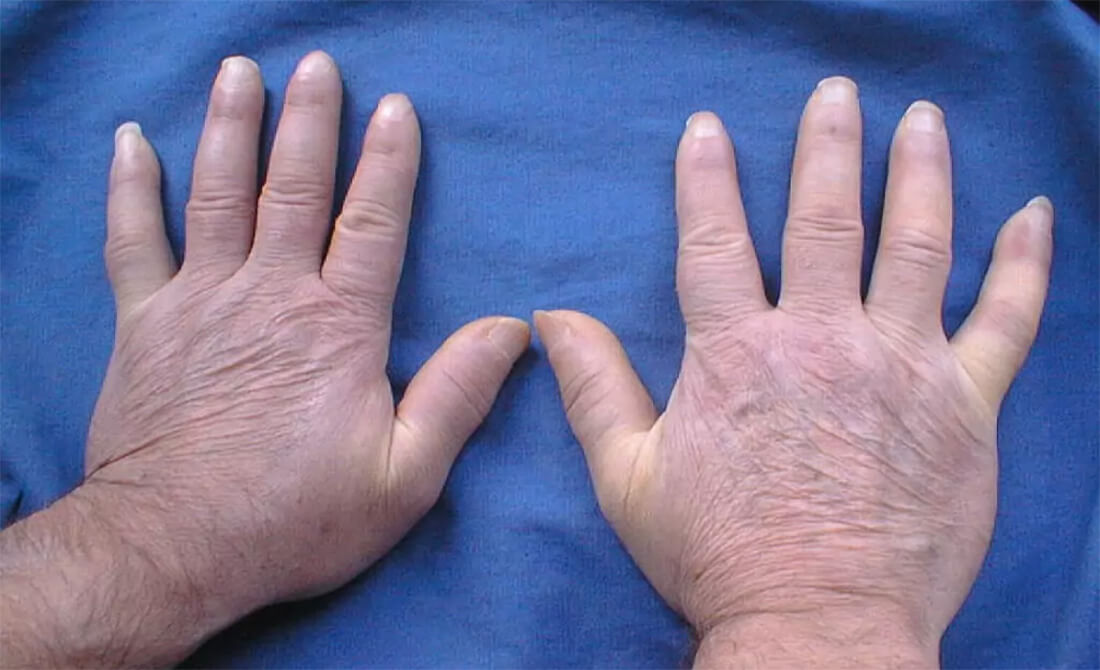
Doctors distinguish three stages of the disease:
To diagnose SS, a doctor does an examination and determines if characteristic symptoms are present. Such research methods as radiography of the joints, CT scan, ultrasound of internal organs, capillarography, echocardiography of the heart, etc. can be prescribed. When scleroderma is suspected, tests usually include:
At the moment, the disease is considered incurable. Therapy is aimed at removing the symptoms and slowing down the process of tissue fibrosis.
Traditional treatment of systemic scleroderma includes the use of drug therapy:
In addition, doctors recommend nutrition correction, moderate exercise. In some cases, surgery may be used to remove specific lesions.
The prognosis for patients with systemic scleroderma differs markedly depending on the form and stage of the pathology. With a diffuse type of the disease, after 3-5 years, violations in the work of internal organs are added to the skin manifestations. With limited systemic sclerosis, the prognosis is more favorable, this form progresses more slowly. It is difficult to treat the disease in the later stages. However, with the right treatment strategy and the use of the latest therapies, the disease can be controlled.
One of the most promising methods of treating the disease is cell therapy. Studies have shown that transplantation of one’s own stem cells works better than the use of immunosuppressive drugs, improves survival and quality of life of the patient. Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that can develop into various cell types, including skin, muscle, and nerve cells. Due to this, they have unique regenerative properties, can improve the functioning of the immune system, and reduce the degree of inflammation in the body.
The use of cell therapy allows to influence such manifestations of the disease as thickening of the skin, joint stiffness and damage to internal organs. In addition, the technique has a longer lasting effect compared to traditional treatment. Cell therapy can significantly improve the condition of patients with a poor prognosis. Research on the method is still ongoing, the nuances of the technology are being worked out, but today some clinics have included this treatment method among those used.
Stem cells for the procedure are taken from the patient’s bone marrow or adipose tissue. After sampling, they are grown to the desired concentration. then administered intravenously to the patient. The doctor calculates the dosage individually for each client.
This disease is treated by rheumatologists. You can go to high-profile foreign clinics where there are doctors who specialize in systemic scleroderma. In such clinics, a personalized approach to patients is used and the most productive methods of treatment are used. And today you have the opportunity to get into clinics that use cell therapy and demonstrate good results.
The MedTour platform will help you find the best option for therapy. Our medical coordinators will select a clinic and doctor for you according to your needs. Send us a request via the contact form to find out more about the treatment options for systemic scleroderma in the best clinics.
You have a unique opportunity to consult with the best specialists in cell therapy.
You can sign up for an online consultation with Andriy Kovalchuk. Dr. Andriy Kovalchuk is a Candidate of Medical Sciences, surgeon, biotechnologist, director of the stem cell bank of TOV “Genome”.
You also have the opportunity to consult with Ivan Badyin, PhD, rehabilitation specialist, physiotherapist, cell therapy specialist with 20 years of experience.
With these doctors, you can discuss the possibilities of using stem cell therapy, find out the prospects and get personalized forecasts for such treatment. Contact us to book an online consultation!
Why does systemic scleroderma develop?
The exact causes of SS have not been elucidated. The disease is characterized by an autoimmune inflammatory reaction, when the immune system begins to attack its own cells in the body. A certain role in the development of the disease is played by heredity. It is also believed that contact with aggressive chemicals, some infections, and stress can act as provoking factors.
Which joints are affected in systemic scleroderma?
Most often, the hands, joints of the fingers are affected, and the elbow and knee joints can also be involved in the process. There may be sensations of joint stiffness, discomfort and pain, possibly limiting their mobility. Against the background of systemic scleroderma, arthritis can develop.
What organ is most often affected in systemic scleroderma?
The main organ that affects this disease is the skin, it suffers from any kind of disease. In addition, quite often the kidneys, lungs, and heart are involved in the pathological process. However, if you contact good specialists and choose the right treatment, then most likely you will be able to take control of the condition: stop or slow down the fibrous replacement of tissues in the body.
Please rate the work of MedTour
