Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
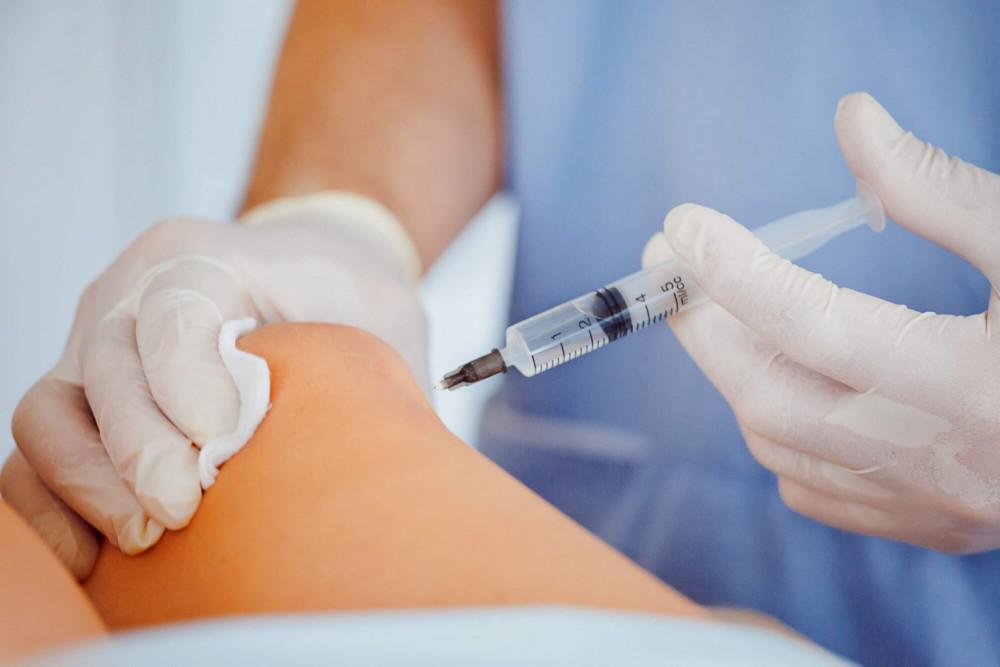
The joints have a complex anatomical structure. Every day they are exposed to heavy loads during the performance of normal tasks, work and sports. Over time, the articular cartilage covering the heads of the bones loses moisture, becomes more fragile and wears out. This process is often accompanied by severe pain, inflammation, and stiffness.
To alleviate the symptoms at the first stage, conservative drug therapy is prescribed. If it does not help, the only way to restore the quality of life is an arthroplasty (complete or partial replacement of the joint). However, not all patients are candidates for surgery. Some of them are afraid of possible side effects, others have contraindications to surgery. With the development of regenerative medicine, a new method of treatment has appeared, which, in certain cases, can be considered as an alternative to endoprosthetics. It’s about stem cell therapy.
When it comes to large joints such as the knee and hip, symptomatic osteoarthritis is the most common cause requiring hip replacement surgery. More than 80% of hip and 96% of knee surgeries are associated with symptomatic degenerative changes in the articular surfaces caused by osteoarthritis.
Other possible reasons for arthroplasty are:
However, they are much less common.
Osteoarthritis is a progressive, painful condition that can affect both young and old people. The symptomatic form occurs in 10% of men and 18% of women over 45 years of age.
The current treatment strategy for osteoarthritis focuses on reducing pain and controlling symptoms rather than addressing the cause of the disease. Pharmaceutical therapies are limited and are associated with the risk of side effects.
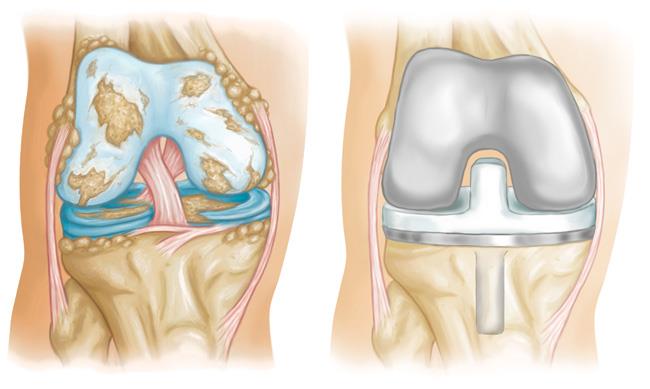
Total joint replacement is currently the standard choice for symptomatic osteoarthritis that is not controlled with conservative therapy. The number of such operations carried out in the world is steadily growing. However, this treatment method is not without its drawbacks. Approximately 20% of patients will continue to experience pain and other symptoms after a hip or knee replacement. There is also a risk of serious complications such as thromboembolism and infection requiring readmission, which occur in 2% of patients.
Stem cell therapy is a method that can help delay or avoid arthroplasty when treated in the early stages of osteoarthritis, when cartilage has not yet been completely destroyed. Mesenchymal stem cells are used to restore joints. The essence of the technique is to introduce them into the damaged area.
More than 40 years have passed since mesenchymal stem cells were described by Dr. Alexander Friedenstein. Initially, they were found in the bone marrow. Later, they were also found in peripheral and umbilical blood, skeletal muscle, heart, and adipose tissue.
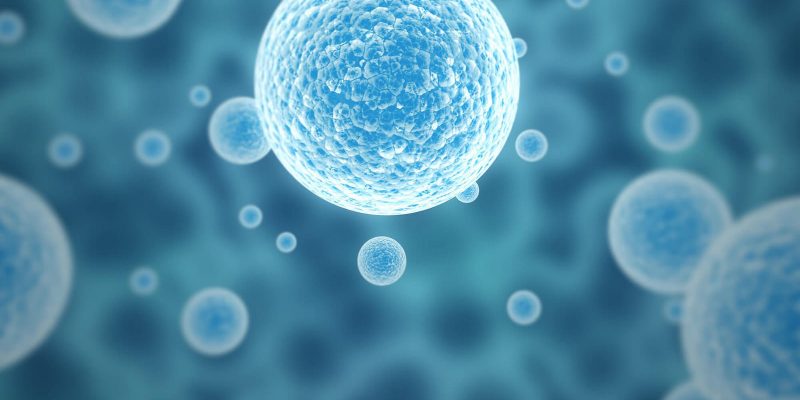
MSCs are capable of differentiating (transforming) into bone cells (osteoblasts), cartilage (chondrocytes), and adipose tissue (adipocytes). Their presence throughout the body suggested that they play a role in tissue repair and regeneration.
Currently, scientists are considering two mechanisms of action of mesenchymal stem cells:
In general, treatment contributes to the restoration of damaged articular structures. In the first few days after administration, the inflammatory process decreases until it is completely eliminated, which is accompanied by pain relief. In addition, cell therapy contributes to:
In recent years, numerous clinical trials have been conducted that have proven the effectiveness of the treatment of joint diseases with stem cells. As an example, there are several studies conducted at the Prodromos Stem Cell Institute in Maryland.
The therapeutic process includes the following steps:
The price of joint cell therapy varies depending on the severity of the disease, the type of stem cells used, and the duration of the treatment. In general, we can say that the cost of therapy is comparable to the price of arthroplasty, but at the same time, stem cell therapy is not associated with operational risks and does not require long-term recovery.
Where do stem cells come from?
Stem cells can be autologous (own) or donated. In the treatment of own cells, they are obtained from the blood, bone marrow or adipose tissue of the patient. Then they are cultivated and propagated in the laboratory. The preparation time is from 14 to 21 days. When using donor cells, there is no need to wait. They are picked up in a cryobank and administered to the patient immediately after the diagnostic examination and drug preparation.
What orthopedic diseases can be treated with stem cells?
Cell therapy can be effective in treating:
What is the success rate of stem cell treatment?
As with many other treatments, the success of stem cell therapy depends on many factors. These include: the severity of the disease, the age of the patient, the presence of concomitant diseases, the list of medications taken. Therefore, you can only find out if you are a candidate for cell therapy after an examination by a doctor.
How quickly can the result of joint stem cell treatment be assessed?
The time it takes to see the result of cell therapy varies from patient to patient. Some people report feeling better as soon as a couple of days after the procedure. However, on average, a significant improvement in symptoms and improvement in physical activity occurs after 4-6 weeks.
Stem cells can be autologous (own) or donated. In the treatment of own cells, they are obtained from the blood, bone marrow or adipose tissue of the patient. Then they are cultivated and propagated in the laboratory. The preparation time is from 14 to 21 days. When using donor cells, there is no need to wait. They are picked up in a cryobank and administered to the patient immediately after the diagnostic examination and drug preparation.
Cell therapy can be effective in treating:
As with many other treatments, the success of stem cell therapy depends on many factors. These include: the severity of the disease, the age of the patient, the presence of concomitant diseases, the list of medications taken. Therefore, you can only find out if you are a candidate for cell therapy after an examination by a doctor.
The time it takes to see the result of cell therapy varies from patient to patient. Some people report feeling better as soon as a couple of days after the procedure. However, on average, a significant improvement in symptoms and improvement in physical activity occurs after 4-6 weeks.
Please rate the work of MedTour
