Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA

Prostate carcinoma (or prostate cancer) is a malignant neoplasm that arises from the epithelium of an organ. This cancer is common among middle-aged and elderly men. In a number of countries, prostate cancer is the third most common cancer after lung and stomach cancer.
The prostate gland is a small organ located under the bladder. Consists of glandular and muscle tissue.
The function of the prostate is to produce secretions. It is part of the semen, which supports the production of male germ cells. The prostate is involved in the formation of a man’s sexual desire (libido).
Oncologists all over the world have not come to a single conclusion that to a greater extent affects the onset of the disease. Scientists identify the main risk factors that every man must take into account:
At the initial stage of development, prostate cancer is asymptomatic. When a malignant tumor grows, the patient develops complaints that are characteristic of other diseases. Most often noted:
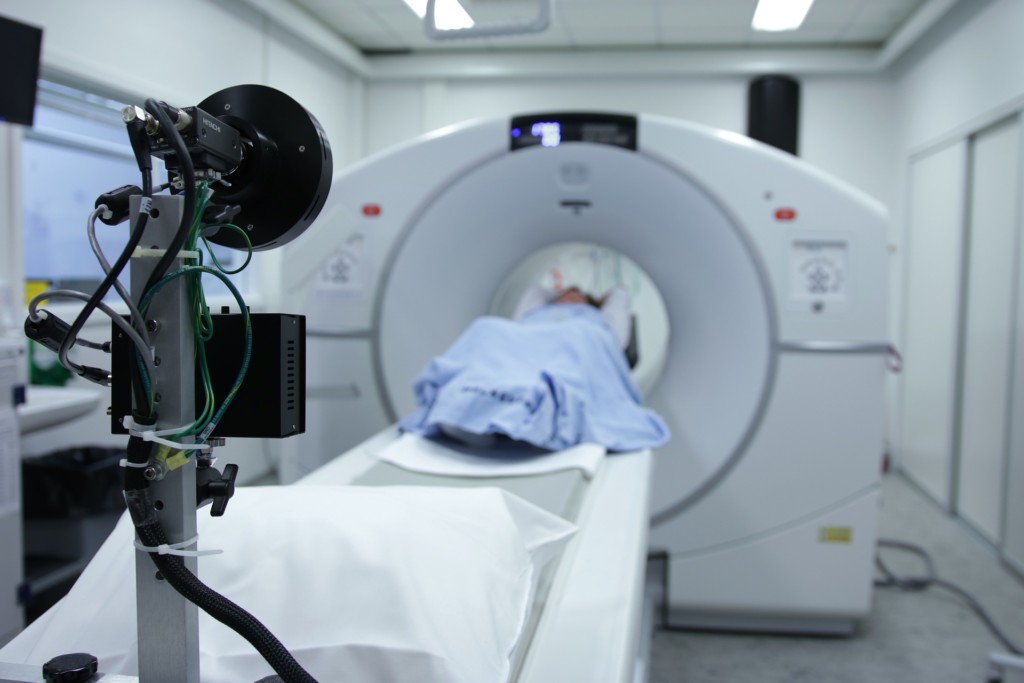
Oncologists most often use the following methods for diagnosing carcinoma:
Examples of the cost of a PET-CT examination in the best countries for the treatment of prostate carcinoma:
The life expectancy of patients with prostate cancer depends on many factors: a person’s health status, stage of cancer, the effectiveness of treatment, and many other components of the survival prognosis.
In the early stages of the disease, a complete cure is possible, in some patients relapses occur and the cancer metastasizes. Then the survival prognosis worsens.
With a timely visit to a doctor, life expectancy is 15 years or more.
According to international medical protocols, the methods of surgery and therapy depend on the stage of the cancer.
Doctors classify these stages of the disease and their corresponding treatment options:
TURP (transurethral resection of the prostate)
TURP is indicated at the earliest stage of the disease. During the operation, the doctor removes the tumor with a special needle through the urethra.
This operation does not require external incisions, so the patient recovers quickly.
Minimally invasive surgery
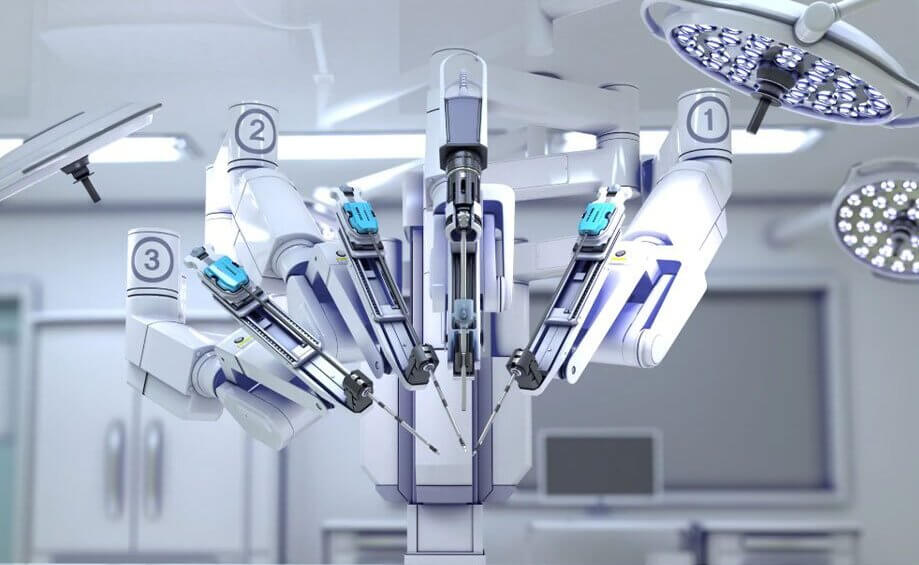
Options for minimally invasive surgery for prostate cancer:
Open radical prostatectomy
Thanks to such a surgical intervention, the doctor can remove the tumor at the 4th stage, when minimally invasive surgery is not indicated. Open radical prostatectomy is performed through 1 incision up to 12 cm in size on the anterior abdominal wall. It is possible to remove the tumor through an incision up to 4 cm between the scrotum and the anus.
With a widespread neoplasm, the doctor removes the patient’s regional (nearby) lymph nodes and seminal vesicles.
NanoKnife operation
A device with which doctors carry out a radical removal of a tumor. A malignant neoplasm is destroyed using an electric current. The advantage of the NanoKnife is that it allows you to target tumors in hard-to-reach areas.
The procedure takes about 45 minutes. After using the NanoKnife, the patient can go home the next day.
Orchiectomy (removal of the testicles)
The surgeon performs this operation to reduce the patient’s testosterone production. This helps prevent recurrence of cancer. Doctors perform orchiectomy in addition to prostatectomy in men with hormone-dependent cancers.
Cryosurgery (cryoablation)
Cryoablation is the process of freezing a malignant tumor using liquid nitrogen. As a result of exposure to low temperatures, neoplasm is suppressed.
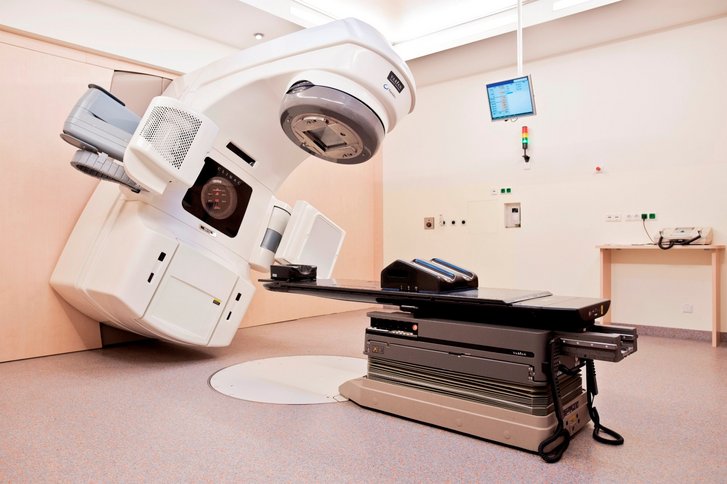
Radiotherapy
In the course of radiotherapy, the tumor is destroyed by exposure to radiation beams. For this, oncologists use linear accelerators. Such devices irradiate the neoplasm with an accuracy of 0.5 mm, therefore, they do not harm the adjacent healthy tissues.
Brachytherapy
The procedure is an internal contact radiation therapy. The doctor places special radioactive granules in the tumor. Their size is almost 3 times smaller than a normal grain of rice. Thus, there is a point irradiation of the prostate tumor.
Brachytherapy does not affect the surrounding healthy tissue. Radioactive granules gradually lose their charge. They remain in the prostate and are absolutely safe for the body.
HIFU therapy (ultrasound ablation)
HIFU is a technique by which a tumor is destroyed by exposure to high-intensity ultrasonic waves. The procedure takes place without damaging the skin and tissues adjacent to the prostate.
Chemotherapy
As prescribed by the doctor, the patient takes intravenous or in tablet form chemotherapy drugs that destroy the tumor and metastases. As an independent method of treatment, it is not often used, usually in combination with surgical intervention.
Hormone therapy
Through the use of this therapy, it is possible to stop the production of the hormone testosterone, which promotes the growth of malignant tumors. Such treatment is indicated for hormone-dependent prostate cancer, which metastases to other organs and does not respond to other treatment methods.
A malignant tumor can develop for more than 10 years and does not affect the general condition of the body. Therefore, for older patients with an initial stage of carcinoma, doctors may recommend a waiting tactic. This means that the oncologist does not prescribe any treatment. In this case, the patient needs to undergo regular diagnostics. If during the examinations an active oncological process is revealed, the doctor selects the appropriate therapy and surgical treatment.
The final cost of prostate carcinoma treatment is influenced by a number of factors:
Examples of the cost of surgery for prostate cancer treatment
Prostatectomy in foreign clinics:
Surgical intervention with the Da Vinci robot:
The total cost is influenced by the amount of examinations and the treatment prescribed by the doctor. It depends on the stage of the cancer, the drugs used, and the method of surgery.
If the patient chooses treatment abroad, then the costs increase due to the organization of the flight and accommodation for the accompanying persons. Leave a request on the MedTour website and our coordinating doctors will select the best option for you.
Prostate cancer prognosis: how many people live with prostate cancer
In 90% of cases, patients with the first stage of prostate cancer live for 5 years. At the first stage, prostate carcinoma responds well to treatment, but in rare cases, the patient turns to the oncologist precisely at the beginning of the development of the disease. Most often, prostate cancer is diagnosed during histological examination of tissues after resection of prostate adenoma, as well as using the PSA test.
The survival rate for the 2nd stage of prostate cancer is 80-90%. The prognosis depends on the degree of cell malignancy and the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment.
At the 3rd stage, prostate cancer spreads beyond its limits: into the bladder neck and seminal vesicles. In this case, there are no metastases in the lymph nodes. The 10-year survival rate in the third stage is 45-60% if modern treatment methods are used.
Poor prognosis for the 4th stage of prostate cancer. On average, life expectancy in the fourth stage of prostate cancer within 5 years was noted in 15% of patients.
With continuous palliative care, the prognosis for survival is no more than 7 years.
Please rate the work of MedTour
