Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
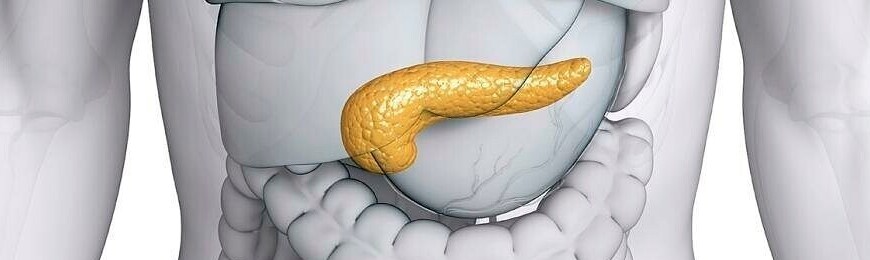
Pancreatic cancer is a malignant tumor that arises from the epithelium of the glandular tissue of an organ. The pancreas is conventionally divided into 3 parts, in each of which abnormal cells can develop. In 60% of cases, the tumor is localized in the head of the gland, in the body of the organ – 10%, in the tail – up to 10%. In 20% of cases, cancer affects the entire organ at once. The disease is difficult to diagnose by standard methods, therefore, patients often turn to an oncologist at a later stage.
Scientists still do not know the exact cause of pancreatic cancer (carcinoma). According to the US National Cancer Institute, the disease can develop from two types of cells in the pancreas: exocrine and neuroendocrine cells. The exocrine type is more common and is usually found late. Neuroendocrine neoplasms (islet cell tumors) are less common but have a better prognosis.
Oncologists have identified factors that increase the risk of developing pancreatic cancer:
How quickly pancreatic cancer develops depends on the type of cancer and the reason why it has arisen – it can be a primary or secondary tumor.
The key symptoms of pancreatic cancer are abdominal pain and jaundice. These signs are detected in 90% of patients with cancer. Often with jaundice, there is light stool and dark urine.
Pancreatic cancer symptoms:
In the early stages, pancreatic cancer does not have severe symptoms. Primary symptoms are similar to those of other, less dangerous diseases. Therefore, in the presence of several symptoms, it is necessary to undergo a diagnosis and obtain a conclusion from narrowly specialized specialists – a gastroenterologist and an oncologist.
What symptoms of pancreatic cancer may occur in a patient will depend on the location of the tumor and the degree of damage to adjacent structures.
Pancreatic cancer is the most difficult cancer to diagnose. This is due to the fact that most of the organ is covered by the stomach, bile ducts and intestines. This complicates the process of studying the state of the organ during standard examination procedures for ultrasound or CT.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the oncologist uses the results of modern types of diagnostics:
In some cases, patients develop cysts that can develop into malignant tumors. Only experienced specialists know how to distinguish a cyst from pancreatic cancer, because it can be a benign neoplasm. Specialized diagnostics plays an important role, since it is impossible to distinguish pancreatic cancer from pancreatitis under the conditions of standard examinations in a regular clinic.
Examples of the cost of PET-CT for pancreatic cancer in clinics around the world:
The overall prognosis for survival in pancreatic cancer is influenced by the individual parameters of the patient: age, general condition, stage of cancer and concomitant diseases. Also, the group to which the cancer belongs determines the effectiveness of a particular treatment method. The main groups of doctors include: operable, borderline and inoperable pancreatic cancer.
General projections for five-year survival, depending on the stage and group of the disease:
Stage 4 thyroid cancer with an inoperable group of the disease has a poor prognosis. The five-year survival rate does not exceed 1%.
According to the averaged statistical data, after complete removal of the pancreas followed by the use of replacement therapy, about 10% of patients live at the 5-year mark without relapse. How long you can live with pancreatic cancer without surgery will depend on the rate of progression of the disease and the occurrence of complications.
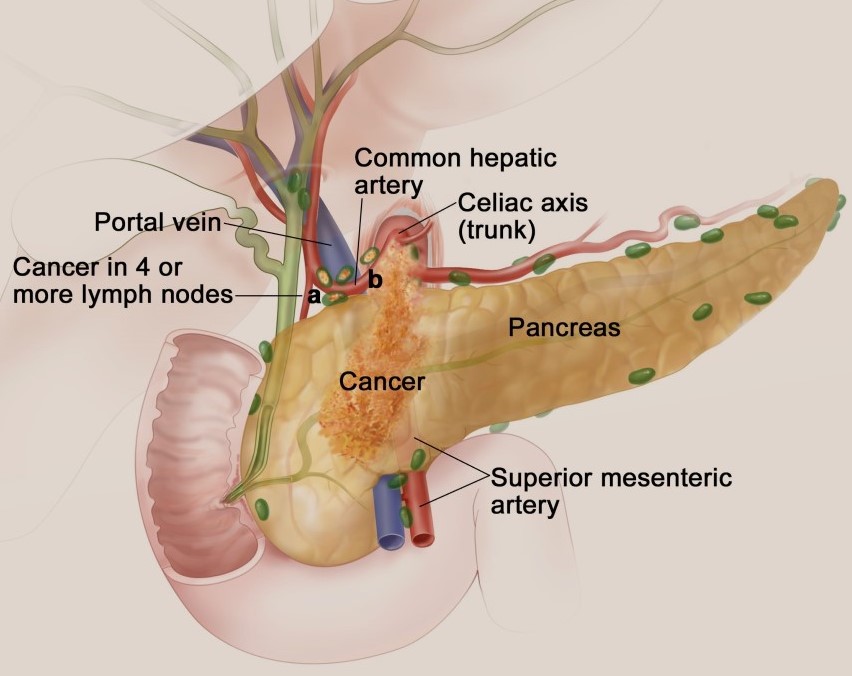
The earliest stage of cancer is 0 (carcinoma in situ). The disease then progresses to stage 4 pancreatic cancer.
How to stage pancreatic cancer according to clinical presentation:
In addition to the stages of cancer, the way the cancer spreads plays an important role in diagnosis and treatment. The tumor can spread in the following ways:
An effective treatment method that increases the survival rate for pancreatic cancer is surgery – pancreatoduodenal resection followed by chemotherapy.
Depending on the stage of the cancer, doctors can combine modern methods of oncology treatment. There are treatment standards that are most effective in oncological practice for pancreatic carcinoma.
In modern pancreatic surgery, doctors use one of three types of surgery. The choice of intervention technique will depend on the size and location of the tumor.
Operation Whipple
Pancreatoduodenectomy (or Whipple surgery) is done to treat cancer of the head of the pancreas. An experienced doctor can carry out all the manipulations through 4-5 thin incisions laparoscopically. The surgeon removes the head of the organ, part of the bile duct, gallbladder, duodenum and part of the stomach. This eliminates the further spread of cancer cells to neighboring organs.
Total pancreatectomy
The operation is indicated for removal of a tumor in pancreatic cancer.
The surgeon removes not only the organ itself, but also a segment of the small intestine, part of the stomach, bile duct, gallbladder, spleen, regional lymph nodes. This helps prevent cancer recurrence.
Distal resection
The operation is performed to remove neoplasms in cancer of the tail of the pancreas. The surgeon removes the entire gland and spleen. The resection is performed by an open or laparoscopic method. In some clinics, such operations are performed on a Da Vinci robot.
Any option of surgical treatment must be supplemented with therapy – this helps to reduce the size of the tumor before the intervention and destroy the remnants of metastases after the operation. In some cases, therapy is the only treatment that can be used to improve the patient’s quality of life.
Radiation therapy for pancreatic cancer
Radiation therapy is a treatment for tumors that uses high-energy X-rays or other types of radiation to completely kill or prevent the growth of cancer cells. External beam therapy uses a device outside the body to precisely direct the radiation to the area affected by the cancer.
Pancreatic cancer chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a treatment that uses drugs to stop the growth and division of cancer cells. Chemotherapy drugs are taken orally, injected into a vein or muscle. This is how drugs enter the bloodstream and can reach cancer cells throughout the body – this is called systemic chemotherapy. Combination chemotherapy is treatment using several types of anticancer drugs.
Targeted therapy for pancreatic cancer
Targeted therapy is a type of treatment that uses drugs to identify and target certain cancer cells. This treatment does less harm to healthy cells than chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Doctors of foreign clinics can supplement the main treatment according to the protocols with innovative methods. Thanks to the modern equipment of hospitals and access to modernized drugs, foreign oncologists are using new ways to fight pancreatic cancer at different stages.
Pancreatic cancer immunotherapy
Immunotherapy drugs activate the patient’s immune system so that the body knows what to do if pancreatic cancer has invaded healthy tissue. Similar drugs are used in some clinics in the CIS countries, but no more than 20 types of them are available. In hospitals in Europe and Turkey, doctors use more than 70 types of drugs for immunotherapy. This makes it possible to choose the most effective medicine individually for each case.
Irreversible electroporation
The NanoKnife is a device that destroys a tumor by using a pulsating electric current. This does not damage the surrounding healthy tissue, blood vessels and bile ducts. Doctors use the Nano Knife to treat pancreatic cancer in combination with chemotherapy or during surgery to completely destroy cancer cells after the tumor has been removed.
Pancreatic cancer radiosurgery
Stereotactic radiation therapy with TrueBeam and Novalis linear accelerators is a non-surgical treatment of pancreatic tumors at different stages. The radiologist enters the parameters of the tumor into the computer and sets the radiation power. Further, the system itself regulates the direction and accuracy of the exposure using high-energy X-rays. This is how the destruction of malignant cells occurs.
The cost of treatment is influenced by the volume of diagnostic procedures, the stage of pancreatic cancer, and the methods of surgery and therapy. If the patient presents at a late stage, the treatment process can be more complicated and costly than at an early stage of the disease.
The cost of innovative drugs for targeted, immuno- and chemotherapy in all foreign clinics is the same. Prices for services in medical centers and additional services may differ.
Examples of prices for medicines in foreign hospitals:
Whipple surgery cost in foreign clinics:
Please rate the work of MedTour
