Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
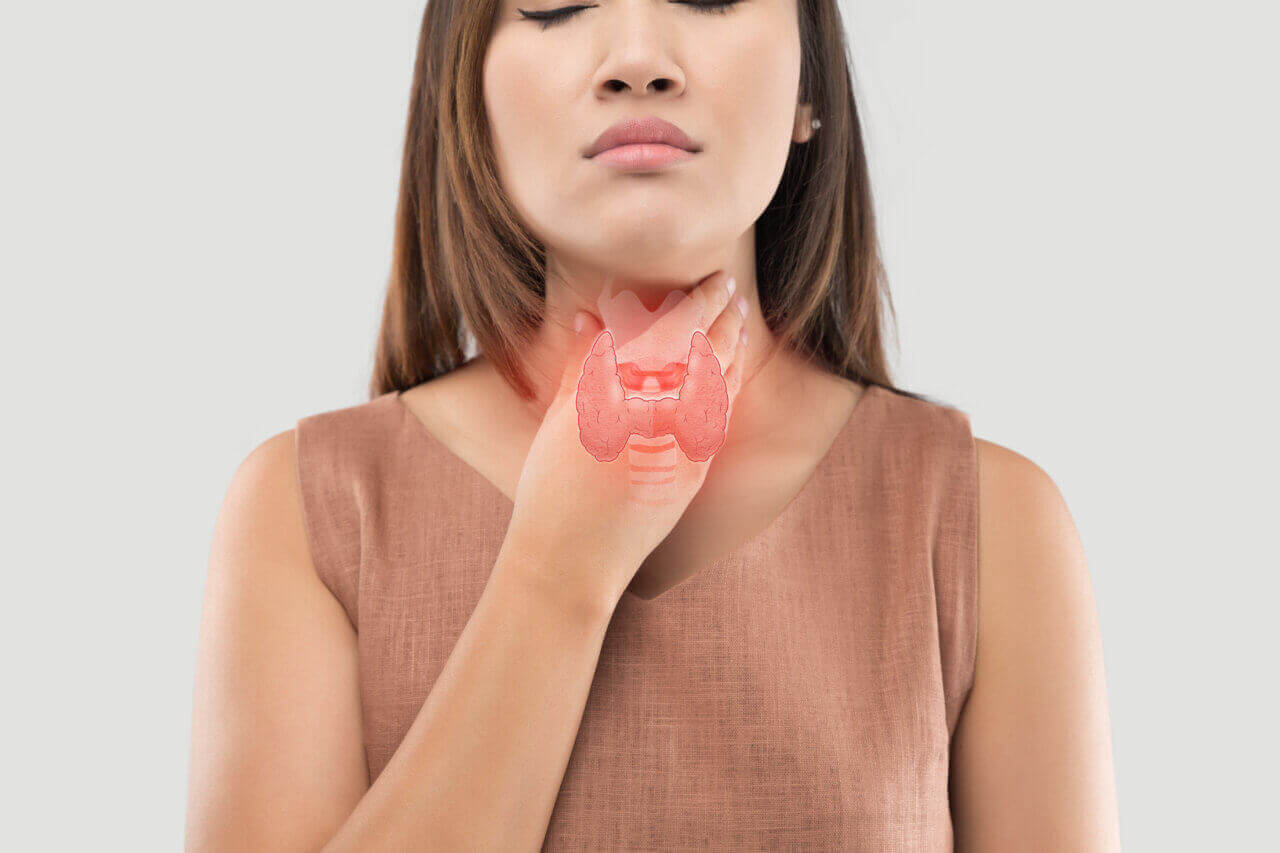
According to the World Health Organization, about 200 million people worldwide suffer from hypothyroidism. In women, this disease is diagnosed 10 times more often than in men. Without prompt medical attention, thyroid hormone deficiency can lead to serious complications such as heart failure.
This is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones. Hormonal deficiency leads to health problems such as chronic fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, thinning and hair loss.
In women, hypothyroidism can cause menstrual irregularities and difficulty conceiving, as well as an increased risk of miscarriage during pregnancy. In some cases, the disease leads to the development of myxedema, a syndrome accompanied by convulsions, a drop in blood pressure and the risk of coma. Early detection and treatment of hypothyroidism helps prevent serious complications and improve the patient’s quality of life.
There are two most common causes of the disease: inflammation of the thyroid gland and some treatments that affect the organ’s ability to produce enough hormones.
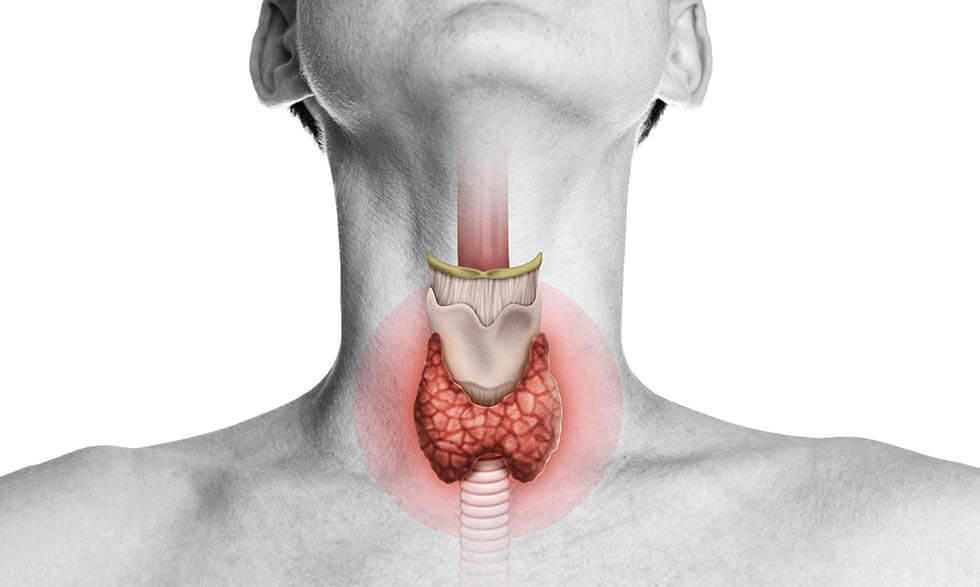
Hypofunction often occurs as a result of a previous or ongoing inflammation of the thyroid gland, as a result of which a large number of organ cells are damaged and lose their normal hormone-producing ability.
The most common type of inflammation and the most common cause of primary hypothyroidism is autoimmune thyroiditis, also known as Hashimoto’s disease. This form of inflammation is caused by a malfunction of the immune system, in which lymphocytes mistakenly attack healthy thyroid cells.
Some therapies or medications can interfere with the ability of the thyroid gland to produce hormones. Many of them are used to treat other thyroid diseases. Hypothyroidism in this case develops as a side effect of therapy.
For example, with hyperthyroidism, nodes and malignant tumors, sometimes surgical removal of part or all of the organ is required. If as a result of the operation an insufficient amount of hormone-producing tissues remains, the patient may develop hypofunction.
Another medical reason is radioactive iodine therapy, widely used for hyperthyroidism, cancer, and diffuse toxic goiter. It involves the destruction of part of the thyrocytes to prevent the growth of a goiter, the destruction of cancer cells, or to reduce the function of an organ. In people treated with radioactive iodine, hypothyroidism usually develops within one to two years.
Less common causes of low thyroid function include:
Patients may feel very tired, lethargic and weak. Some of them experience drowsiness and difficulty concentrating, as well as sleep disturbances. Symptoms of hypothyroidism also include a constant feeling of coldness, peeling skin, puffiness under the eyes, a decrease in overall activity, and a lack of desire to exercise.
Patients often note weight gain, since hypothyroidism is associated with a slowdown in metabolism. In general, the disease significantly reduces the quality of life of patients. Therefore, complex treatment of hypothyroidism is very important.
The main manifestations of the disease are: fatigue, drowsiness, insomnia, decreased energy, problems with memory and concentration, weight gain, dysfunction of the cardiovascular and nervous systems. External signs may include: pale, dry and flaky skin, thinning hair, swelling under the eyes, brittle nails.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism in men include:
Symptoms of hypothyroidism in women include:
The diagnosis of hypothyroidism is often based on a simple blood test called a thyroid panel. However, in some cases, other diagnostic methods are also used.
The study involves measuring the levels of two key hormones: T4 (thyroxine) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). For each of these, there is a “normal” range that has been calculated based on measurements from tens of thousands of people. If the level of thyroid hormones is outside the normal range, this indicates hypo- or hyperfunction of the gland.
In the typical and most common form of hypothyroidism caused by an underactive gland, T4 levels in the blood will be low and TSH levels will be high. This means that the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones. The pituitary gland recognizes and responds to this by secreting more TSH to make the gland work harder.
In more rare cases, when hypofunction is due to pituitary insufficiency, the level of both hormones, both T4 and TSH, will be low. The thyroid gland behaves “correctly” under these conditions, because it can only produce hormones in response to TSH secreted by the pituitary gland. Since in this case the pituitary gland does not produce enough TSH, the thyroid gland will not produce enough T4.
Diagnosis and treatment of hypothyroidism are individual. For some patients, blood tests will be sufficient, while others will require additional studies such as CT, ultrasound, biopsy, and thyroid scintigraphy.
The main goals of therapy are to reduce symptoms, control thyroid hormone levels, and prevent the risk of complications, including heart disease and osteoporosis.
The good news is that the disease usually responds well to treatment. For most patients, it is sufficient to take synthetic thyroid hormone once a day, preferably in the morning. Replacement therapy helps to normalize hormonal levels and reduce symptoms.
In recent years, a new direction, called regenerative medicine, has been intensively developing. It uses the patient’s own resources to restore damaged cells and tissues. The use of stem cells is one of the most promising areas for the development of modern medicine. The data obtained indicate the effectiveness of cell therapy in the treatment of a number of serious diseases, including endocrine diseases. Hormone replacement therapy for endocrine disorders does not allow to fully restore the complex process of metabolic interaction of hormones in the body. Therefore, stem cell transplantation is considered a more physiological approach to the treatment of thyroid diseases.
In recent years, a number of studies have been conducted that have proven the high efficiency of small-scale treatment of hypothyroidism with stem cells. One of the experiments studied the nature of microscopic changes in thyroid tissue after mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) transplantation. The study showed an increase in free T3 and free T4 levels, as well as a decrease in TSH levels after 6 weeks. After 8 weeks, the stem cell injection practically restored the function and histological structures of the thyroid gland. However, after 10 weeks, progress slowed down. Therefore, the authors of the study recommended the re-introduction of MSCs.
Another study has proven the effectiveness of cell therapy in autoimmune thyroiditis – the main cause of hypofunction. The introduction of mesenchymal stem cells led to a decrease in antibodies to thyroglobulin in the blood serum and normalization of the immunoregulatory index. In addition, cell therapy contributed to the normalization of the level of thyroid hormones, which indicates the positive effect of such a correction and the high promise of stem cells in the treatment of thyroid disorders.
If you want to learn more about the possibilities of cell therapy, call one of the numbers listed on the site or fill out the feedback form. The medical coordinator of MedTour will contact you, consult for free on all questions that have arisen and select the best clinic for treatment.
It all depends on whether the patient is under medical supervision. If left untreated, the disease can lead to serious (and sometimes potentially fatal) complications such as myxedema, heart failure, and severe depression. Life expectancy can vary depending on many factors, such as age, gender, and the presence of other medical conditions. However, with timely and proper treatment, patients can live long and relatively healthy lives.
In order not to worsen their condition, doctors recommend patients:
The cost depends on the price of drugs used as part of substitution therapy. There are both cheap and more expensive synthetic thyroid hormones.
The price of cell therapy depends on the dosage of the drug and the number of sessions. The stem cell treatment program is developed individually for each patient. If you want to know the exact cost of treatment, please contact the medical coordinator of MedTour by phone or using the feedback form.
Andriy Kovalchuk, biotechnologist, candidate of medical sciences, director of the Genome stem cell bank, head of the cord blood, tissue and human cell bank at Gorbachevsky National Medical University, spoke about the achievements and features of regenerative medicine.
If you want to learn more about the possibilities of cell therapy, call one of the numbers listed on the site or fill out the feedback form. The medical coordinator of MedTour will contact you, consult for free on all questions that have arisen and select the best clinic for treatment.
Please rate the work of MedTour
