Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
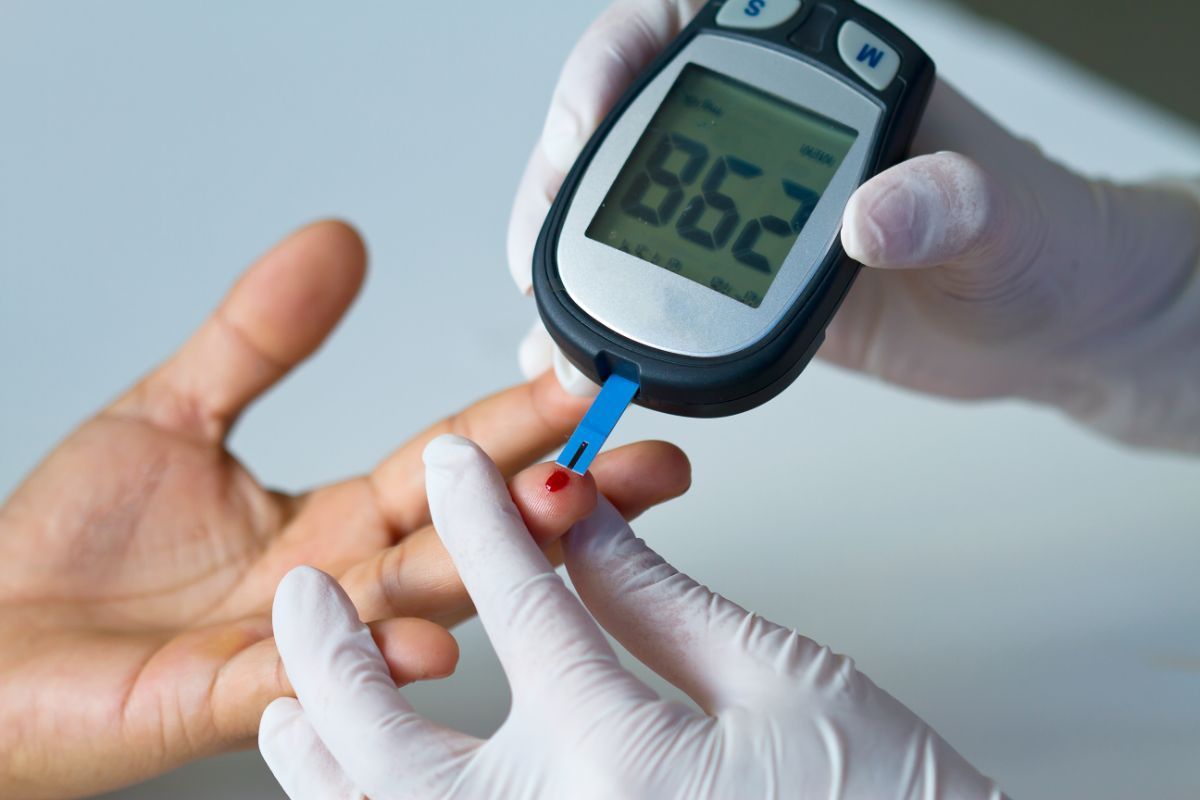
According to the International Diabetes Federation, about 400 million people worldwide are living with diabetes, and this number is expected to rise to almost 600 million by 2035. Many people can control the disease with diet, exercise, regular insulin injections, and antidiabetic medications. But at the same time, there is always a risk of developing such serious complications as kidney failure, neuropathy, heart disease and other health problems.
Therefore, today there is an active search for new, safer and more effective methods of treatment, and stem cell therapy is one of the most promising areas in this field of medicine. Below, we’ve compiled the most up-to-date diabetes-related information for you, including innovative treatments for this common condition.
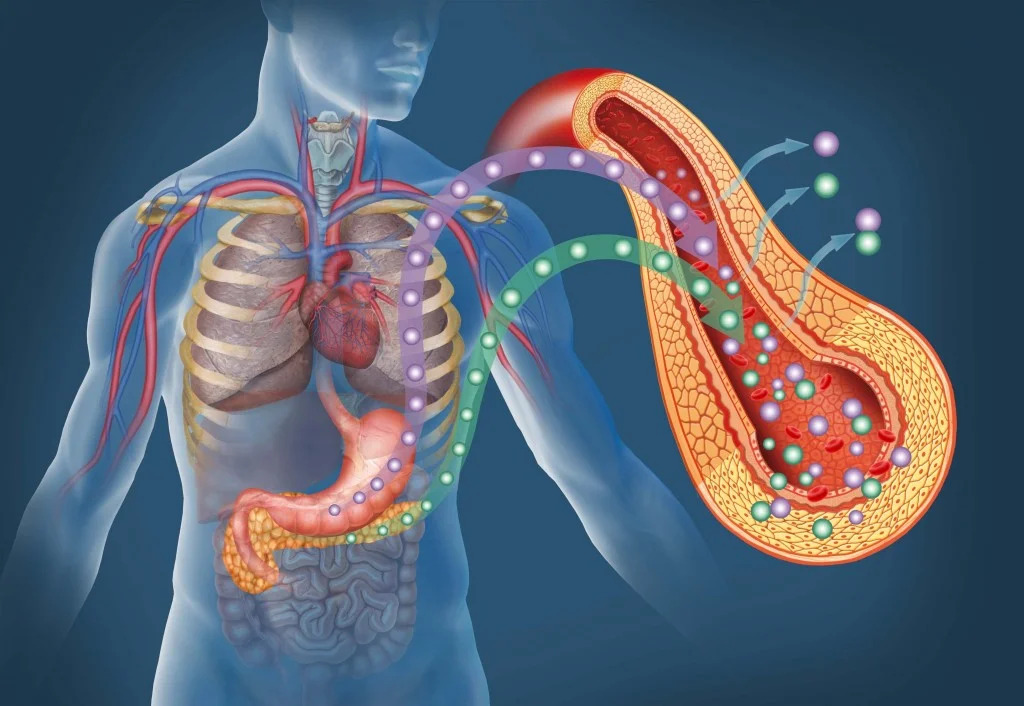
This is a condition in which the body is unable to regulate or properly metabolize the sugar (glucose) in the blood. The pancreas plays a critical role in this process. This organ contains clusters of hormone-producing cells known as the islets of Langerhans.
The most important of these are beta cells, which produce a hormone known as insulin. It is released into the bloodstream when sugar levels get too high. Thus, the hormone signals to other cells of the body about the need to absorb glucose, which is their main source of energy. Diabetes mellitus develops when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin, or because the body’s cells do not respond properly to the released hormone.
Type 1
In this type of diabetes, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the beta cells in the pancreas. The destruction of beta cells leads to a decrease in insulin production and an increase in blood sugar levels. If the disease is not controlled, it can lead to damage to the kidneys, nervous system, eyes, and other organs.
Type 2
This type is due to the development of body cell resistance to insulin. In response to this, beta cells begin to produce more insulin, but ultimately cannot compensate for the resistance. As with type 1 disease, high levels of glucose in the blood can cause serious damage to the body. The main risk factors for developing this disease are heredity, obesity and a sedentary lifestyle.
Doctors also distinguish between gestational diabetes, which is diagnosed in about 14% of pregnant women, and prediabetes, a condition in which blood sugar is higher than normal but has not yet reached the level of diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes occurs due to a malfunction of the immune system. It mistakenly starts attacking healthy pancreatic beta cells. This leads to an absolute deficiency of insulin.
The development of type 2 diabetes is due to insulin resistance. The cells of the body become less sensitive to the action of the hormone. In response to this, the pancreas begins to produce it with greater intensity. Hyperfunction leads to wear and tear of the organ, resulting in a decrease in insulin production over time. Risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes are:
It is important to note that both types of diabetes have a complex and multifaceted etiology. Many factors can interact with each other, affecting the risk of developing the disease.

Type 1 disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
In type 2 diabetes, polyuria, polydipsia, and polyphagia can also be seen, but they are usually less severe. Additional manifestations of the disease are:
The MedTour company cooperates with leading specialists in the treatment of diabetes and other endocrine diseases. Call by phone or fill out the feedback form, and our coordinating doctor will select an experienced specialist and the best clinic for you, taking into account your personal needs.

At the initial stage, the doctor conducts a physical examination and listens to the patient’s complaints. Symptoms such as frequent urination, thirst, weight loss, and fatigue may indicate the development of diabetes. Additionally, the following tests are carried out:
Other studies may also be prescribed, allowing the doctor to clarify the diagnosis or choose the most effective therapeutic strategy.
People with type 1 diabetes are given insulin to control their blood glucose levels. The need to constantly monitor sugar and inject insulin several times a day reduces the quality of life of patients with diabetes. New technologies, such as insulin pumps, have made it possible to administer insulin without injection, with the ability to set the time and dosage of the hormonal drug. However, insulin pumps cannot accurately replicate the complex mechanism of insulin production in a healthy body.
Type 2 diabetes can be controlled through diet and physical activity. However, many people suffering from this condition end up having to take insulin injections to maintain their blood glucose levels or other medications.
Today, scientists are actively searching for new treatments for diabetes that could help patients maintain a high quality of life and reduce the risk of complications. Cellular therapy is one of the most promising areas in this field. Stem cells have unique abilities. They can not only transform into other cells of the body, restoring damaged tissues, but also produce various substances that regulate the function of the immune system, reduce inflammation and slow down the process of destruction of pancreatic cells.
Relatively recently, an innovative method for the treatment of insulin-dependent diabetes has been developed. Its essence lies in the transplantation of pancreatic islet beta cells. However, the growing incidence of diabetes in the world, the limited number of donors and the need for lifelong immunosuppression (drugs that prevent rejection of donor cells) limit the widespread use of this technique. The scientists continued their research and found out that the use of stem cells allows to achieve a good therapeutic result.
Studies have shown that the effectiveness of MSCs in type 1 diabetes mellitus is provided by two factors:
Cell therapy helps to improve the course of the disease, namely:
In general, the use of stem cells helps to significantly improve the quality of life of patients with diabetes.
Standard therapy for insulin resistant diabetes usually includes lifestyle changes, dietary changes, and medications. However, conventional therapies come with many limitations. Drug therapy can cause side effects, including hepatotoxicity, hypoglycemia, gastrointestinal disturbances, a tendency to respiratory tract infections, and others. In addition, the use of drugs only alleviates the symptoms, but does not prevent the decline in beta-cell function.
In type 2 diabetes, three types of cells have proven their effectiveness: mesenchymal, hematopoietic and induced pluripotent stem cells. The use of mesenchymal stem cells is preferred because they are easy to isolate from autologous (own) or allogeneic (donor) tissues.
Studies have shown that MSCs injections help reduce insulin resistance and insulin dependence. The conclusions reached by the scientists:
Thus, cell therapy is an effective and safe treatment for insulin resistant diabetes.

Conducting stem cell therapy allows:
The positive effects after MSCs therapy were long lasting and observed for 1-3 years.
Stem cell therapy includes the following steps:
If a patient wishes to use his own stem cells, doctors first take the cell material from the patient and then culture it for some time (usually 3 weeks) in the laboratory. Donor stem cells can be injected immediately.
The MedTour company cooperates with leading medical centers specializing in the treatment of endocrine disorders and the treatment of diabetes in particular. Today we can offer our patients both standard methods of treatment and innovative methods of regenerative medicine – stem cell therapy. To learn more about the new options for treating diabetes, contact our coordinating physician in a convenient way for you and get a detailed free consultation.
The MedTour platform cooperates with the best doctors specializing in the treatment of diabetes. We can also offer consultations of doctors who treat various diseases with the help of stem cells. One of them is Ivan Badyin, Ph.D., who has over 17 years of experience in the application of regenerative cell technologies.
Please rate the work of MedTour
