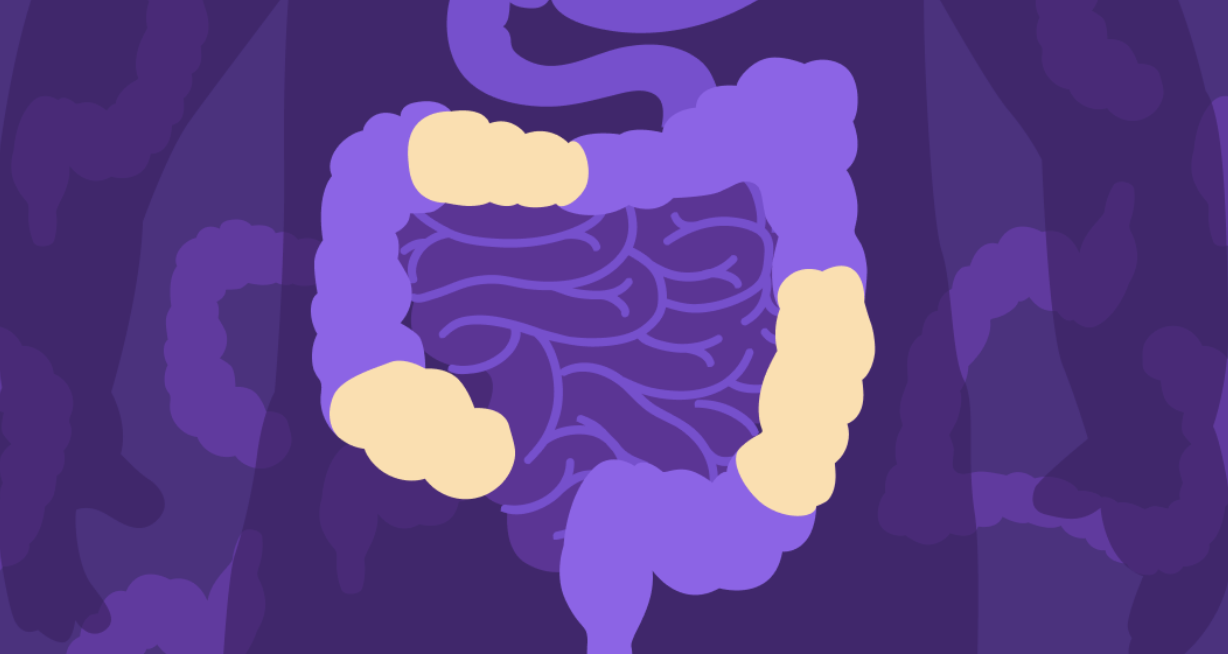
What is Crohn`s disease in simple words?
Crohn`s disease is a chronic inflammatory condition that occurs in the digestive tract. It can be characterized by inflammation, swelling and irritation in any part of the digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus, but most often affects the small intestine and / or colon. Inflammation can lead to a range of symptoms, including
abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, fatigue, and sometimes malnutrition. As a rule, Crohn`s disease is a lifelong disease.
Causes of Crohn`s disease and what provokes it
The exact cause of Crohn`s disease has not yet been fully clarified, but it is believed that it is caused by a combination of genetic, environmental and immune factors.
Some of the potential factors that may contribute to the development of the disease
include:
- Genetics – studies have shown that people with a complicated family history are more likely to develop this disease. Some genes have been identified that appear to increase the risk of Crohn`s disease.
- Dysfunction of the immune system. Crohn’s disease is believed to be an autoimmune disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues of the digestive tract, causing inflammation.
- Environmental factors – Some environmental factors, such as smoking, a high-fat diet and certain types of bacteria in the intestine, have been associated with the development of pathology.
- Stress, although stress is not a direct cause of Crohn`s disease, it can trigger outbreaks in some people with this disease.
- Medications – Some medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and antibiotics, may increase the risk of developing the disease.
- Some health conditions. Certain health conditions, such as infections and autoimmune disorders, can also increase the risks of the onset and development of the disease.
The causes of Crohn`s disease may vary from person to person, but some common
factors that can trigger symptoms or outbreaks include:
- Diet: Certain foods can cause symptoms in people with a pre-existing disease or at risk. Common trigger foods include high-fat foods, spicy foods, and dairy products.
- Stress: Emotional stress can also cause symptoms or flare-ups in some people.
- Medications – Some medications such as non-foreign anti-inflammatory drugs can cause a painful condition or worsen it.
- Infections – infections in the digestive tract can trigger symptoms or exacerbations of the disease.
- Hormones – Changes in hormone levels, such as during menstruation or pregnancy, can also cause symptoms or exacerbations in some people.
Symptoms of Crohn`s disease
Symptoms of Crohn`s disease can vary from person to person and depend on the location and severity of inflammation in the digestive tract. Some common symptoms of Crohn`s disease include:
- Abdominal pain and cramps are one of the most common symptoms, they can manifest to a mild or severe degree.
- Diarrhea, chronic diarrhea is also a common symptom, and in some cases it may contain blood.
- Weight loss. People with Crohn`s disease may experience unintended weight loss due to poor nutrient absorption or decreased appetite.
- Fatigue – chronic inflammation in the body often causes fatigue and a general feeling of malaise.
- Anemia. Chronic inflammation in the digestive tract can lead to iron deficiency anemia, which can cause fatigue, weakness and shortness of breath.
What is the danger of Crohn`s disease?
Crohn`s disease can be a dangerous condition, especially if it is untreated or poorly
controlled. Some of the potential dangers of this pathology include:
- Malnutrition: Crohn`s disease can disrupt the body`s ability to absorb nutrients, which can lead to malnutrition and other complications.
- Intestinal obstruction. Inflammation caused by Crohn`s disease can lead to narrowing of the intestinal lumen, which leads to blockage causing pain, vomiting and other symptoms.
- Fistulas. Fistulas are abnormal connections between two organs or between an organ and the skin. Fistulas can form between the intestines and other organs, such as the bladder or vagina.
- Colon cancer – People with Crohn`s disease have an increased risk of developing colon cancer, especially if the disease affects the colon.
- Intestinal perforation, in severe cases, inflammation caused by Crohn`s disease can weaken the intestinal wall, leading to perforation or a hole in the intestine.
- Autoimmune complications. Crohn`s disease is an autoimmune disease, which means it can affect other parts of the body, such as the skin, eyes, and joints.
It is important to note that not everyone with Crohn`s disease faces all these dangers, and many people with this disease can effectively cope with their symptoms with medications, lifestyle changes and other treatments. Nevertheless, it is important for such patients to have a good and experienced attending physician and is in close cooperation with him to monitor their condition and receive proper care to prevent complications.
Crohn`s disease extra-intestinal manifestations
Crohn`s disease mainly affects the gastrointestinal tract and leads to the complications described above, but there are also some extra-intestinal manifestations of the disease. They are less common and patients know little about
them, but nevertheless they can be quite dangerous:
- Conjunctivitis, keratitis, uveitis – it is impossible to say exactly how Crohn`s disease is associated with these eye diseases, but there is a correlation with the inflammatory form of Crohn`s disease; – Aphthous stomatitis – there is also a correlation with the inflammatory form of the disease;
- Monoarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis are autoimmune diseases of the joints, sometimes found in Crohn`s disease;
- Nodular erythema, angiitis (inflammation of blood vessels), gangrenous pyoderma (inflammatory skin disease) – sometimes skin inflammation occurs simultaneously with intestinal inflammation;
Fatty liver dystrophy, sclerosing cholangitis, cholelithiasis, cirrhosis of the liver, a higher risk of cholangocarcinoma – many diseases of the liver and bile ducts in Crohn`s disease occur more often;
- Nephrolithiasis, pyelonephritis, cystitis, hydronephrosis and even amyloidosis of the kidneys occur more often, and sometimes are directly a consequence of Crohn`s disease.
Crohn`s disease and ulcerative colitis
Both of these diseases are chronic inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), which can cause inflammation and damage to the digestive tract. Despite the fact that they have some similarities, these are different diseases with different nature and manifestations.
The key differences between Crohn`s disease and ulcerative colitis are as follows:
- Localization of inflammation: Crohn`s disease can affect any part of the digestive tract, while ulcerative colitis primarily affects the colon and rectum.
- Inflammation model: in Crohn`s disease, inflammation often occurs in the form of areas with healthy tissue between them, while in ulcerative colitis, inflammation is continuous and begins in the rectum, and then spreads to other parts of the colon. Also, with ulcerative colitis, the mucous and submucosal layers become inflamed, that is, the inflammation is more superficial, and with Crohn`s disease, all layers become inflamed.
- Depth of inflammation – Crohn`s disease can affect all layers of the intestinal wall, while ulcerative colitis primarily affects the inner lining of the colon.
- The symptoms of Crohn`s disease and ulcerative colitis may be similar, but there are some differences. For example, diarrhea is more common in ulcerative colitis, and abdominal pain and cramps are more common in Crohn`s disease.
- Complications. Although both conditions can cause complications such as malnutrition, fistulas, and intestinal obstruction, some complications are more common in one condition than the other. For example, people with Crohn`s disease have an increased risk of developing intestinal strictures, and people with ulcerative colitis have an increased risk of developing colon cancer.
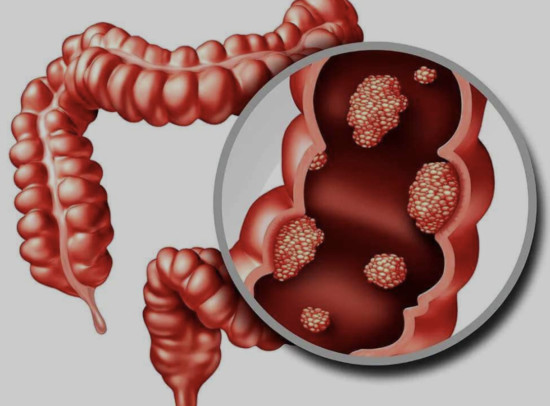
Diagnostics of Crohn`s disease
The diagnosis of Crohn`s disease usually involves a combination of clinical assessment, anamnesis, physical examination, laboratory tests, imaging studies and endoscopy.
Here are some of the key steps needed to diagnose this disease:
- Medical history and medical examination. The doctor asks questions about the symptoms, medical history and family history of inflammatory bowel disease. He also conducts a medical examination, which most often includes a rectal examination.
- Blood tests. Blood tests can help identify signs of inflammation or infection in the body, as well as check for anemia, vitamin deficiency and other health problems that may be associated with this pathology.
Stool tests. Stool tests can help identify infections, inflammation and other abnormalities in the digestive tract.
Visualization studies. Imaging studies such as X-rays, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging can provide detailed images of the digestive tract, helping to identify areas of inflammation, ulcers or other abnormalities.
- Endoscopy (during endoscopy, a thin flexible tube with a camera is inserted into the digestive tract to visualize the intestinal mucosa and collect tissue samples for biopsy). This can help confirm the diagnosis of Crohn’s disease and rule out other conditions.
What analysis confirms Crohn`s disease?
Crohn`s disease can be confirmed by a specific analysis – the determination of antibodies to saccharomyces (baker`s yeast) Saccharomus cerevisiae (ASCA). This is an immunological analysis, it is specific and allows you to definitively establish or refute the diagnosis of Crohn`s disease.
Colonoscopy for Crohn`s disease
Colonoscopy is a common procedure used to diagnose and monitor Crohn`s disease. During a colonoscopy, a long flexible tube with a camera is inserted through the rectum and moves along the colon to look for signs of inflammation, ulcers or other abnormalities.
Colonoscopy is especially useful in the diagnosis of Crohn`s disease, as it allows doctors to examine the entire colon and take a biopsy of any suspicious areas. A biopsy involves taking small tissue samples from the colon for examination under a microscope, which can help confirm the diagnosis of the disease and rule out
other conditions.
In addition to the diagnosis of Crohn`s disease, colonoscopy can also be used to monitor the course of the disease. Repeated colonoscopies may be recommended at regular intervals to check for changes in the colon and to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
Colonoscopy for Crohn`s disease shows the presence of ulcers. The nature of the lesion has a specific type of “cobblestone pavement” – a combination of longitudinal and transverse ulcers-cracks in the form of protruding areas.
Although colonoscopy is generally safe, there are some risks associated with this procedure, including bleeding, infection, and perforation of the colon.
Which is better to do an MRI of the intestine or a colonoscopy?
Both intestinal MRI and colonoscopy can be useful in the diagnosis and monitoring of Crohn’s disease. However, the choice of which test to use depends on many factors, including the patient`s specific symptoms and medical history, as well as the experience and knowledge of medical personnel.
The most important factors that are important when choosing between intestinal MRI and colonoscopy:
- Diagnostic accuracy. Both MRI and colonoscopy are very accurate in diagnosing Crohn’s disease, but they give different types of information. An MRI can provide a detailed image of the entire intestine, and a colonoscopy can provide direct imaging and biopsy samples from the colon.
- Comfort and convenience. MRI is a non—invasive study that does not require sedatives or bowel preparation, which makes it a more comfortable and convenient option for some patients. However, colonoscopy may be necessary for patients with more severe symptoms or complications of the disease.
- Cost and Availability – MRI may be more expensive than colonoscopy and may not be available in all medical institutions. In some cases, insurance coverage and access to healthcare resources can also influence the choice of the test.
Prevention of Crohn`s disease
There are some foods and lifestyle factors that can worsen the symptoms of Crohn`s disease, and it is usually recommended to avoid or limit their consumption. Most often it is:
- Foods high in fiber – they are difficult to digest and can worsen diarrhea and abdominal pain in people with Crohn`s disease. It is usually recommended to limit foods with a high fiber content, such as nuts, seeds, popcorn, raw fruits and vegetables.
- Dairy products. Many people with Crohn`s disease suffer from lactose intolerance, which can cause gas formation, bloating and diarrhea. Therefore, it may be helpful to limit or avoid dairy products such as milk, cheese, and ice cream.
- Fatty and fried foods. These types of foods can be difficult to digest and can cause deterioration in people with Crohn`s disease. It is recommended to limit the consumption of fatty and fried foods, such as fast food, fried meat and potato chips.
- Spicy food. Spicy food can irritate the digestive tract and worsen the symptoms of Crohn`s disease. It is recommended to limit or avoid spicy foods such as hot peppers, salsa and curry.
- Alcohol and caffeine: These substances can cause dehydration and worsen diarrhea and other symptoms of digestive disorders in people with Crohn`s disease. It is recommended to limit or avoid the consumption of alcohol and caffeinated beverages, such as coffee, tea and carbonated drinks.
It is important to note that different products can aggravate the manifestations of the disease in different patients. Therefore, it is important to focus not only on general recommendations, but also on individual experience of using certain products, as well as consult with your doctor.
Treatment of Crohn`s disease. Is it possible to be cured forever?
Treatment for Crohn`s disease usually involves a combination of medications, dietary changes and, in some cases, surgery. The goals of treatment are to control inflammation, relieve symptoms and prevent complications.
The main methods of treatment of Crohn`s disease:
- Medications. There are several types of medications used to treat Crohn`s disease, including anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, and biologics. The choice of medication depends on the severity and localization of the disease, as well as on the patient`s general health and medical history.
- Dietary recommendations: Although there is no specific diet that could cure Crohn`s disease, excluding certain types of foods can help alleviate symptoms and prevent exacerbations. It is not only the rejection of foods that cause symptoms, eating smaller portions and more frequent meals, as well as the profile of dehydration that are useful.
Enzyme supplements and vitamins. Some patients with c may benefit from the use of specialized formulas to ensure proper nutrition and restore the digestive tract.
- Surgery. In some cases, surgical intervention may be required to remove
damaged or diseased areas of the intestine or eliminate complications such as
fistulas or strictures.
Is it possible to live normally with Crohn`s disease?
Most patients with Crohn`s disease are able to live a normal and fulfilling life. Although there is currently no cure for Crohn`s disease, there are many treatment options available that can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. These treatments may include medications to reduce inflammation, surgery to remove damaged areas of the intestine, and lifestyle changes such as stress management and dietary modifications.
During exacerbations, the ability of such patients to study or work may be limited, but periods of disability are rarely long. Some patients with a severe degree of pathology need to remove the stoma, in this case, patients have to face quite large difficulties and lifestyle features. In other cases, patients with Crohn`s disease do not face disability more often than the average in the population and do not live less.
Modern methods of treatment of Crohn`s disease
Treatment of Crohn`s disease using stem cells is a promising new treatment method. For this purpose, only mechenchymal stem cells are used. Mesenchymal stem cells are partially differentiated stem cells that have anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory and regenerative properties, but their main effect is the differentiation of stem cells into the tissues of the body that are damaged or absent in the required amount. Thus, stem cells in Crohn`s disease contribute to the fact that the number of normally functioning stem cells becomes larger, and the
immune system affects intestinal cells to a lesser extent. Accordingly, patients receive full-fledged etiopathogenetic rather than symptomatic treatment, and their condition becomes better.
Mechenchymal stem cells are found in bone marrow, cartilage, amniotic fluid, umbilical cord blood, and adipose tissue. For the treatment of Crohn`s disease, they are usually extracted from adipose tissue. Adipose tissue is taken with a needle with a special cannula, after which stem cells are isolated from it and injected back into the patient`s body in the form of an injection. If necessary, stem cells are influenced by growth factors to increase their number.
Which clinics best treat Crohn`s disease?
The MedTour team has extensive experience in treating patients with stem cells. For patients with Crohn’s disease, it was possible to identify several clinics where successful treatment of this pathology was carried out. Such clinics include:
- Cellthera;
- SmartCell;
- Institute of Cell Therapy;
- Emcell;
- Froceth;
- Good cells.
These are Ukrainian, Czech and Georgian clinics. They are characterized by high efficiency of treatment and a relatively low price.
Our specialist doctors
Among the doctors who have extensive clinical experience in stem cell treatment are Dr. Kovalchuk (Ukraine) and Dr. Badyin (Serbia).
FAQ
1. How can stem cells help with Crohn`s disease?
Stem cells contribute to the replacement of cells damaged by the immune system with healthy ones, and thus, reducing the manifestations of the disease.
2. How many courses are required for the treatment of Crohn`s disease using stem
cells?
As a rule, chronic immunological diseases require lifelong treatment. Therefore, patients undergo 1-2 courses per year or another period of time.
3. What is the cost of treating Crohn`s disease with cell therapy?
It depends on the severity of clinical symptoms, the general condition of the body and the chosen clinic. You can check the cost with the doctor-coordinator of MedTour.
Any other questions? For all aspects related to the treatment of Crohn`s disease, including the relative new method of stem cell treatment, contact the MedTour coordinator doctor for a free consultation.



