Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
According to statistics, more than 1 billion people suffer from neurological disorders. These diseases can be caused by various factors such as: genetic predisposition, environmental exposure, head trauma, aging and other reasons. Symptoms of neurological diseases are: frequent headaches, convulsions, impaired coordination of movements, memory impairment and many other manifestations that significantly reduce the quality of life of patients. Therefore, the development of new effective methods of treatment is an important task of modern medicine.
Innovative cell therapy has given hope to millions of people who have tried all available traditional treatments and have not received results. The unique properties of stem cells, which can transform into other types of cells in the body, including nerve cells, make it possible to fight many diseases that were previously considered incurable.
Cellular therapy can effectively treat almost any disorder that is accompanied by damage to the central nervous system. It promotes the regeneration of nervous tissue, as well as the restoration of normal interneuronal and neuromuscular connections.
The use of stem cells makes it possible not only to slow down the progression of the disease, but also helps to eliminate the cause that caused it. This allows to achieve a stable improvement in the patient’s condition.
Cerebral palsy is a condition of physical disability caused by brain damage during childbirth, prenatal or postpartum. Despite the fact that the disease has a direct impact on motor activity, it is not caused by problems in the muscles or nerves. Cerebral palsy causes damage to the areas of the brain that control muscle movement.
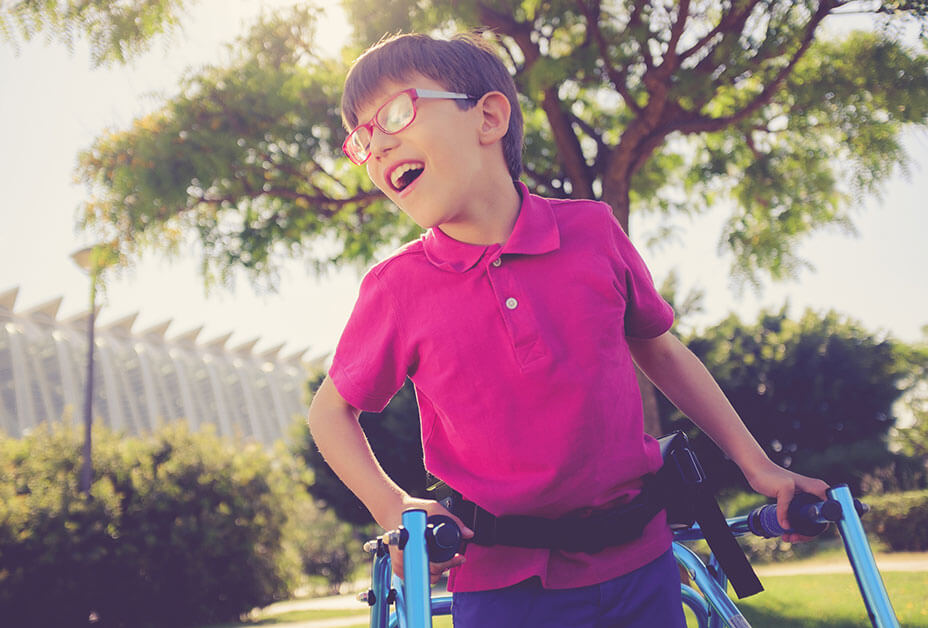

How can stem cells help with cerebral palsy?
Stem cells have the ability to turn into nerve cells. Thus, they replace damaged brain cells in cerebral palsy. The probability of success of treatment is proportional to the age of the patient, the duration and severity of the disease. In some cases, it is possible not only to stabilize the patient’s condition, but also to achieve regression of the disease.
The number of injected cells is determined taking into account the age and weight of the patient. Treatment is with mesenchymal stem cells (derived from the patient’s own adipose tissue or bone marrow) or fetal stem cells. The therapeutic protocol is selected individually. Most often, it includes 3 sessions with an interval of 45 days or for 3 days in a row.
Autoimmune neuropathies are a group of neurological diseases that cause inflammation of the peripheral nerves. Their treatment can be a complex and lengthy process, as the effectiveness of traditional therapies is currently limited. But recent research has shown that the use of stem cells can be an effective treatment for autoimmune neuropathies.
How can stem cells help with autoimmune neuropathies?
Stem cells are versatile cells that can develop into various types of tissues. In the treatment of autoimmune neuropathies, they replace damaged and destroyed cells of the nervous tissue, restoring the function of peripheral nerves. This is due to the ability of stem cells to differentiate and regenerate tissues.
There are several methods of using stem cells to treat autoimmune neuropathies. One of them is the transplantation of blood stem cells of a patient after chemotherapy. This method allows to replace damaged blood cells that are involved in the immune response that causes inflammation of the peripheral nerves.
Another method is to inject stem cells directly into damaged nerves. This can contribute to the restoration of myelin, a substance that ensures the normal functioning of nerve fibers.
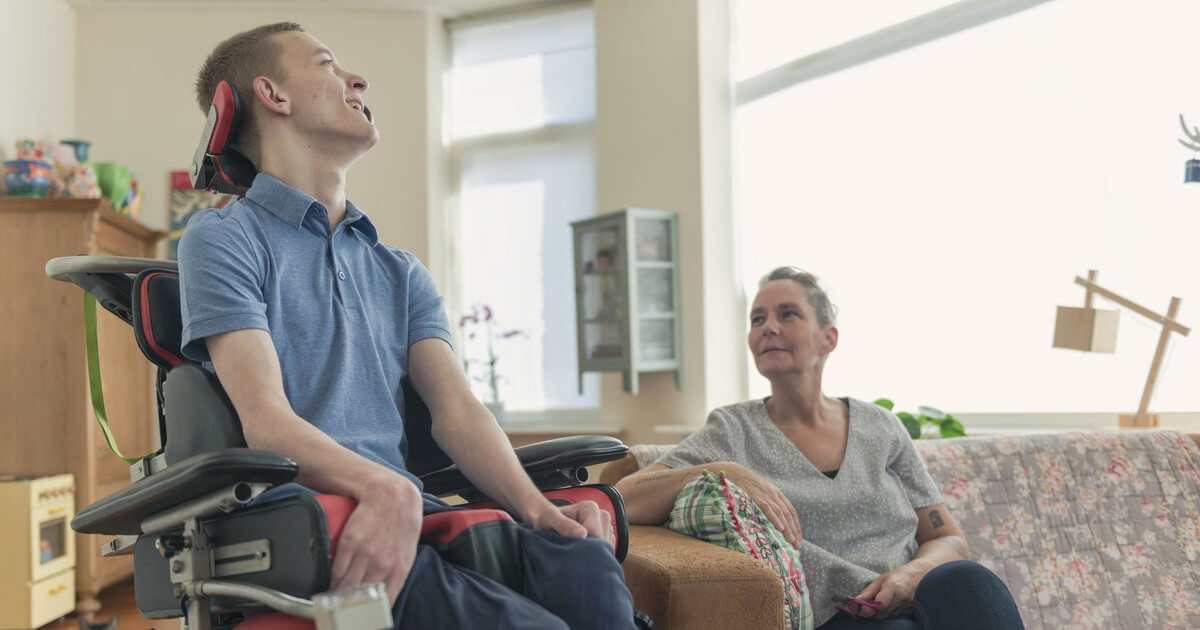
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive neurological disease characterized by the loss of motor nerve neurons in the brain and spinal cord. This leads to progressive weakness and paralysis of the muscles, and provokes impaired speech, breathing and swallowing.
Treatment for ALS includes pharmacological therapy, physical rehabilitation, and other supportive therapies. There are drugs that can slow the progression of the disease and relieve some of the symptoms, such as muscle weakness and spasticity. Physical rehabilitation helps ALS patients improve muscle tone, maintain mobility, and reduce the risk of complications such as pressure sores and infections.
However, the effectiveness of these treatments is limited. Over time, muscle weakness progresses, leading to disability and limited life opportunities. Therefore, researchers are actively looking for new treatments for ALS that could extend the life of patients, such as gene therapy or stem cell transplantation.

How can stem cells help patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis?
ALS cell therapy promotes the regeneration of damaged nerve cells and tissues, which can improve muscle function and slow the progression of the disease.
A review of studies on the use of stem cells in the treatment of patients with ALS who have not responded to medical therapy found that:
Cell therapy does not eliminate the true cause of the disease, which is not yet fully understood. However, stem cell transplantation has a significant impact on pathological processes and helps prevent the progression of the disease. Cell therapy improves the quality of life of patients with ALS and increases their life expectancy, and is especially effective at the initial stage of the disease, when the disease has not turned into an aggressive form.
Multiple sclerosis is a disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the myelin sheath cells of nerve fibers. The myelin sheath can be compared to the insulating layer of a cable. Its function is to electrically isolate the nerve, protect it and ensure the proper functioning of the nervous system. Damage or degeneration of this protective layer causes nerve dysfunction.
Multiple sclerosis leads to impaired coordination of movements, decreased visual acuity, problems with memory and thinking, fatigue, and depression. The disease progresses over time, and its manifestations become more pronounced. Symptoms may increase as a result of physical or emotional stress, and temporarily disappear during periods of remission. However, over time, they become more persistent and have a significant negative impact on the patient’s quality of life.
Current pharmacological therapies target the immune system. There are drugs that slow down the destruction of the myelin sheath of nerve fibers. However, this treatment is not able to completely stop the progression of the disease and repair the damage that has already occurred. Stem cell therapy has the potential to repair damaged myelin, making it a promising treatment for multiple sclerosis.
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in multiple sclerosis
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are found in the bone marrow and give rise to all blood cells, including most immune system cells. Since multiple sclerosis is associated with a malfunction of the immune system, it is HSC that is used to treat this serious disease.
In multiple sclerosis, autologous stem cells, that is, stem cells taken from the patient himself, are more often used. The treatment procedure is called autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (aHSCT).
A 2022 meta-analysis that pooled data from several previously published studies examined disease outcomes after aHSC transplantation in 4831 people with multiple sclerosis. Data are from 50 published studies, including eight clinical trials.
Five years after cell therapy:
Thus, cell therapy is a promising direction in the treatment of multiple sclerosis.
The cost of stem cell treatment varies. The exact cost depends on factors such as the type of disease, its severity, the amount of stem cells needed, and the therapy sessions. To find out the exact cost of treatment, contact the medical coordinator of MedTour by phone or using the feedback form.
MedTour cooperates with the best clinics providing stem cell treatment around the world. The coordinating doctor will help you choose the most appropriate one in accordance with the type of disease and resolve all organizational issues.
What are stem cells?
Most cells in an adult organism are terminally differentiated, that is, they are fully mature and cannot change into another type of cell. For example, a liver cell cannot transform into a brain or skin cell. Stem cells are undifferentiated cells in the body that can self-renew and grow into all other cell types, making them a valuable tool in the treatment of a wide variety of diseases.
What is the success rate of stem cell therapy for cerebral palsy?
Although the success of treatment varies depending on the age of the patient and the severity of the disease, the success rate of cell therapy in cerebral palsy ranges from 43 to 87%.
What are the properties of mesenchymal stem cells?
The high therapeutic potential of MSCs is based on several unique properties of MSCs, such as:
What determines the effectiveness of cell therapy in multiple sclerosis?
Several factors affect the effectiveness of autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (aHSCT) for multiple sclerosis, including:
Can stem cell therapy cure multiple sclerosis?
Research shows that certain stem cell therapies can slow the progression of multiple sclerosis. In particular, autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is considered generally effective in reducing disease activity and slowing the progression of disability, especially in young people with aggressive relapsing disease resistant to highly effective disease-modifying agents.
How effective is stem cell therapy for multiple sclerosis?
According to an analysis of published studies, about two-thirds of people with multiple sclerosis who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation had no disease activity for five years after the procedure (meaning that these patients had no recurrence, disability progression, and new myelin damage detected on MRI).
Please rate the work of MedTour
