Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA

Neurodegenerative diseases are a serious problem of modern health care, as they lead to a gradual deterioration in cognitive functions and limit the patient’s capabilities. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), about 50 million people in the world suffer from dementia, and every year this figure is increasing by 10 million. In addition, there are more than 10 million diagnosed cases of Parkinson’s disease in the world, and more than 2 million of Alzheimer’s disease.
In recent years, there has been an active search for new, more effective methods of treating neurodegenerative diseases, and cell therapy has become one of the most promising areas. This method is based on the use of stem cells, which can differentiate (transform) into various types of cells in tissues and organs, including nerve cells. Cell therapy contributes to the replacement of damaged or lost neurons, and also stimulates the regeneration of damaged tissue.
One of the most pressing problems in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases is the limitations of existing treatments. Despite the fact that various drugs and rehabilitation methods are currently used, none of them provides a complete cure and stop the process of degeneration of the nervous tissue. Moreover, many of the existing treatments have serious side effects.
Cellular therapy is one of the most promising approaches to solving the problem of diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Stem cell therapy not only helps repair damaged nerve tissue, but reduces inflammation, which some scientists believe plays an important role in the development of degenerative disorders of the nervous system.
Parkinson’s disease is one of the most common neurodegenerative diseases. It is characterized by the gradual death of neurons in certain areas of the brain, which leads to impaired motor functions (hand tremor, loss of balance, slowness of movement, etc.).

Recent studies have suggested that stem cell transplantation is a promising treatment for Parkinson’s disease. So, an experiment conducted by scientists from the University of California showed that stem cell transplantation helps to improve motor functions in patients with Parkinson’s disease and reduce the dosage of drugs needed to control the symptoms of the disease.
One of the latest studies in this area was carried out recently (in February 2023) by scientists from Lund University in collaboration with Skåne University Hospital and the University of Cambridge. The patient was transplanted with stem cells that transformed into dopamine-producing cells to replace cells destroyed by Parkinson’s disease.
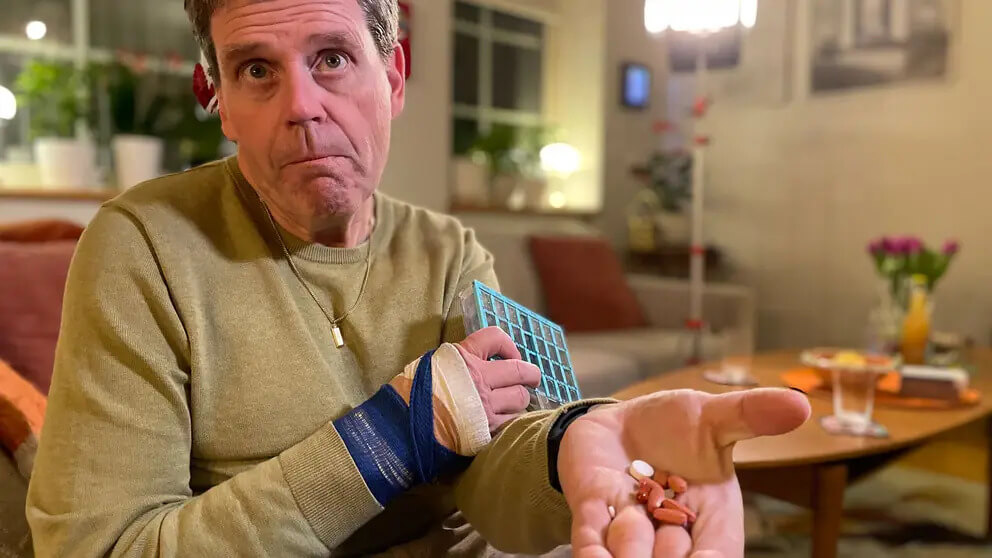
Despite the fact that the study is ongoing, journalists have already managed to talk with the patient. His name is Thomas Matsson. The first symptoms of the disease appeared in a man at only 42 years old, and over the course of 17 years it progressed. Thomas says those were very difficult years. And the worst thing is that the drugs taken on an ongoing basis have changed his personality, causing serious psychological addictions. Now Thomas is very hopeful that cell therapy will help change his life.
Alzheimer’s disease is a disease that causes progressive neuronal degradation, memory and cognitive impairment. Its main symptoms are:
The danger of this disorder lies in the fact that it not only limits a person’s ability to self-service, but also leads to a decrease in the quality of life, social isolation. In addition, Alzheimer’s disease has a strong impact on relatives and loved ones who care for patients.

The complexity of the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease is associated with the lack of effective therapeutic strategies. At the moment, only drugs are available that can slow the progression of the disease, but not stop it.
Recent studies have shown that stem cells may have the potential to repair damaged neurons and improve cognitive function in Alzheimer’s patients. Mesenchymal stem cells isolated from the bone marrow were administered to patients with mild to moderate disease, which were aimed at restoring damaged brain tissues. As a result, the subjects improved cognitive function and decreased the amount of amyloid protein, one of the key factors causing the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
Vascular dementia is a neurodegenerative disease caused by impaired blood circulation in the brain. It is the second most common type of dementia after Alzheimer’s disease. The symptoms of the disease are:
The development of vascular dementia can provoke various reasons, such as:
Treatment of the disease can be complex and depends on the causes that caused it. The main therapeutic tactics include:
This therapeutic tactic is primarily focused on reducing the severity of symptoms. It does not help slow or stop the progression of the disease. However, recent research has shown that stem cells can be effective in combating vascular dementia.
One study published in Stem Cell Research & Therapy in 2020 examined the effect of multipotent mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) infusion in the treatment of patients with vascular dementia. The first group of 24 people received MSC obtained from bone marrow of donors, and the second (with the same number of participants) received placebo therapy.
The results showed that patients who received the MSC infusion experienced a significant improvement in cognitive tests and daily functions, as well as a reduction in inflammation.
Research in this area is ongoing, but it can already be said that cell therapy is a potentially new and effective treatment for vascular dementia.
With age, the human body and mind undergo numerous changes, and one of them is the deterioration of memory. Forgetfulness, difficulty with organizing and completing tasks, disruption of social ties – all this significantly reduces the quality of a person’s life.

Researchers believe that there are three main reasons why memory begins to deteriorate with age.
As we age, the hippocampus shrinks in size. Namely, this part of the brain, apparently plays a large role in memory function. Memory consolidation and spatial memory are dependent on the hippocampus. Here, short-term memories turn into long-term ones, after which they are stored in another part of the brain. Any damage to the hippocampus can affect memory function.
The hormones and proteins that repair damaged neurons and stimulate the growth of new neurons decline with age. Researchers have found that as we age, the number of stem cells present in the brain decreases. The brain stem cells are mainly located in the hippocampus. They are the building blocks of the body and allow new cells to be created. From them arise neurons located in the brain and responsible for various memory functions.
As we age, the amount of blood flowing to the brain decreases. Even though the brain only makes up about 2% of body weight, it uses about 20% of the blood flow and oxygen in the human body. The blood flow keeps neurons alive in the brain by providing a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients. Two arteries are responsible for delivering blood to the hippocampus. If any of these are blocked, the hippocampal cells begin to die, leading to memory loss.
Elderly patients are much more likely to suffer from chronic inflammatory diseases. Inflammation can damage joints, internal organs, tissues, and cells. Some researchers believe that chronic inflammation in the brain can cause memory loss and cognitive decline.
Memory deterioration in old age may indicate the development of neurodegenerative diseases. This is a group of diseases in which there is a progressive destruction of neurons and other cells of the nervous system, which leads to impaired functions of the brain and spinal cord, such as memory, thinking, movement and coordination. Therefore, memory impairment in the elderly is a symptom that cannot be ignored.
Researchers are actively looking for treatments for memory impairment in the elderly. And cell therapy is one of the most promising areas in this area. Stem cells have unique properties that can address the underlying issues that cause memory loss.
Stem cells stimulate the body to restore damaged organs and tissues. Regardless of what causes memory impairment – a degenerative process or a violation of cerebral circulation, cell therapy can help.
In addition, stem cells have anti-inflammatory properties, which have been shown in numerous studies. They play a role in the functioning of the immune system and may prevent inflammation in the brain. The combined properties of stem cells make them a promising method for preventing memory loss.
MedTour company cooperates with the best clinics and laboratories around the world that provide stem cell treatment. If you or your loved ones need treatment for neurodegenerative diseases, please contact us by phone or using the feedback form. The medical coordinator of MedTour will answer all your questions and select the clinic that is best suited for the treatment of your disease.
Please rate the work of MedTour
