Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
The axolotl, a small amphibian native to Mexico, is known for its extraordinary ability to regrow limbs as well as regenerate organs, including the heart and even the brain.
This regenerative feature, which is also seen in starfish, has attracted the attention of scientists. It turned out that its secret lies in the unique properties of stem cells. Since that time, a huge amount of research has been carried out, which resulted in a new direction in medicine – cell therapy. The use of stem cells today allows us to successfully cope with diseases that were previously difficult to treat.

Cell therapy is a treatment that uses stem cells (SCs) to repair body tissues that have been damaged by injury or disease. Stem cells are non-specialized. This means that they can transform into other types of cells.
The study of these conditions and the possibilities of stem cells today form the basis of regenerative medicine. Cell therapy has huge potential. Today, it is used to treat a wide range of diseases: autoimmune disorders, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, kidney and liver disease, autism, cerebral palsy, and many others. The use of SC in injuries and diseases of the joints in many cases can avoid surgical intervention. Cell therapy is also actively used in cosmetology to restore the beauty and youthfulness of the skin.
All stem cells can self-renew (copy themselves) and differentiate (develop into more specialized cells). Nevertheless, there are different types of SC, the functions and abilities of which differ significantly. Currently, scientists are studying two main types of stem cells – embryonic and adult.
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs)
These cells are obtained from the inner cell mass of the blastocyst, a hollow ball of cells that forms 3-45 days after fertilization by a spermatozoon. The size of the human blastocyst does not exceed the size of the dot above this “i”.
Under normal development, the cells within the cell mass give rise to the more specialized cells that make up all the tissues and organs of the human body. However, when scientists grow the cell mass in special laboratory conditions, it retains the properties of embryonic SCs. They are pluripotent, that is, they can turn into any type of cell in the body, and this is their most valuable ability. But there are also disadvantages, the main of which is an ethical issue. Despite the fact that embryonic stem cells are obtained primarily from blastocysts created by in vitro fertilization, many people find their medical use unacceptable. Therefore, scientists continued their research and found that other types of cells can be used as part of regenerative therapy.
Adult stem cells
These are cells that are produced by the adult body in small quantities. The main disadvantage is that they are often already at the initial stage of differentiation, which significantly reduces the possibility of their medical use. But there are benefits. These cells can be obtained from the patient’s own tissues, thereby eliminating the risk of rejection after transplantation.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)
MSCs are a type of adult stem cell that can differentiate into a wide range of cell types. They are found in a variety of tissues and can be isolated from virtually any source, including bone marrow, fat, peripheral and cord blood. MSCs have many possible applications in the field of regenerative medicine. They are actively used to restore cartilage in degenerative joint diseases. In addition, there are good results in the treatment of autoimmune disorders, pancreatic necrosis, scleroderma, eczema, trophic ulcers, macular degeneration and many other diseases with the help of MSCs.
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs)
iPSCs are adult cells reprogrammed into a state similar to embryonic SCs by introducing specific proteins and factors. iPSCs were first obtained by Japanese scientist Shinya Yamanaka and colleagues at Kyoto University in 2006. For their work, they were jointly awarded the 2012 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
iPSCs have many advantages over embryonic stem cells. Since they are obtained from the patient’s own body and then reprogrammed, the risk of rejection after transplantation is reduced. In addition, the use of adult SC completely solves the ethical problem.
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs)
HSCs are cells present in the blood and bone marrow. HSCs are able to form mature blood cells such as red blood cells (carry oxygen), platelets (control blood clotting), and white blood cells (fight infections).
HSCs are used in the treatment of many malignant (eg, leukemia, lymphoma) and non-malignant (eg, sickle cell anemia) diseases. The technique is called a bone marrow or stem cell transplant. HSCs have also proven effective in the treatment of a number of autoimmune and genetic disorders. In general, bone marrow transplantation is used to treat more than 75 different diseases.
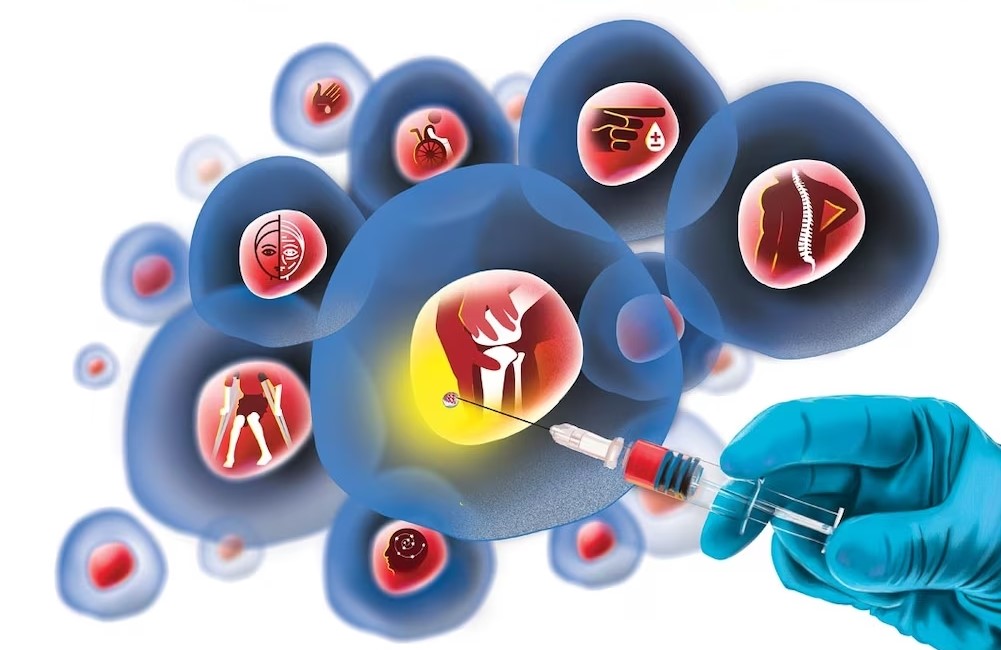
The list of diseases in which cell therapy has shown excellent results is quite extensive. Below are just a few of them.
Cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy is a neurological disorder that is accompanied by developmental, learning, and speech delays, as well as neuromuscular problems. Patients with cerebral palsy need a long and expensive rehabilitation. Standard methods of treatment can only slightly improve the quality of life of patients, but, unfortunately, they are not able to restore impaired functions.
Stem cells can transform into nerve cells, thus repairing damaged brain tissue. The effectiveness of therapy depends on the age of the patient, the duration and severity of the disease. In some cases, treatment of cerebral palsy with stem cells helps not only to stabilize the patient’s condition, but also to achieve disease regression..
Muscular dystrophy
A disease accompanied by rigidity and muscle atrophy. Cell therapy in various types of myopathies acts in several directions. SCs replace damaged muscle cells, promoting the regeneration of muscle tissue. Hereditary myopathies are often accompanied by inflammation. Cell therapy can reduce the inflammatory process and improve the patient’s condition. In addition, stem cells produce factors that positively affect neuroregulation. According to studies, regenerative therapy helps to significantly improve muscle strength and motor skills in about half of patients.
Autism
Cell therapy has shown positive results in patients with autism. There is evidence that stem cells given intravenously improve overall immune system regulation and neural connectivity in the brain. Treatment for autism is important to start as early as possible. Andriy Kovalchuk is one of the few doctors who accepts children from 5 months. Older patients can receive stem cell treatment for autism at EMCell.
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is a severe, debilitating disease. The methods of therapy used today can only slow down its progression, but do not lead to a cure. The treatment of multiple sclerosis with stem cells has shown good results. Studies have shown that transplantation of autologous (taken from the patient’s own) hematopoietic SCs helps to slow down damage to the myelin sheath of nerve fibers, and in some cases repair the damage caused by the disease. The therapy is especially effective in young people suffering from a highly active form of multiple sclerosis.
Diabetes mellitus type 1
Stem cell therapy holds great promise for diabetic patients. Despite the fact that stem cell therapy for diabetes does not lead to a complete cure, it helps to significantly improve the condition and quality of life of patients. A comprehensive therapeutic program helps to reduce the amount of insulin administered, eliminate diabetic ketoacidosis, normalize metabolism, and slow down the destruction of pancreatic beta cells.
Diabetes mellitus type 2
Mesenchymal stem cells can be used to treat type 2 diabetes. Scientific studies have shown that MSC therapy helps to reduce the amount of antidiabetic drugs taken, normalize blood sugar levels, and reduce C-peptide levels. Cell therapy does not cause side effects. In addition, it is safer than standard treatment for advanced type 2 diabetes.
Optic nerve atrophy
With atrophy of the optic nerve, stem cells can be injected both directly into the eyeball and intravenously. According to studies, the treatment of atrophy with stem cells can improve the function of the optic nerve by 70-90%. Cell therapy promotes the emergence of new neural connections, reduces the death of neurons, and normalizes blood supply to the eye. Such a complex effect makes it possible to improve vision by about 30%.
Macular degeneration
Age-related macular degeneration is a common disease that leads to a decrease in central vision. In the late stage of AMD, massive loss of retinal neurons occurs. Mesenchymal stem cells are able to transform and replace damaged neurons. There are studies that have shown that after transplantation, MSCs can differentiate into light-sensitive ones, thus restoring visual function. The use of stem cells in the treatment of the retina also helps to reduce the inflammatory process that is present in macular degeneration.
Treatment of joints with stem cells
Cell therapy has proven itself in the treatment of injuries and diseases of the joints. MSCs are able to transform into cartilage and connective tissue cells, restoring the damaged joint. In many cases, regenerative therapy avoids highly traumatic surgical intervention. Treatment of osteoarthritis with stem cells helps to reduce inflammation, relieve pain and improve patient mobility. Stem cell treatment of the knee joint also helps to achieve good results. They are injected directly into the affected area in order to achieve a pronounced therapeutic effect.
Cirrhosis
Treatment of the liver with stem cells is possible at any stage of cirrhosis. The therapy is well tolerated by patients and has no side effects. The introduction of SC in cirrhosis helps to slow down the death of hepatocytes, reduce liver inflammation, improve blood biochemical parameters and the general condition of patients. The cells are injected intravenously or directly into the hepatic artery.
Erectile dysfunction
Unfortunately, only 10% of men suffering from erectile dysfunction go to the doctor. More than 50% of them stop treatment because they consider it insufficiently effective. Innovative techniques, such as cell therapy, can dramatically change the current situation. Scientists from Denmark have found that just one injection of stem cells derived from adipose tissue can improve erectile function and lead a full life for at least one year. Andriy Kovalchuk has extensive experience in treating impotence with stem cells. He was one of the first to perform penile injections to normalize blood flow in the segmental arteries of the penis.
This is not a complete list of diseases in which cell therapy has shown high efficiency. To find out about a specific condition, contact us in any way convenient for you and get a free consultation from a MedTour coordinating doctor. The medical coordinator will tell you if the disease you are interested in can be treated with stem cells, and will also help you choose a clinic and organize treatment.

Skin aging begins at 28-30 years of age. This is because the number of fibroblasts, the cells that produce collagen, decreases by 2% every year. By the age of 40, a person loses approximately 20% of fibroblasts. The first signs of aging appear on the skin: flabbiness, dullness, fine wrinkles.
One of the innovative methods of rejuvenation is cell therapy. Fibroblasts are isolated from a small sample of skin taken from the patient behind the ear. After that, they are cultured (propagated) for several weeks in the laboratory and administered to the patient.
Ivan Badin has extensive experience in cell anti-aging therapy, he consults patients in Serbia at the ultra-modern Polyclinic Tara 70. In addition to injecting fibroblasts, Dr. Badin actively uses PRP therapy. The essence of this method is the injection of platelet-rich plasma into the skin. The drug is made from the patient’s own blood. Once in the body, platelets release growth factors that contribute to the active production of collagen and skin regeneration at the cellular level. After a course of treatment, it becomes more elastic, toned, young and radiant.
The use of own (autologous) cells is completely safe, as there is no risk of rejection and other undesirable reactions of the body associated with the introduction of donor material. However, cell therapy is not recommended in the following cases:
Before treatment with stem cells, a doctor’s consultation is mandatory. The specialist checks for contraindications and determines the appropriateness of using cell therapy in each specific case.
Each patient wants to feel the therapeutic effect as quickly as possible, and this is normal. However, we should not forget that we are all individuals, not only mentally, but also physically. Therefore, the effectiveness of any therapy is influenced by a large number of different factors, such as the nature and duration of the disease, its stage, age and general health of the patient, the presence of concomitant diseases, the state of the immune system, etc.
It should also be taken into account that stem cells divide faster in young patients, so the effect of treatment in them occurs earlier than in older ones. However, older people may well expect a positive result. Cells that enter the body will divide and produce regulators and biostimulants. In a young person, the effect may appear in a week, and in an elderly person – in a month.
The price of cell therapy varies greatly depending on which cells are used and in what quantities. There are specific treatment protocols for different diseases. To find out the cost of regenerative therapy, call or fill out the feedback form. In the near future, the medical coordinator of MedTour will contact you and answer all your questions.
MedTour closely follows innovative developments in the field of medicine. Currently, we cooperate with the best medical centers specializing in cell therapy in Switzerland, Ukraine, Georgia, Turkey, Serbia, the Czech Republic and many other countries. Our coordinating doctor will select an affordable clinic for you, as well as help organize treatment and resolve all emerging issues.
The MedTour platform contains information about leading doctors with extensive experience in the use of stem cells in regenerative medicine. Call the number listed on the site or fill out the feedback form to get a free consultation. The medical coordinator of MedTour will tell you about the available specialists and select a doctor based on the nature of your disease and personal preferences.
Please rate the work of MedTour
