Calls for Ukraine
Calls for Europe
Calls for USA
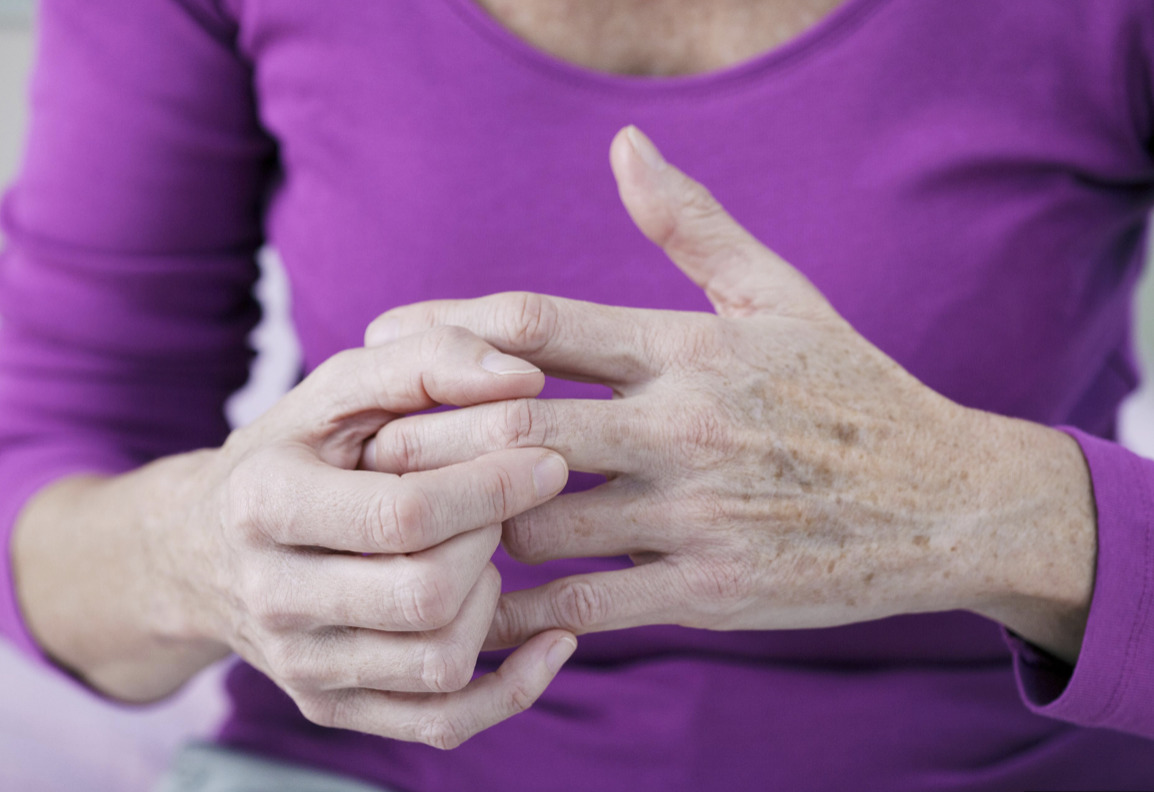

Arthritis is a disease that includes a group of immune diseases affecting joints and cartilage. It can occur in people of any age and gender, but most often occurs in adults over 65 years of age. There are many different types of arthritis, but the two most common are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis occurs when the cartilage in the joints is thinning, which leads to pain and stiffness. Rheumatoid arthritis, on the other hand, is an autoimmune disease in which the body`s immune system attacks the joints, also causing inflammation, pain and stiffness.
Symptoms of arthritis may vary depending on the type of arthritis and severity of the condition, but common symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, redness, and decreased range of motion. In some cases, arthritis can also cause fatigue, fever, and weight loss. Arthritis can be a chronic disease that requires constant monitoring and treatment, including medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes such as exercise and a healthy diet.
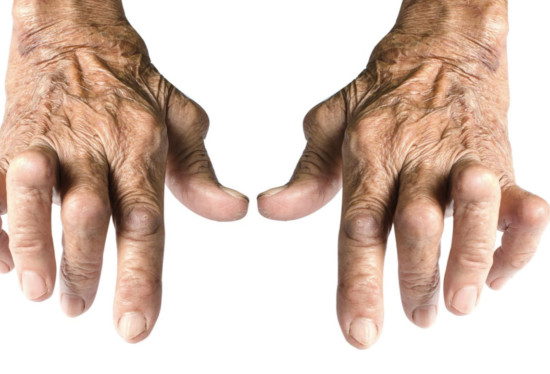
There are many different types of arthritis, and each type can have different symptoms, causes, and severity.
The most common types of arthritis include:
It is incorrect to describe any type of arthritis as «dangerous» because arthritis itself is not life-threatening. However, some types of arthritis can lead to significant joint damage and disability if left untreated, which can affect a person`s quality of life.
Arthritis is a complex disease, and its causes of arthritis in most cases are completely unknown. In general, the causes of arthritis are complex and diverse, and in most cases the development of the disease is facilitated by a combination of genetic factors, environmental factors and lifestyle. In some cases, it is possible to name the exact cause of arthritis, for example, some types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, may be hereditary, and people with a family history of this condition also often get arthritis. However, most often, in the case of arthritis, it is not about the immediate
causes, but about provoking factors such as:
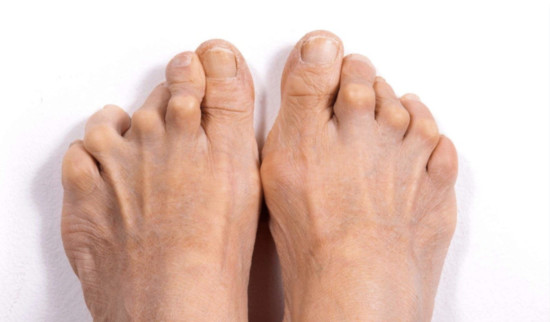
Arthrosis, like arthritis, affects the joints, and their manifestations at the initial stage are similar. However, these diseases have a different nature. Arthrosis refers to degenerative diseases, that is, it occurs and progresses as the body ages, and the cells of the joints and cartilage are insufficiently updated. Unlike arthritis, arthrosis does not have an inflammatory and autoimmune component, and also does not spread to other organs except joints.
The diagnosis of arthritis is usually made comprehensively based on the medical history, physical examination, laboratory tests and image studies. One or more of the following methods are used to diagnose
arthritis:
Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent or slow the progression of joint damage and improve quality of life.
There is no specific blood test showing arthritis. Confirmation of the diagnosis of arthritis occurs with the help of a comprehensive assessment of the indicators of several analyzes:
In general, blood tests are just one of the tools that doctors use to diagnose and monitor arthritis, and the diagnosis of arthritis is usually based on a combination of factors, including medical history, physical examination and imaging studies.
Treatment of arthritis depends on the type and severity of arthritis, as well as on the general state of a person`s health and personal preferences. Here are some of the common treatments for arthritis:
Medications. For the treatment of arthritis, nonsteroidal anti-
inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, anti-rheumatic disease
modifying drugs (BMARPS), and biological agents are commonly
used. These medications can help reduce pain, inflammation, and
joint damage.
In general, the treatment of arthritis is a long process that requires a team approach with the participation of doctors, physiotherapists and other medical professionals. The goal of treatment is to reduce pain and inflammation, improve joint function and mobility, and prevent or slow down joint damage and disability. At the moment, medicine does
not yet have traditional methods of treatment that can lead to a full recovery.
Since traditional methods of treating arthritis are exclusively ways to control symptoms and complications, at the moment, work is actively underway to find new methods of treatment that can eliminate the cause. Such methods include stem cell treatment. Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that can become any cells of the human body.
Their therapeutic effect is that stem cells turn into healthy young cells of a damaged organ or tissue, performing one or another function in a normal way. Depending on the extent of the lesion and the age of the patient, he may need different types of stem cells. There are the following types of them:
Stem cells also rarely make it possible to completely rid the patient of the manifestations of arthritis, however, they allow the patient to improve his condition without toxic drugs and influencing the cause,
not the symptoms.
A healthy diet can be an important part of treating arthritis and reducing inflammation. Here are some dietary recommendations that may be useful for people with arthritis:
It is also important to avoid dehydration by drinking a lot of water during the day. Although there is no universal diet for the treatment of arthritis, following a healthy balanced diet can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health. Consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized nutrition advice. MedTour offers Dr. Kirilenko Alexandra Evgenievna as such a specialist. She has experience in making dietary recommendations for patients with chronic diseases, including gout and rheumatoid arthritis, taking into account the number of allowed harmful products and compliance with the required number of calories.
The life expectancy of people with arthritis does not differ from the average life expectancy in the population, except for the life expectancy of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The life expectancy of these patients has increased over the past few decades due to advances in treatment and overall improvements in healthcare. However, RA is still a chronic and potentially disabling disease that can affect life expectancy, especially if it is not properly controlled or if it leads to complications such as cardiovascular disease.
According to a study published in 2018 in the journal Rheumatology, the life expectancy of people with RA has improved significantly over the past few decades. The study showed that in the past, people with RA had a lower life expectancy than the general population.
However, in recent years, this gap has narrowed, and now people with RA live longer.
The study showed that the life expectancy of people with RA who were diagnosed between 1999 and 2011 was the same as that of the general population. However, people with RA who had other diseases or who were older at the time of diagnosis had a shorter life expectancy.
In general, the life expectancy of people with RA depends on many factors, including the severity of the disease, how well it is controlled by treatment, as well as the presence of other diseases.
The MedTour team works closely with the most modern medical centers that provide assistance in the treatment of arthritis with both traditional and innovative methods. Dr. Kovalchuk (Ukraine) and Dr. Badyin (Serbia) have achieved great success in the treatment of various diseases with stem cells, including arthritis.
1. When should I start treating arthritis with stem cells?
Treatment of arthritis with stem cells in the early stages can lead to the complete disappearance of symptoms, in the later stages — to a significant reduction in severe adverse reactions and postponement of joint replacement surgery.
2. How many courses are required for the treatment of arthritis with stem cells?
In the case of arthritis treatment, treatment is likely to be lifelong or regular until remission is achieved, after which it will be discontinued for the period of remission. The question is about the number of injections per year. As a rule, 2-3 injections are carried out 1 time in 6 months, however, this issue is individual and is solved together with the attending physician.
3. How much does it cost to treat arthritis with stem cells?
It depends on the degree of damage to the joints and other organs, as well as on the country in which the clinic is selected. Thus, treatment can cost from several hundred dollars to several thousand dollars per course.
For a free consultation on stem cell treatment, please contact the coordinating doctor of MedTour.
Please rate the work of MedTour
